Method for detecting dsRNA virus of edible fungus
A detection method and edible fungus technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of no effective prevention and control methods for viral diseases, backward research on edible fungus viruses, etc., and achieve short detection time, easy judgment, and test conditions simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] (1) Preparation of test samples: Homogenize fresh or frozen edible fungus samples (mycelia or fruiting bodies) to be tested to obtain a homogenate, and centrifuge the homogenate at a speed of 12000-14000 rpm / min for 1 -2 min, take the supernatant for later use;
[0042] The specific operation of the homogenate is as follows: put 0.5 g of the edible fungus sample into a grinder, add 200 μL of TE buffer solution and a small amount of quartz sand, and quickly grind the homogenate to obtain a homogenate.
[0043] Or put 0.1 g of the edible fungus sample into a 2 mL centrifuge tube containing three steel balls with a diameter of 4 mm, add 50 μL of TE buffer, and place it in a FastPrep nucleic acid extraction instrument for homogenization at a homogenization speed of 4.5K for 15 to 30 s .
[0044] (2) Point film: Cut a film of appropriate size according to the number of samples. The film is nitrocellulose film, nylon film or PVDF film, and divide the film into different squa...
Embodiment 1
[0053] Taking the detection of Lentinus edodes virus as an example, the steps of using dsRNA monoclonal antibody combined with dot blot detection are as follows:
[0054] 1. Cultivation and collection of mushroom strain mycelium
[0055] In the ultra-clean workbench, the mushroom strains were transferred to a 9cm PDA plate, cultured at a constant temperature of 25°C for 15 days, and then the mushroom hyphae were scraped, and used directly for detection of poisonous conditions or stored at -20°C for later use.
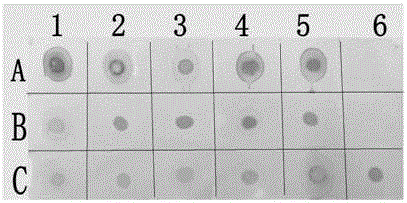
[0056] 2. Dot blot detection
[0057] (1) Preparation of test samples: put 0.1 g of frozen mushroom mycelium with Lentinus edodes virus disease into a 2 mL centrifuge tube containing 3 steel balls with a diameter of 4 mm, add 50 μL of TE buffer in the FastPrep nucleic acid extractor Homogenate (speed 4.5K, time 15 to 30 s), centrifuge at 12000 rpm / min for 1 min, and take the supernatant for later use.
[0058] Take 0.5 g mushroom fruiting body and put it into the grin...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Taking the detection of Agaricus bismuth virus as an example, the steps of using dsRNA monoclonal antibody combined with dot blot detection are as follows:
[0069] (1) Preparation of test samples: Put 0.5 g of the fresh fruiting body of Agaricus bisporus to be tested into a grinder, add 200 μL TE buffer solution and a small amount of quartz sand, and quickly grind and homogenize to obtain a homogenate, which is prepared with Centrifuge at 14000 rpm / min for 2 min, and take the supernatant for later use.
[0070] (2) Dot film: Cut a nylon film of appropriate size according to the number of samples, divide the film into different squares with a pencil line, and use it to distinguish the position of different samples (the size of each square is about 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm), take 3 μL of the centrifuged supernatant after the above homogenization was spotted on the membrane, and the membrane was dried in an oven at 40°C.
[0071] (3) Membrane sealing: According to the size of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com