Method for detecting development toxicity of environmental pollutants by whole-mount in-situ hybridization technique
A technology of environmental pollutants and in situ hybridization, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of uncertainty, inaccuracy, long exposure time, body damage, etc., and shorten the detection cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
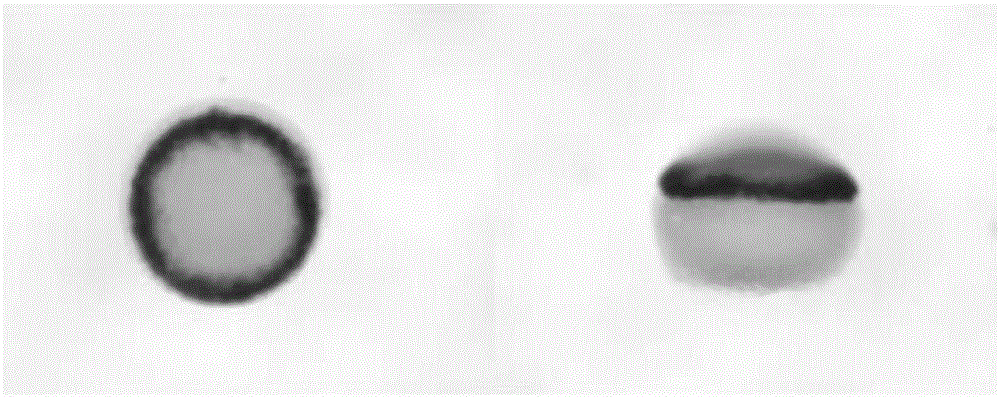
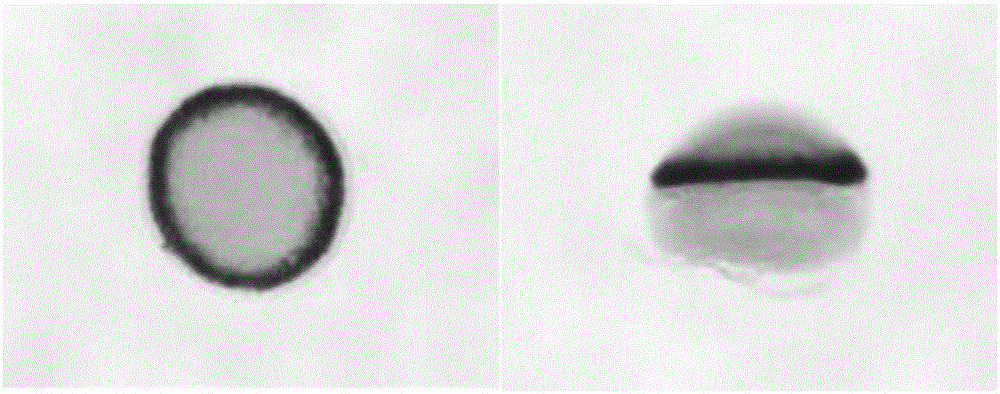
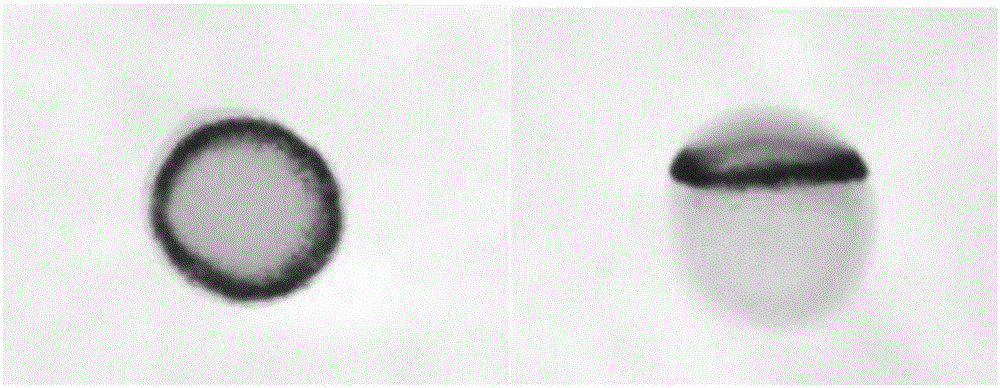
[0034] In this example, according to the embryonic blastocyst predetermined fate map (fate map), the zebrafish blastocyst predetermined fate gene notochord mesoderm marker gene ntl is selected as the biomarker gene, and the environmental pollutants (using nano-silver as the Example) the impact on the changes in the transcription and expression of the biomarker gene ntl to evaluate the potential developmental toxicity of environmental pollutants (taking nano-silver as an example) on the early organs and tissues of zebrafish.
[0035] 1. Preparation of RNA probes for hybridization:
[0036] 1. Total RNA extraction: Take about 30 mg of fresh tissue samples of wild-type zebrafish, add 600 μl Trizol to fully grind, lyse at room temperature for 10 minutes, add chloroform, shake and mix well, let stand at room temperature for 10 minutes to extract, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 15 minutes, absorb the supernatant and add isopropanol The precipitate was collected by centrifugation at 120...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com