FLP/FRT gene knockout method of Candida amazonensis
A gene knockout and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as differences in the function of promoters, and achieve the effect of eliminating the screening process, eliminating hygromycin resistance and normal morphology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Site-directed mutation of the recombinase gene FLP
[0058] Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a template, PCR amplification with primers FLP-F (SEQ ID NO: 19) and FLP-R (SEQ ID NO: 20) was used to obtain the FLP gene sequence (enzyme cleavage site Sal I was introduced upstream of the sequence, and enzyme cleavage site was introduced downstream of the sequence cut site Not I), connected to the PMD 19-T simple vector, transformed into competent E.coli JM109, and obtained the recombinant Ts-FLP. Using the plasmid Ts-FLP as a template, the Stratagene site-directed mutagenesis kit (purchased from Agilent Technologies Co., Ltd.) was used, and primers FLP-1 (SEQ ID NO: 21) and FLP-2 (SEQ ID NO: 22); FLP- 3 (SEQ ID NO: 23) and FLP-4 (SEQ ID NO: 24); FLP-5 (SEQ ID NO: 25) and FLP-6 (SEQ ID NO: 26) undergo three rounds of PCR site-directed mutagenesis to obtain circular like PCR products. The amplification conditions were: 95°C pre-denaturation for 2 minutes, 95°C den...
Embodiment 2
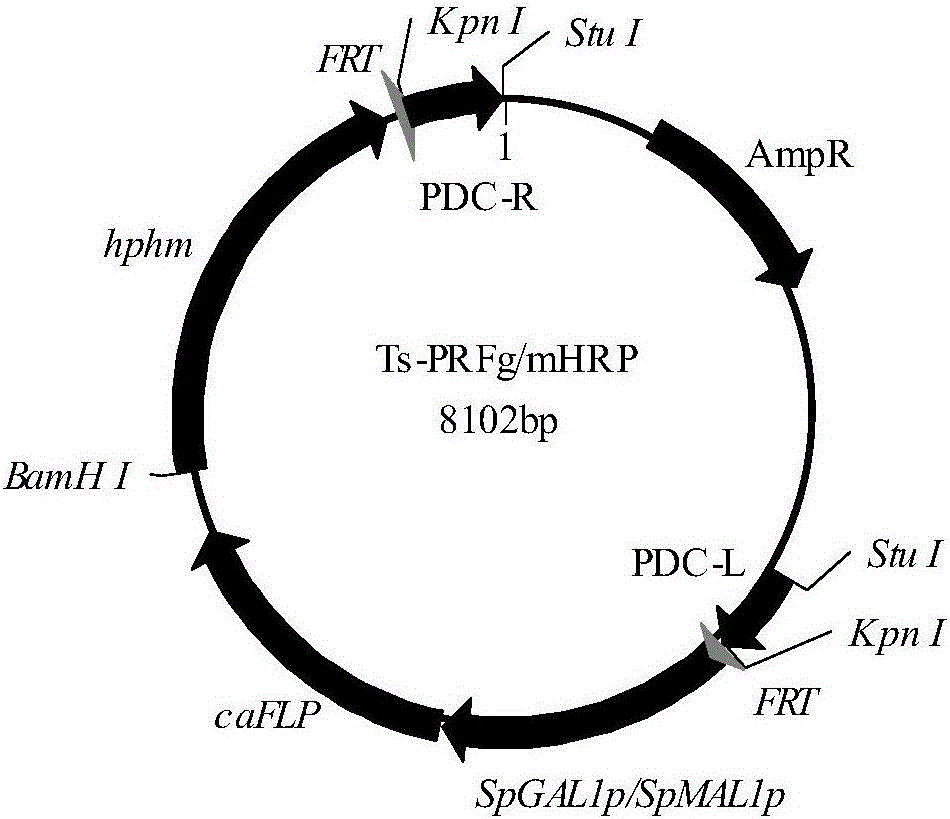
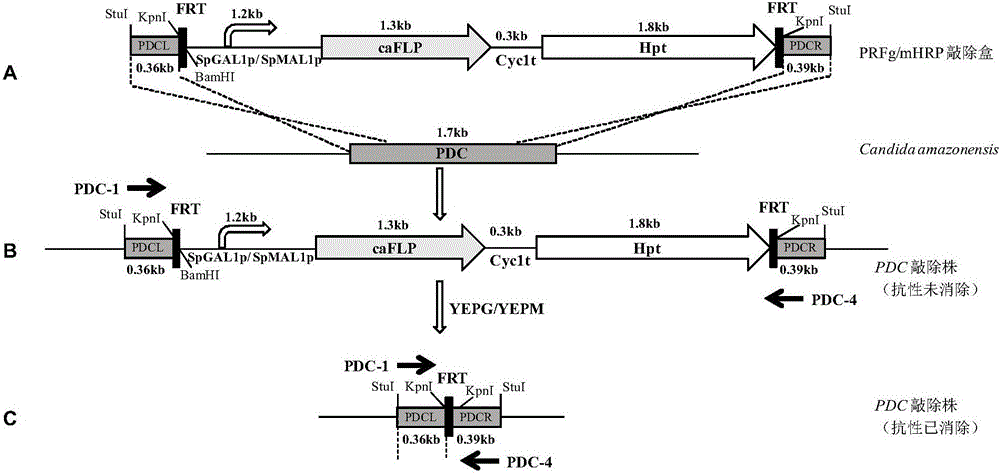
[0059] The construction of embodiment 2PDC gene knockout cassette
[0060] (1) Using the Candida amazonensis genome as a template, use primers PDC-1 (SEQ ID NO: 8) and PDC-2 (SEQ ID NO: 9) to amplify the upstream sequence PDC-L of the 5' end of the PDC gene 360bp, in the fragment The restriction site Stu I was introduced upstream, and the restriction site Kpn I was introduced downstream of the fragment; primers PDC-3 (SEQ ID NO: 10) and PDC-4 (SEQ ID NO: 11) were used to amplify 400 bp of the PDC 3' end The downstream sequence of PDC-R, the restriction site Kpn I was introduced upstream of the fragment, and the restriction site Stu I was introduced downstream of the fragment; the PDC-L and PDC-R sequences were spliced by overlap extension PCR to obtain the PDC gene homologous recombination fragment PDCL -R.
[0061] (2) Connect PDCL-R to PMD19-T simple vector, transform competent E.coli JM109, obtain a positive clone, and name it Ts-PDCL-R. The plasmid Ts-PDCLR was extract...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3 PEG / LiAc method transforms Candida amazonensis CBS 12363
[0068](1) Pick a single colony of Candida amazonensis CBS 12363 from a YPD plate, inoculate it in 20 mL of YPD medium, and culture it overnight at 30°C in a 100 mL shake flask;
[0069] (2) Inoculate the overnight cultured fresh bacterial solution into 50mL YPD medium, and culture it in a 250mL shake flask at 30°C and 200rpm until the bacterial solution OD 600 to around 1.2;
[0070] (3) Centrifuge at room temperature for 5 minutes at 5000 rpm to collect bacterial cells;
[0071] (4) Resuspend the cells in 500 μL of 0.1mol / L LiAc, centrifuge, discard the supernatant, and obtain competent cells;
[0072] (5) Add the following transformation mixture in order to the competent cells: 240 μL 50% PEG3350, 36 μL 1.0mol / L LiAc, 25 μL salmon sperm DNA, 50 μL linear DNA to be transformed, among which the salmon sperm DNA is in boiling water for 10 minutes and then ice-bathed immediately ;
[0073] (6) Sha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com