Photonic crystal waveguide coupler for two-dimensional silicon-based terahertz frequency domain
A photonic crystal waveguide and terahertz technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of little research, low transmission efficiency, and no attention to structural terahertz wave transmission, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing transmission loss, flexible structure, and regular structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Quadrilateral array coupled cavity terahertz waveguide based on (3+1+3) microcavities
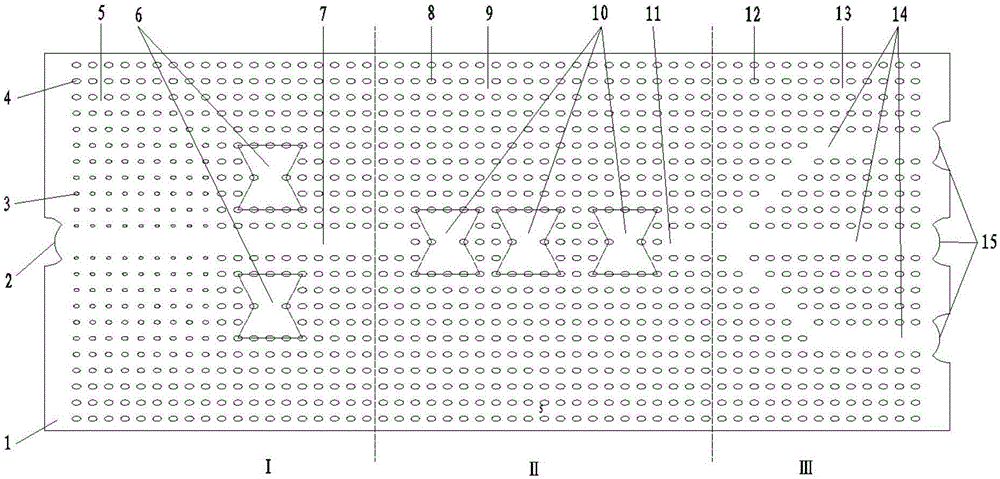
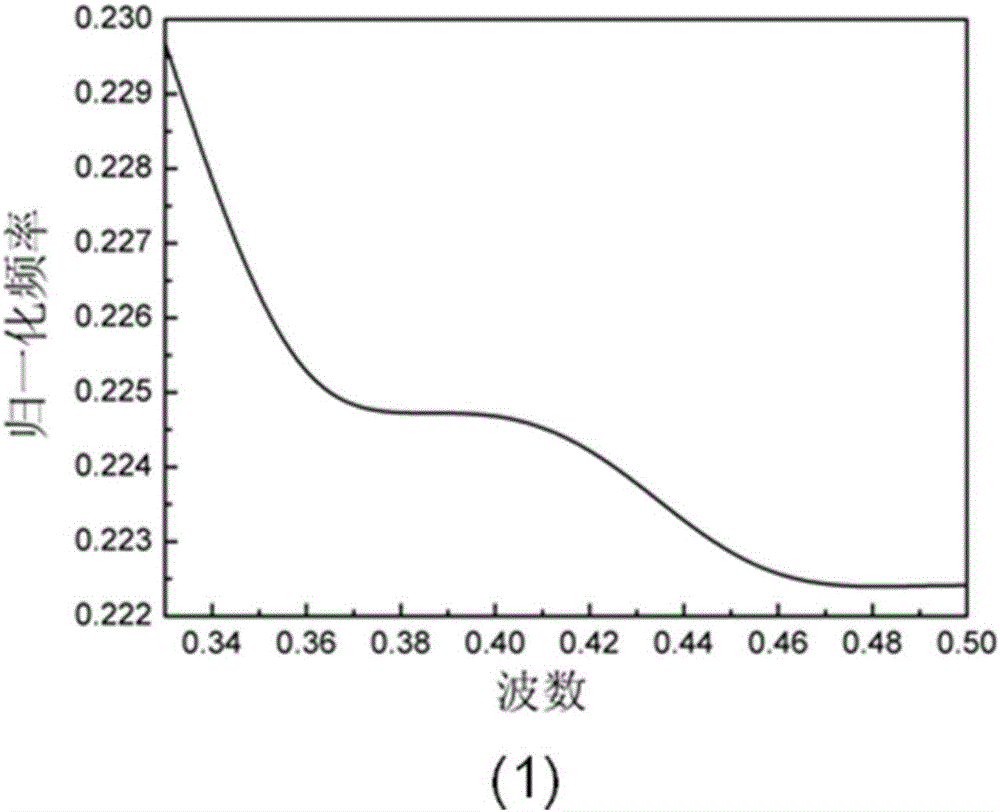
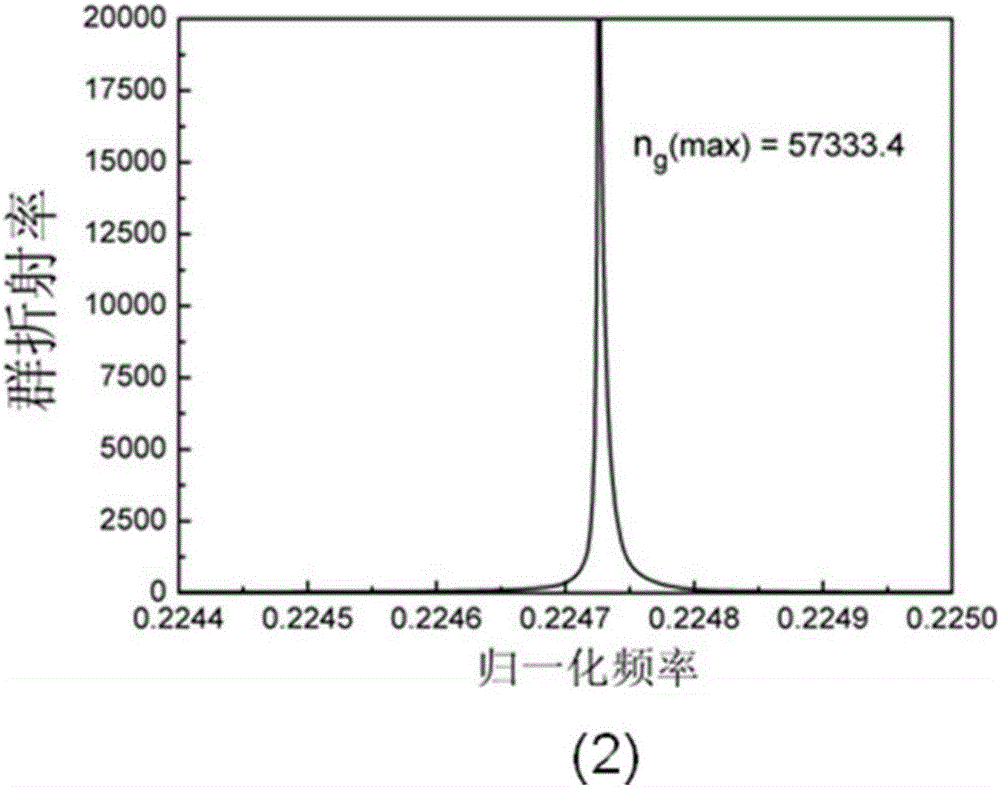
[0044] The structure of the photonic crystal waveguide coupler in the two-dimensional silicon-based terahertz frequency domain described in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the frequency f of the terahertz wave emitted by the external wave source is f=1THz=10 12 Hz, its wavelength is λ=300μm, the terahertz wave emitted by the wave source first reaches the coupling port 2 of the input area of the two-dimensional silicon base 1 through the optical fiber, and the two-dimensional silicon base 1 adopts a two-dimensional silicon wafer with a thickness of 700 μm. It is made of silicon wafers, the dielectric constant of the dielectric column is n=3.50, and the dielectric constant of air is n 0 =1.0, all the scattering elements in the two-dimensional silicon substrate 1 are circular segment scattering elements, and their processing depth is 200-500 μm; the posit...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Incompletely symmetrical terahertz waveguide based on hexagonal arrangement composed of (1+1) microcavities
[0050] The structure of the photonic crystal waveguide coupler in the two-dimensional silicon-based terahertz frequency domain described in this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the transmission area II is a line defect waveguide, and there is no coupling cavity 10 in the transmission area, but there is an output area coupling cavity 16 in the output area III, and the transmission efficiency of the two output area waveguides 14 on the upper and lower sides of the output area III is different. The frequency of the terahertz wave emitted by the wave source is f=1THz=10 12 Hz, its wavelength is λ=300μm. The terahertz wave emitted by the wave source first reaches the coupling port 2 of the input area of the two-dimensional silicon base 1 through the optical fiber. The two-dimensional silicon base 1 adopts a two-dimensional silicon wafer wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com