Method for preparing molybdenum-containing additive and carbon disulfide by vacuum carbon thermal reduction of molybdenum concentrate
A carbon disulfide and molybdenum additive technology, which is applied in the direction of carbon disulfide and carbon sulfur compounds, can solve the problems of polluted gas, high production cost, and large pollution, and achieve the effect of reducing treatment and emission, short process, and easy operation and control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
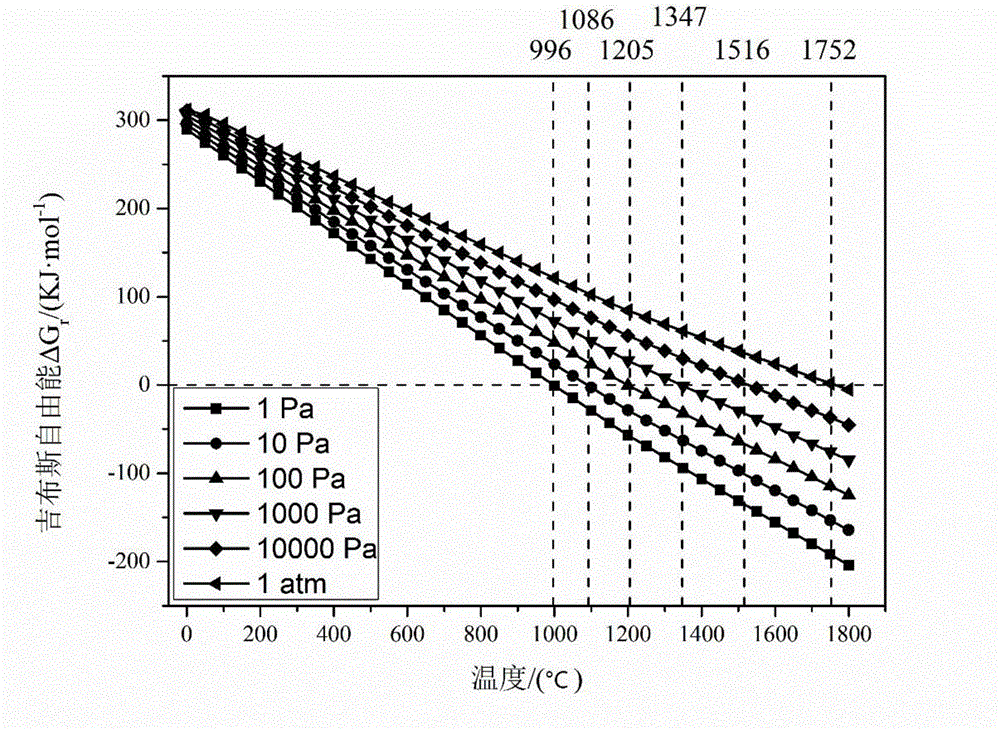
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Make the particle size less than 0.15mm, MoS 2 (mass fraction) be 94% molybdenum concentrate and the active carbon powder of particle size less than 0.1mm according to the actual molybdenum disulfide content in the molybdenum concentrate and active carbon powder molar ratio 1:1.51 batching, and the powder sample total mass is 8g, fully Mix evenly to obtain evenly mixed powder raw materials.
[0027] (3) Put the homogeneously mixed powder raw material obtained in (1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up and evacuate to a vacuum degree of 10Pa, keep it at a calcination temperature of 1300°C for 4 hours, and collect it at a condensation temperature of 25°C to liquid carbon disulfide.
[0028] (3) After the heat preservation is completed, cool down to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a molybdenum-containing steelmaking additive with a molybdenum content of 90.8% and a sulfur content of less than 0.026%.
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Make the particle size less than 0.15mm, MoS 2 (mass fraction) be 94% molybdenum concentrate and the active carbon powder of particle size less than 0.1mm according to the actual molybdenum disulfide content in the molybdenum concentrate and active carbon powder molar ratio 1:1.51 batching, and the powder sample total mass is 8g, fully Mix evenly to obtain evenly mixed powder raw materials.
[0031] (3) Put the homogeneously mixed powder raw material obtained in (1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up and evacuate to a vacuum degree of 50Pa, keep it at a calcination temperature of 1600°C for 2 hours, and collect it at a condensation temperature of 25°C to liquid carbon disulfide.
[0032] (3) After the heat preservation is completed, cool down to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a molybdenum-containing steelmaking additive, the molybdenum content is 92.1%, and the sulfur content is less than 0.017%.
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) The particle size is less than 0.05mm, the purity is the analysis pure molybdenum disulfide of 98% and the activated carbon powder of particle size is less than 0.1mm according to the molar ratio 1:1.5 batching, and the total mass of the powder sample is 5g, fully mixed evenly, and mixed Uniform powder raw material.
[0035] (3) Put the homogeneously mixed powder raw material obtained in (1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up and evacuate to a vacuum degree of 10 Pa, keep it at a calcination temperature of 1500°C for 2 hours, and collect it at a condensation temperature of 25°C to liquid carbon disulfide.
[0036] (3) After the heat preservation is completed, cool down to room temperature with the furnace to obtain pure molybdenum carbide powder, the purity of molybdenum carbide is 98.7%, and the sulfur content is less than 0.012%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com