Method for continuously producing feed-grade urea phosphate from wet-method purified phosphoric acid strip liquor or washing residual liquid
A technology of wet purification and urea phosphate, which is applied in the field of phosphorus chemical industry, can solve the problems of many impurities, poor fluidity, and high cost, and achieve the effects of simple process flow, improved final yield, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
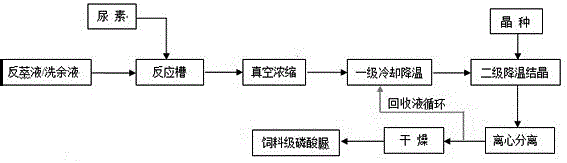
[0025] As shown in Figure 1, turn on the stirring paddle, control the speed at 100~150r / min, add P 2 o 5 For the phosphoric acid back-extraction solution with a concentration of 35% by wet method, steam was introduced to control the reaction temperature at 70°C, and the temperature was kept for 10 minutes; according to the molar ratio of urea and phosphoric acid of 1:1.0~1.1, urea was added to the reaction tank, and the reaction was carried out for 60 minutes; The final feed liquid is pumped to a circulating vacuum concentration device for concentration, the control pressure is -0.05Mpa, the concentration temperature is 80°C, and the reaction solution is concentrated to P 2 o 5 After reaching 50%, the material is pumped to the primary cooling crystallization tank (primary cooling and cooling) to cool down to 40°C, and placed in the secondary cooling tank (secondary cooling crystallization) to cool down to 28°C. During the secondary cooling crystallization process Stirring s...
Embodiment example 2
[0027] Carry out with the production method of embodiment 1 and process parameter, difference is as follows statement, urea and phosphoric acid mol ratio are 1:1.1~1.2, and vacuum concentration pressure is-0.06Mpa, concentrate P 2 o 5 The concentration of urea phosphate is 52%; the temperature of adding seed crystals in the secondary cooling crystallization is 20°C, the stirring speed in the secondary cooling crystallization process is 20~30r / min, and the urea phosphate is collected in the centrifugal separation process. The recovered liquid is transported to the urea phosphate primary cooling crystallization tank; the P in the obtained feed grade urea phosphate product 2 o 5 The yield was 85%, and the N yield was 85.5%.
Embodiment example 3
[0029] As shown in Figure 1, turn on the stirring paddle, control the speed at 100~150r / min, add P 2 o 5 Wet purification phosphoric acid washing liquid with a concentration of 35%, put steam into it to control the temperature at 75~80°C, keep it warm for 10 minutes, add urea into the reaction tank according to the molar ratio of urea and phosphoric acid at 1:1.0~1.05, and react for 70~ 80 min; the reacted feed liquid is pumped to a circulating vacuum concentrator for concentration, the control pressure is -0.05Mpa, and the reaction liquid is concentrated to P 2 o 5 After reaching 50%, the material is pumped to the primary cooling tank, cooled to 30°C and then placed in the secondary cooling crystallization tank to continue cooling down to 25°C, adding seed crystals to crystallize and precipitate urea phosphate; urea phosphate is centrifuged, dried, and dried The temperature is controlled at 55~60°C to obtain the feed grade urea phosphate product, P 2 o 5 The yield was 75...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com