A reusable magnetic Fe that photocatalytically degrades dyes 3 o 4 The preparation method of microsphere and its application
A photocatalysis and dye technology, applied in the preparation of microspheres, chemical instruments and methods, microcapsule preparations, etc., can solve the problems of difficult reuse, low degradation rate of photocatalytic degradation dyes, difficult separation, etc., and improve the catalytic degradation efficiency. , Simple and efficient separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
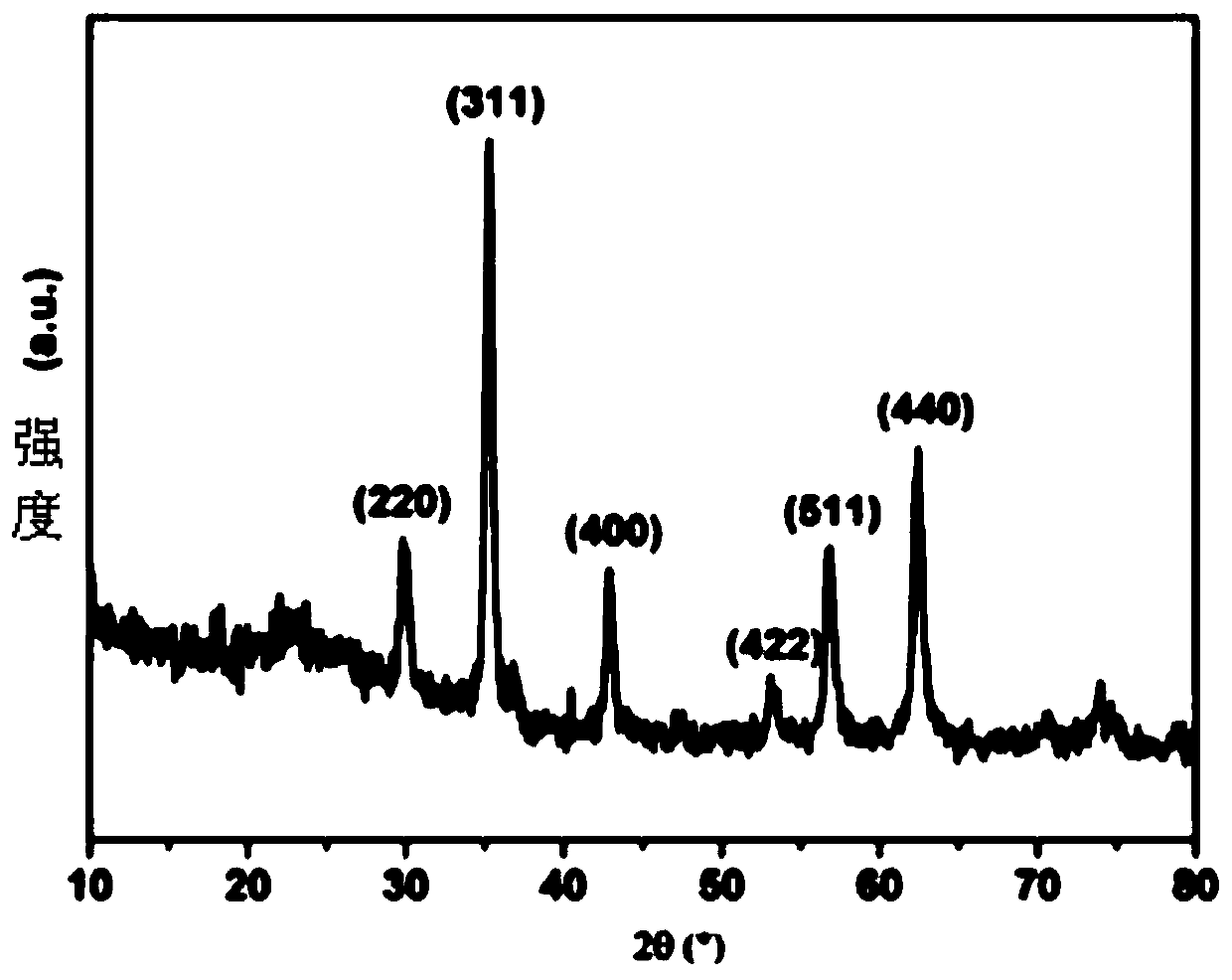
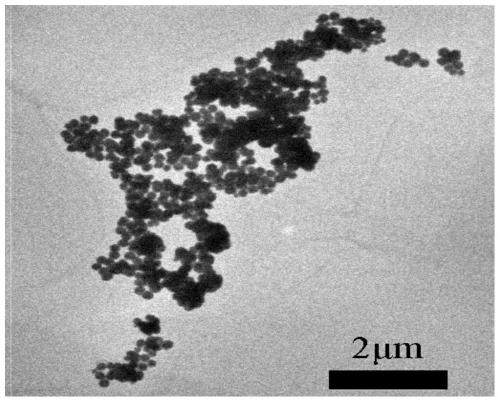
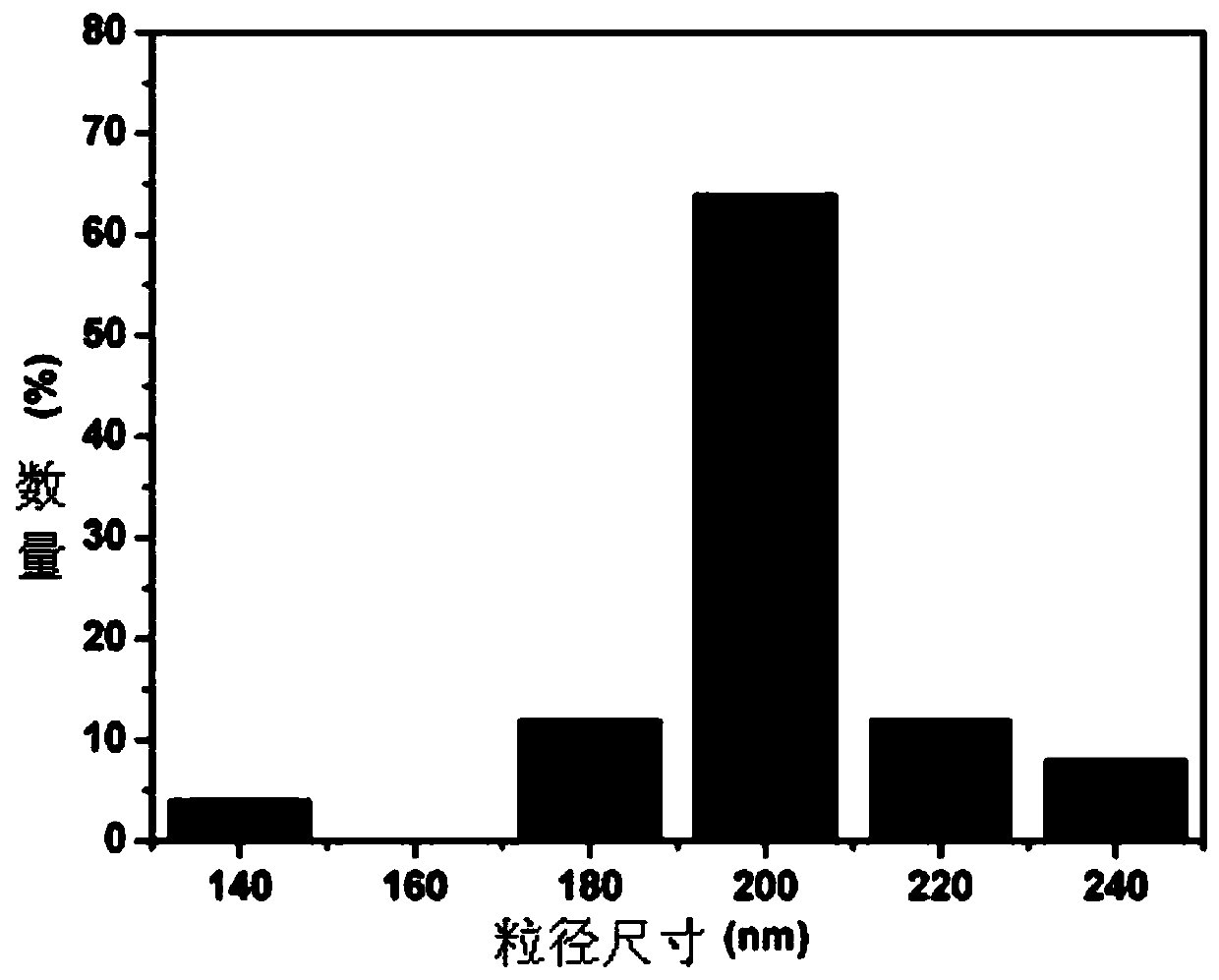
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0023] Specific implementation mode 1: This embodiment can photocatalytically degrade dyes and reusable magnetic Fe 3 o 4 The preparation method of microsphere is carried out according to the following steps:
[0024] 1. Dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate and anhydrous sodium acetate in ethylene glycol at a mass ratio of 1.0: (3.0 to 5.0) to obtain a suspension reaction solution, which is transferred to a water bath constant temperature oscillator and heated to 45 to 45 55°C, then according to the volume ratio of ethylene glycol to ethylenediamine (10.0-4.0):1.0, add ethylenediamine at a temperature of 45-55°C, and magnetically stir the reaction at 25-35°C to obtain a clear reaction solution;
[0025] 2. Transfer the clarified reaction solution obtained in step 1 to a reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, react at a temperature of 180-220°C for 5-7 hours, and then pour the reaction solution in the reaction kettle into a beaker The product was separated with...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that step 1 dissolves 1 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 3 to 5 g of anhydrous sodium acetate in 45 to 50 mL of ethylene glycol to obtain a suspension reaction solution, Transfer to a water bath constant temperature shaker and shake to heat to 45-55°C, then add 5-10mL of ethylenediamine at a temperature of 45-55°C. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0027] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that step 1 dissolves 1 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 3 to 5 g of anhydrous sodium acetate in 45 to 50 mL of ethylene glycol to obtain a suspension reaction solution, Transfer to a water bath constant temperature shaker and shake to heat to 50°C, then add 5-10mL of ethylenediamine at a temperature of 50°C. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com