Nitrided high-speed steel roller used for bar cutting rack and manufacturing method of nitrided high-speed steel roller
A technology of nitriding high-speed steel rolls and a manufacturing method, applied in the field of roll manufacturing, can solve problems such as uneven distribution, high labor intensity of workers, and impact on finished products, achieve reduction of carbide-forming elements, shorten roll changing and slot changing time, and stabilize The effect of product negative margin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
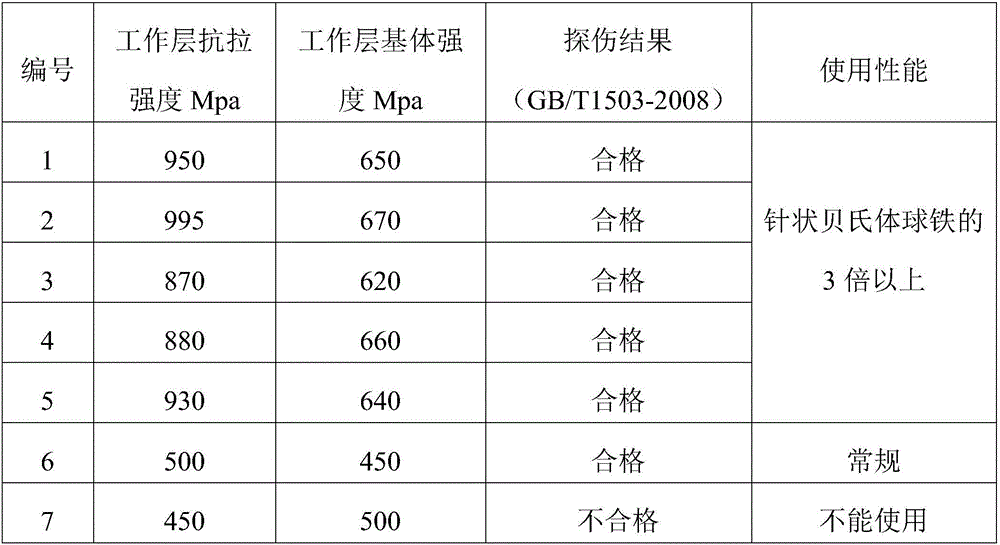
[0047] A centrifugal compound nitriding high-speed steel roll suitable for bar splitting racks and its manufacturing method, including molding, melting, nitriding agent treatment, centrifugal casting, casting transition layer and roll neck operation, and pouring core , unpacking, machining and heat treatment steps.
[0048] Step A. Modeling
[0049] The casting box includes a roll body box, a roll neck box and a bottom box. The roll body box is made of metal spray paint, the roll neck box is made of silica sand clay, and the bottom box is connected to the overflow pipe;
[0050] 2. Medium power frequency furnace smelting, molten steel smelting in the working layer of the roll, the melting temperature is 1500-1650°C, the alloy composition of the working layer and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are 1.2-2.2C, 7.0-13.5Cr, 0.2-1.2Ni, 0.5~1.5Mo, 1.0~2.5V, 1.0~2.5W, 1.0~3.0Nb, 0.05~0.1Re, P≤0.04, S≤0.04, Mn≤0.5, 0.6~1.5Si, and the rest is Fe.
[0051] The transitio...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the alloy composition of the working layer and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 1.7C, 10.5Cr, 0.6Ni, 1.0Mo, 1.8V, 1.6W, 2.0Nb, 0.08Re, P ≤0.04, S≤0.04, Mn≤0.5, 1.1Si, the rest is Fe;
[0060] The alloy composition of the transition layer and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 2.8C, 0.3Cr, 0.1Re, P≤0.03, S≤0.02, Mn0.5, 1.8Si, and the rest is Fe;
[0061] The alloy composition of the core and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 3.2C, 0.4Cr, 0.5Ni, 0.1Re, P≤0.03, S≤0.02, Mn0.7, 1.8Si, and the rest is Fe.
Embodiment 3
[0063] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is: the alloy composition of the working layer and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 2.2C, 13.5Cr, 1.2Ni, 1.4Mo, 2.4V, 2.5W, 3.0Nb, 0.1Re, P ≤0.04, S≤0.04, Mn≤0.5, 1.5Si, the rest is Fe;
[0064] The alloy composition of the transition layer and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 3.0C, 0.1~0.5Cr, 0.1Re, P≤0.03, S≤0.02, Mn0.8, 2.0Si, and the rest is Fe;
[0065] The alloy composition of the core and the weight percentage of each alloy composition are: 3.6C, 0.5Cr, 0.8Ni, 0.1Re, P≤0.03, S≤0.02, Mn1.0, 2.0Si, and the rest is Fe.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com