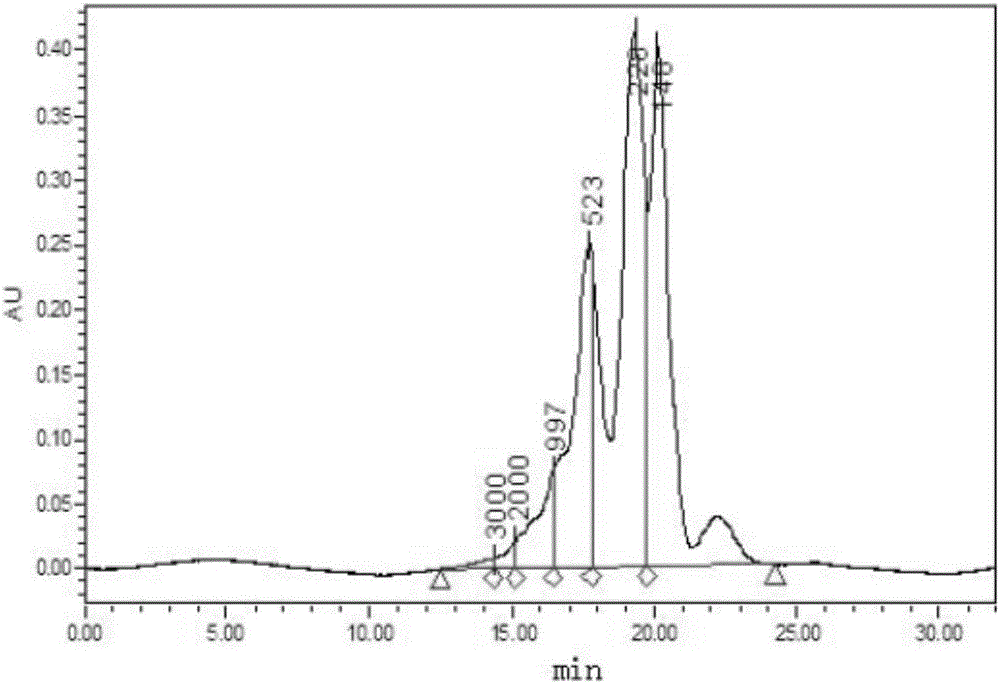
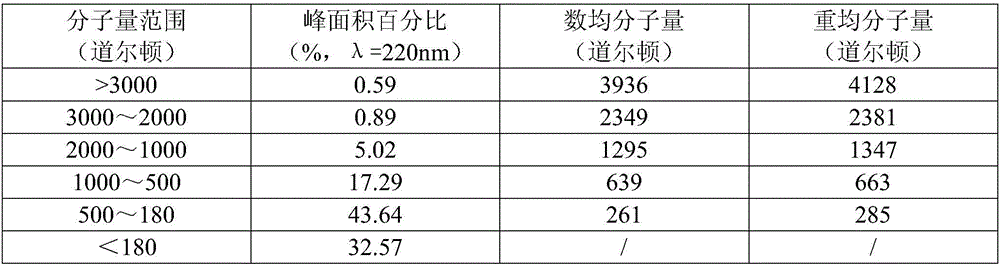
Micromolecular shellfish polypeptide extraction method
An extraction method and small molecule technology, applied in the preparation methods of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of undeveloped small molecule shellfish peptides, technology and application gaps, etc., to achieve a broad market space and economical. Value, strong operability, guaranteeing the effect of biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The extraction method of the small molecule shellfish polypeptide of embodiment 1 comprises the following steps:
[0023] (1) Rough washing: use fresh sea red and meretrix clams as raw materials, wash the surface sediment with clean water;
[0024] (2) Shelling: Mix the washed raw materials with shells and tap water heated to 100°C in a weight ratio of 1:1, cook for 12 minutes, and then take out the shellfish;
[0025] (3) Soaking and fine washing: Soak the shellfish in tap water at 2°C for 24 hours, and then wash it repeatedly for 3 times with tap water at 2°C;
[0026] (4) Drying: use a fan to blow air for 10 hours with a 6-level wind force, until the water content of the shellfish is lower than 40%;
[0027] (5) Enzymolysis: Add the dried shellfish and tap water or pure water to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank at a weight ratio of 1:2, and add collagenase and papain to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank. The addition amount is 0.6% of the weight of t...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The extraction method of the small molecule shellfish polypeptide of embodiment 2 comprises the following steps:
[0032] (1) Rough washing: use fresh razor clams as raw materials, wash the surface sediment with clean water;
[0033] (2) Shelling: Mix the washed raw materials with shells and tap water heated to 100°C in a weight ratio of 1:1, cook for 15 minutes, and then take out the shellfish;
[0034] (3) Soaking and fine washing: Soak the shellfish in tap water at 4°C for 24 hours, then wash it repeatedly 4 times in tap water at 4°C;
[0035] (4) Drying: use a fan to blow air for 8 hours with a wind force of level 6, until the water content of the shellfish is lower than 40%;
[0036] (5) Enzymolysis: Add the dried shellfish and tap water or pure water to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank at a weight ratio of 1:1, and add collagenase and papain to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank. The addition amount is 0.5% of the weight of the dried shellfish, the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The extraction method of the small molecule shellfish polypeptide of embodiment 3 comprises the following steps:
[0041] (1) Rough washing: use fresh sea red, meretrix meretrix and razor clam as raw materials, wash the surface sediment with clean water;
[0042] (2) Shelling: Mix the washed raw materials with shells and tap water heated to 100°C in a weight ratio of 1:1, cook for 10 to 20 minutes, and then take out the shellfish;
[0043] (3) Soaking and fine washing: Soak the shellfish in tap water at 1°C for 24 hours, and then wash it repeatedly 5 times in tap water at 1°C;
[0044] (4) Drying: use a fan to blow air for 18 hours with a 6-level wind force, until the water content of the shellfish is lower than 40%;
[0045] (5) Enzymolysis: Add the dried shellfish and tap water or pure water to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank at a weight ratio of 1:3, and add collagenase and papain to the biological enzymatic hydrolysis tank. The amount added is 0.9% of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com