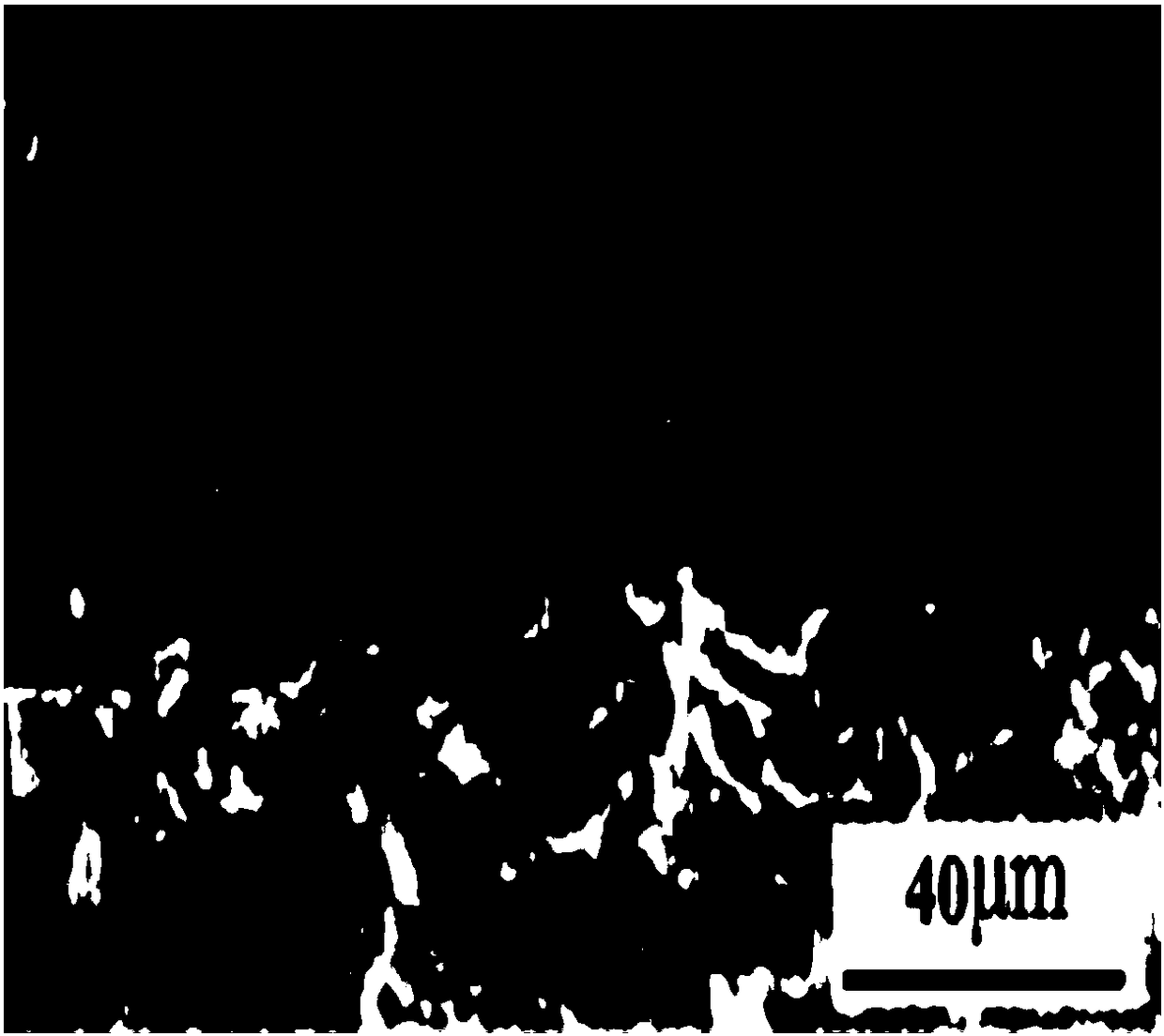
Method and device for depositing silicon carbide on the surface of graphite parts
A technology for surface deposition and graphite parts, which is applied in the field of preparation of inorganic non-metallic materials, and can solve the problems of high hardness of graphite parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
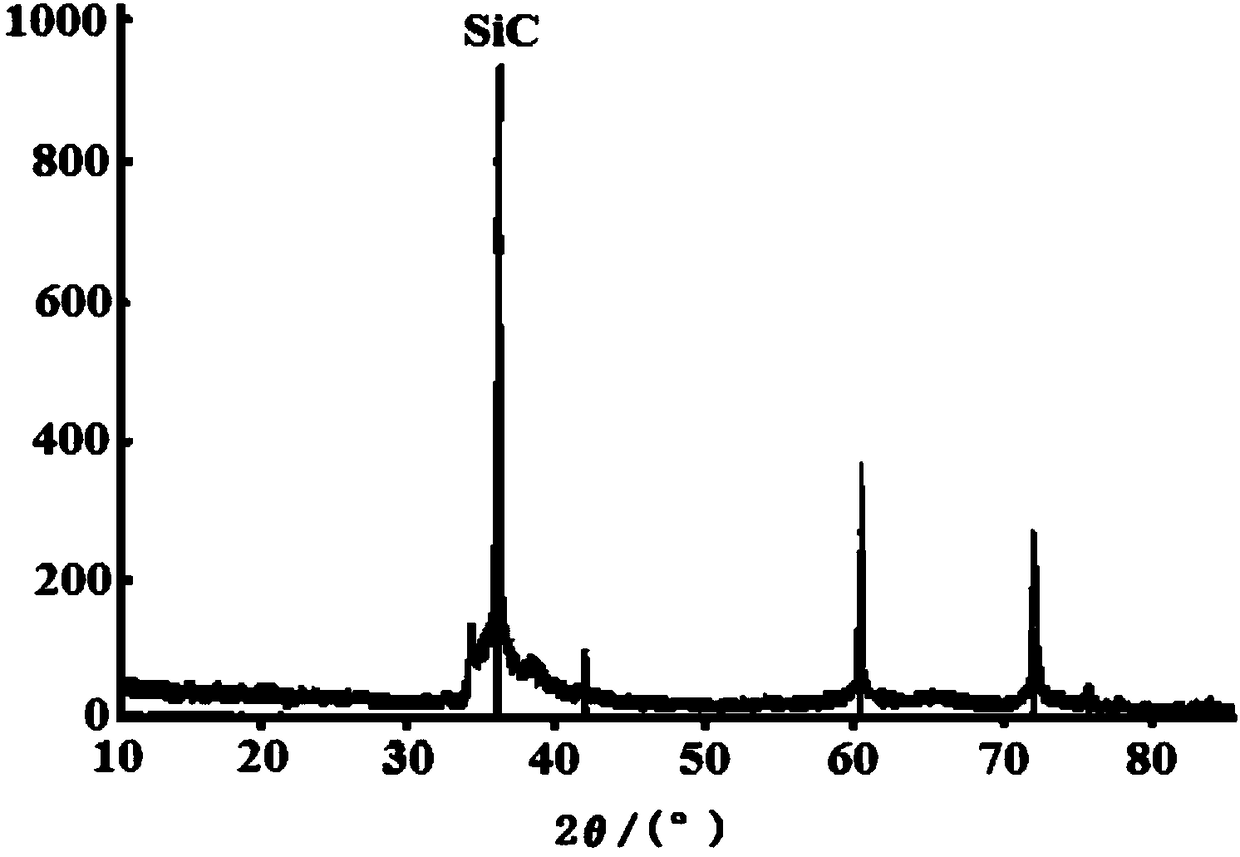
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
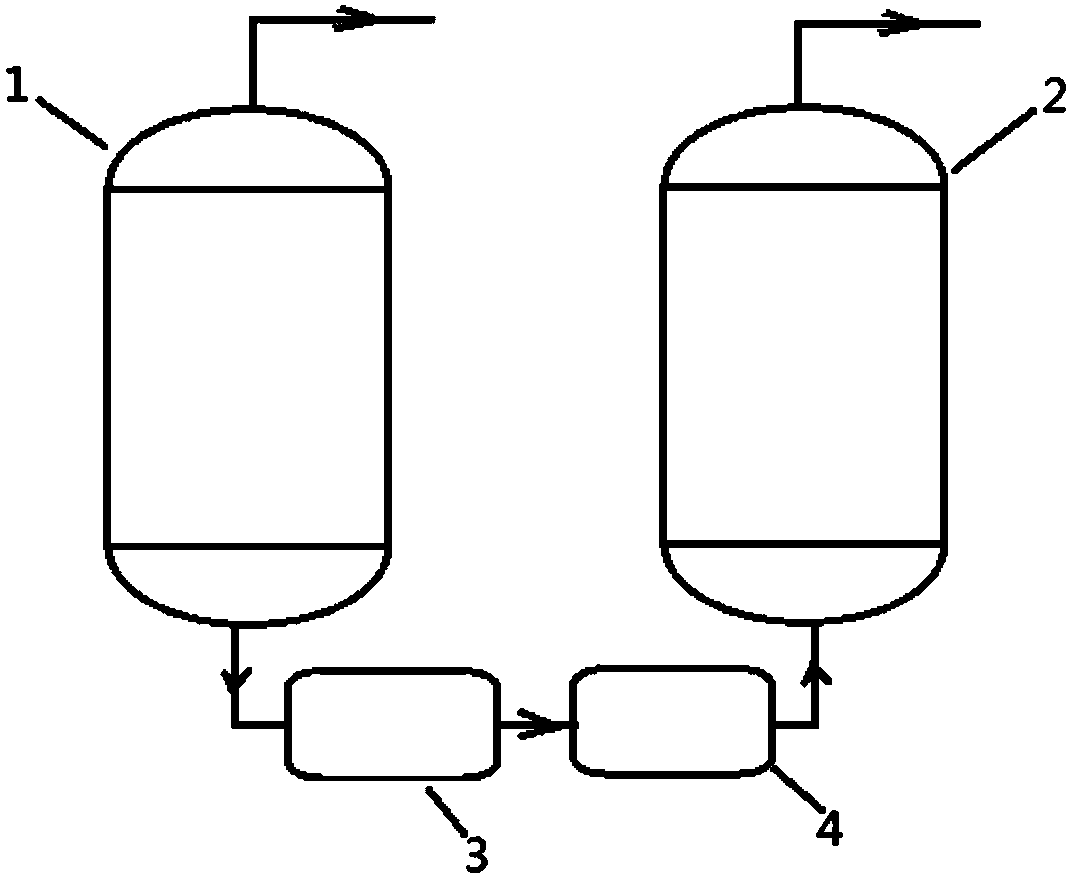
[0043] A method for depositing silicon carbide on the surface of a graphite piece, comprising the steps of:
[0044] (1) Impurity removal on graphite surface:
[0045] 1.1 Lower the bottom flange, open the furnace tube, and put in the substrate;
[0046] 1.2 Lift the flange and close the furnace tube;
[0047] 1.3 Vacuum replacement, vacuum degree 0.5mbar;
[0048] 1.4 Heat the heater inside the furnace drum to 600°C, and start to feed nitrogen to a vacuum of 80mbar;
[0049] 1.5 Continue to heat up to 1600°C, feed chlorine gas to a vacuum of 1.0 bar, and maintain 1600°C for 20 minutes;
[0050] 1.6 Continue to heat up to 2000 ° C, maintain 2000 ° C for 8 hours after purification, and then slowly cool down;
[0051] 1.7 Cool down to 1800°C, stop feeding chlorine gas, and maintain 1800°C for 30 minutes;
[0052]1.8 Continue to reduce the vacuum degree while maintaining the nitrogen gas supply, and when the temperature continues to drop to 800°C, the vacuum degree in the fu...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A method for depositing silicon carbide on the surface of a graphite piece, comprising the steps of:
[0069] (1) Impurity removal on graphite surface:
[0070] 1.1 Lower the bottom flange, open the furnace tube, and put in the substrate;
[0071] 1.2 Lift the flange and close the furnace tube;
[0072] 1.3 Vacuum replacement, vacuum degree 1mbar;
[0073] 1.4 Heat the heater inside the furnace drum to 600°C, and start to feed nitrogen to a vacuum of 80mbar;
[0074] 1.5 Continue to heat up to 1500°C, feed chlorine gas to a vacuum of 0.9 bar, and maintain 1500°C for 30 minutes;
[0075] 1.6 Continue to heat up to 1900°C, maintain 1900°C for 12 hours of purification, then slowly cool down;
[0076] 1.7 Cool down to 1500°C, stop feeding chlorine gas, and maintain 1500°C for 30 minutes;
[0077] 1.8 Continue to reduce the vacuum degree while maintaining the nitrogen gas flow, and when the temperature continues to drop to 500°C, the vacuum degree in the furnace will dr...
Embodiment 3
[0093] A method for depositing silicon carbide on the surface of a graphite piece, comprising the steps of:
[0094] (1) Impurity removal on graphite surface:
[0095] 1.1 Lower the bottom flange, open the furnace tube, and put in the substrate;
[0096] 1.2 Lift the flange and close the furnace tube;
[0097] 1.3 Vacuum replacement, vacuum degree 0.5mbar;
[0098] 1.4 Heat the heater inside the furnace barrel to 700°C, and start to feed nitrogen to a vacuum of 60mbar;
[0099] 1.5 Continue to heat up to 1600°C, feed chlorine gas to a vacuum of 1.2bar, and maintain 1600°C for 5 minutes;
[0100] 1.6 Continue to heat up to 2000 ° C, maintain 2000 ° C for 7 hours after purification, and then slowly cool down;
[0101] 1.7 Cool down to 1600°C, stop feeding chlorine gas, and maintain 1600°C for 5 minutes;
[0102] 1.8 Continue to reduce the vacuum degree while maintaining the nitrogen gas flow, and when the temperature continues to drop to 600°C, the vacuum degree in the furn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com