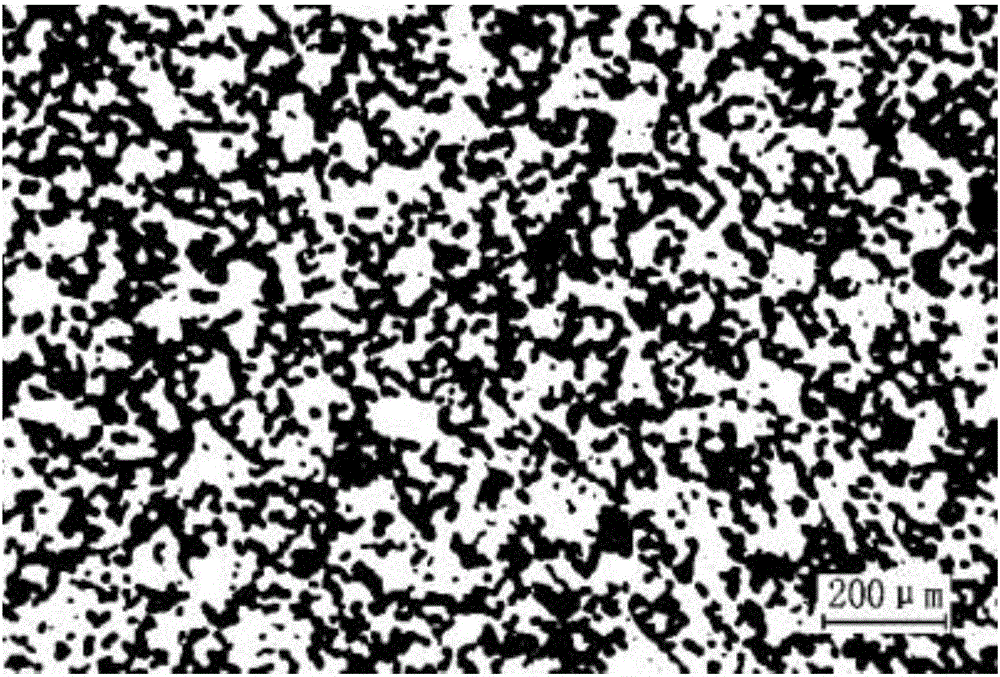
Medical implant porous Ti alloy and preparation method
A titanium alloy and particle size technology, applied in the field of medical implantation of porous titanium alloys and its preparation, can solve the problems of single pore size, shortened service life, base metal pollution, etc., and achieves low inclusion content, improved strength, and high elastic modulus. the effect of strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
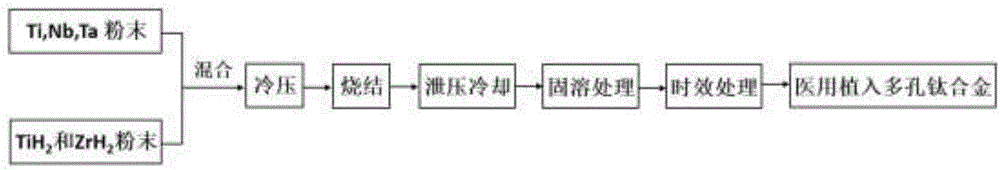
[0045] With high purity Ti, Nb, Ta, TiH 2 and ZrH 2 The powder is used as a raw material to prepare an alloy. The weight and particle size of each component are: Ti powder 40.467g, of which 20μm and 50μm Ti powder have the same weight; Nb powder 38.000g, 25μm; Ta powder 2.000g, of which 10μm and 20μm Ta powder have the same weight; Ti H 2 Powder 16.187g, 10μm; ZrH 2 Powder 4.088g, 10μm. The weight percent of each alloy element is: Nb: 38wt%; Zr: 4wt%; Ta: 2wt% and the balance is Ti. Put the powder into a vacuum ball mill tank, mix it in a three-dimensional motion mixer for 6 hours, and then cold press the powder into a cylindrical green body in a mold with a pressure of 200MPa; put the cylindrical green body into a vacuum sintering furnace , filled with argon with a purity of 99.990vol% and a pressure of 0.10MPa after vacuumizing in a cold state. Then heat up to 900°C at a heating rate of 300°C / h and keep the temperature for 3h. After the sintering is completed, open the...
Embodiment 2
[0047] With high purity Ti, Nb, Ta, TiH 2 and ZrH 2 The powder is used as a raw material to prepare an alloy. The weight and particle size of each component are: Ti powder 40.987g, of which 20μm, 50μm and 70μm Ti powder have an equal weight; Nb powder 37.300g, of which 25μm and 50μm Nb powder have an equal weight; Ta powder 1.300g , 15 μm; TiH 2 Powder 17.625g, 20μm; ZrH 2 Powder 3.577g, 15μm. The weight percent of each alloy element is: Nb: 37.3wt%; Zr: 3.5wt%; Ta: 1.3wt% and the balance is Ti. Put the powder into a vacuum ball mill tank and mix it in a three-dimensional motion mixer for 6.5 hours, then cold press the powder into a cylindrical green body in a mold with a pressure of 180MPa; put the cylindrical green body into a vacuum sintering furnace In the cold state, after evacuating in a cold state, it is filled with argon gas with a purity of 99.999vol%, and the pressure is 0.12MPa, and then heated to 950°C at a heating rate of 285°C / h, and kept for 2.5h. After the...
Embodiment 3
[0049] With high purity Ti, Nb, Ta, TiH 2 and ZrH 2 The powder is used as the raw material to prepare the alloy. The weight and particle size of each component are: Ti powder 40.546g, of which 50μm and 70μm Ti powder have the same weight; Nb powder 37.000g, 50μm; Ta powder 1.000g, 20μm; TiH 2 Powder 20.273g, of which 15μm and 25μm TiH 2 Powder weight is equal; ZrH 2 Powder 2.044g, 25μm. The weight percent of each alloy element is: Nb: 37wt%; Zr: 2wt%; Ta: 1wt%, and the balance is Ti. Put the powder into a vacuum ball mill tank and mix it in a three-dimensional motion mixer for 8 hours, then cold press the powder into a cylindrical green body in a mold with a pressure of 150MPa; put the cylindrical green body into a vacuum sintering furnace , after the cold state is vacuumized, it is filled with argon with a purity of 99.999vol%, and the pressure is 0.15MPa, and then heated to 1050°C at a heating rate of 250°C / h, and kept for 1.5h. After the sintering is completed, open th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com