Fluorescence detection method for hydrolase activity
A fluorescence detection and hydrolytic enzyme technology, applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve the problems of insufficient anti-interference ability, poor anti-interference ability and high detection cost, and achieve the effect of short detection time, strong anti-interference ability and high sensitivity detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The method of the invention is used in a feasibility analysis experiment for detecting alkaline phosphatase activity.
[0035] 20μL 0.05mg mL -1 Alkaline phosphatase samples were added to 2980 μL containing 2 mM ascorbic acid-2-phosphate and 0.03 mM Cu 2+ - After incubating at 25° C. for 15 minutes in the detection solution of the bathocuproine disulfonic acid fluorescent probe, record the fluorescence emission spectrum of the detection solution.
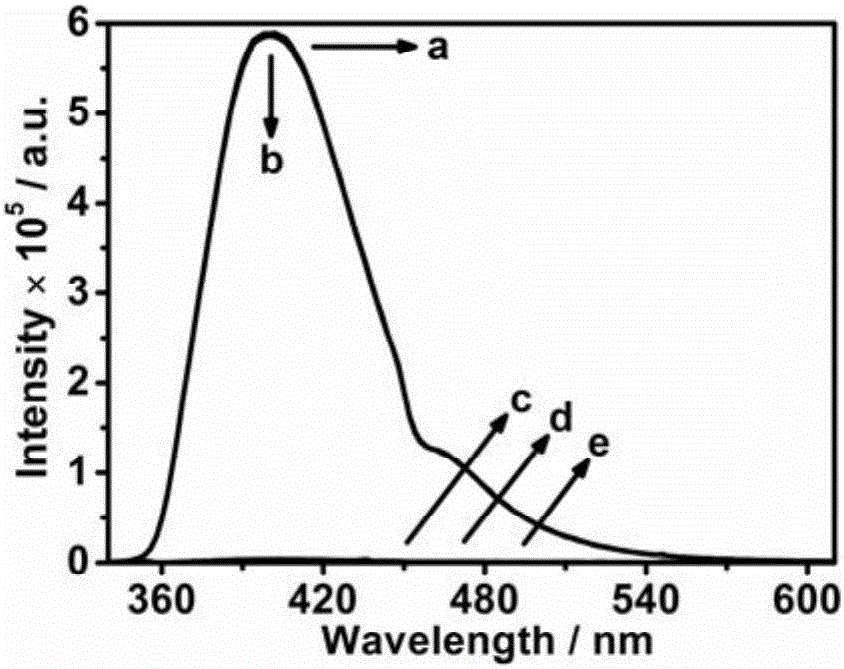
[0036] In feasibility analysis experiments, missing components were replaced with the same volume of buffer. from figure 1 As can be seen, when alkaline phosphatase (a) or substrate (b) are not added in the detection solution, the fluorescence emission intensity of the detection solution at 402nm is stronger; in the detection solution, bathocuproine disulfonic acid ( c), without adding Cu 2+ - When the bathocuproine disulfonic acid fluorescent probe (d) or all components are present (e), the fluorescence emission intensit...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The method of the invention is used to detect the relationship between the fluorescence emission intensity of the alkaline phosphatase activity and the alkaline phosphatase activity.
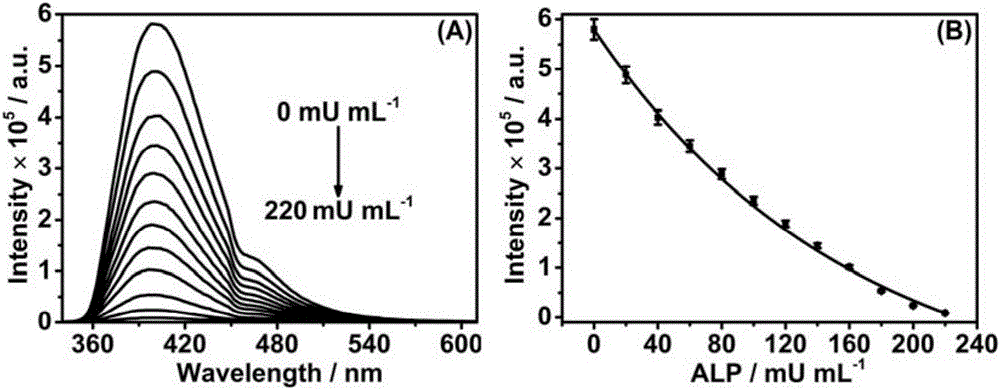
[0039] Make 20 μL of concentrations of 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, 180 and 220 mU mL -1 The alkaline phosphatase samples were added to 2980 μL containing 2 mM ascorbic acid-2-phosphate and 0.03 mM Cu 2+ - After incubating at 25° C. for 15 minutes in the detection solution of the bathocuproine disulfonic acid fluorescent probe, record the fluorescence emission spectrum of the detection solution.
[0040] from figure 2 It can be seen that with the increase of the alkaline phosphatase activity in the sample, the fluorescence emission intensity of the detection solution at ~402nm is correspondingly weakened, and the fluorescence emission intensity has a good quantitative relationship with the alkaline phosphatase activity. It can be seen that the fluorescence analysis method of ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The method of the invention is used to detect the selectivity of alkaline phosphatase activity.
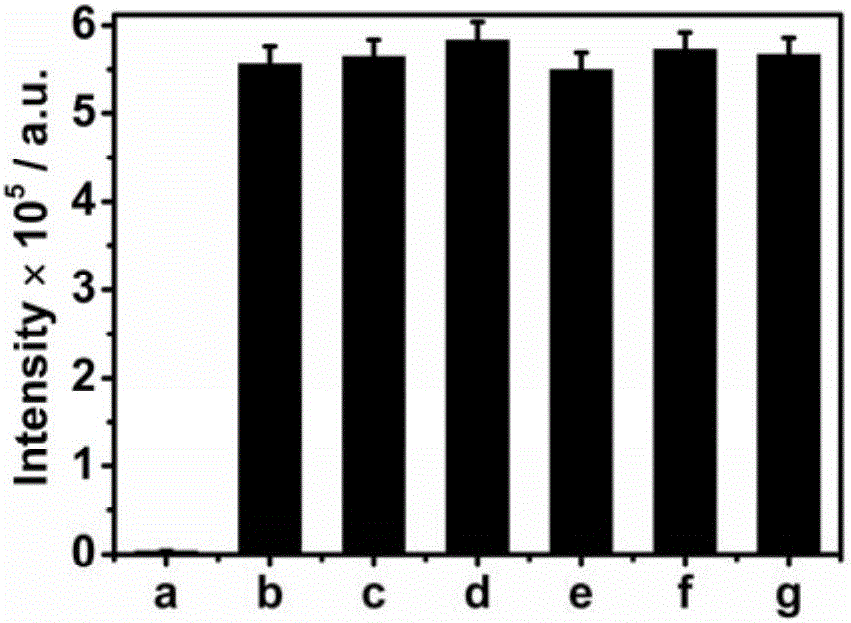
[0043] 20μL 0.05mg mL -1 Alkaline phosphatase or 20 μL 0.5mg mL -1 The other protein solution was added to 2980 μL containing 2 mM ascorbic acid-2-phosphate and 0.03 mM Cu 2+ - In the detection solution of the bathocuproine disulfonic acid fluorescent probe, after incubating at 25° C. for 15 minutes, record the fluorescence emission intensity of the detection solution at ~402 nm.
[0044] from image 3 It can be seen that compared with the blank control, although the concentration of other proteins is 10 times the concentration of alkaline phosphatase, only when alkaline phosphatase is added, the fluorescence emission intensity of the detection solution at ~402nm will decrease significantly. It can be seen that the fluorescence analysis method of the present invention has high selectivity when used to detect alkaline phosphatase activity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com