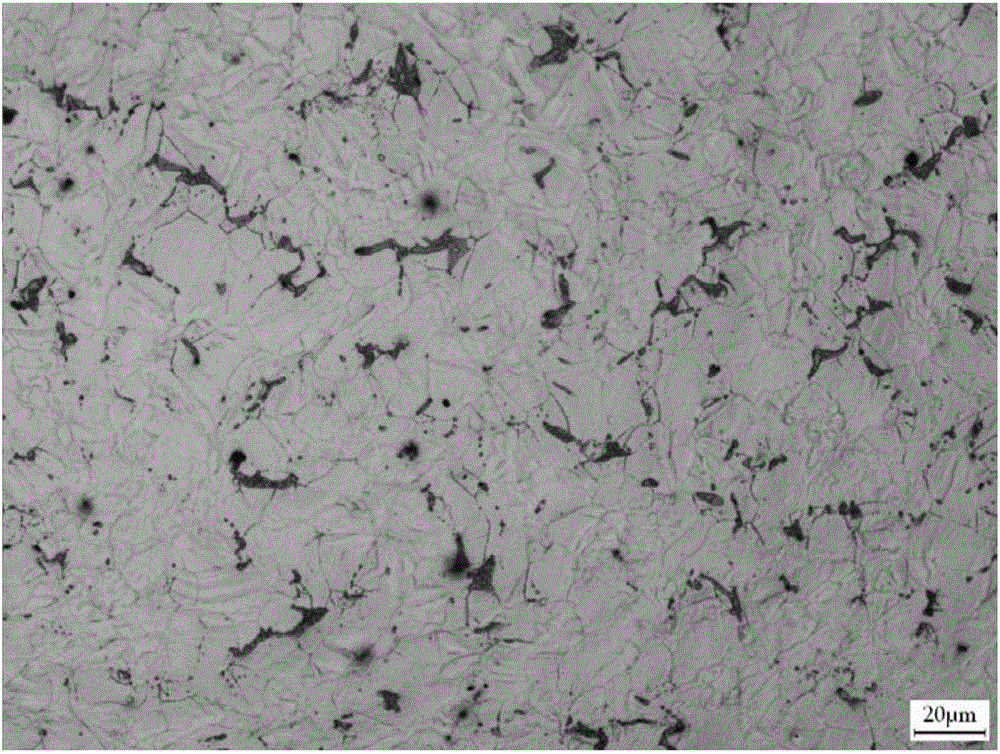
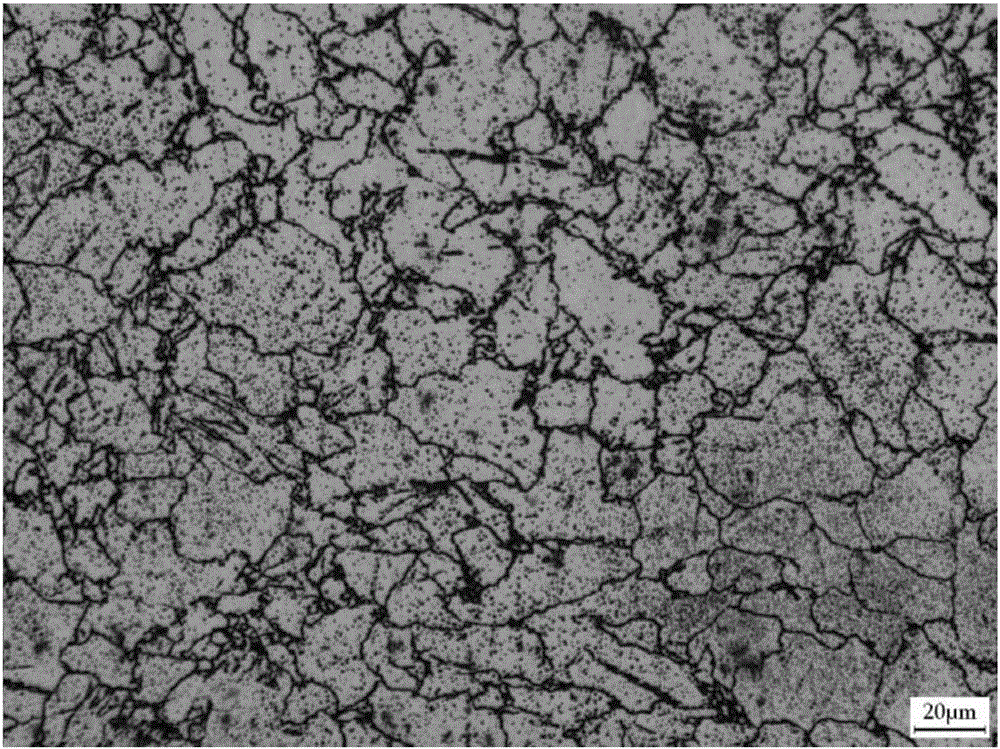
Machining method of small-specification high-strength magnesium alloy bars
A processing method and magnesium alloy technology, which is applied in the field of forming and processing of non-ferrous metals, can solve problems such as thermal cracking, narrow deformation temperature range, and grain growth, and achieve short process flow, improved yield strength, and increased tensile strength. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
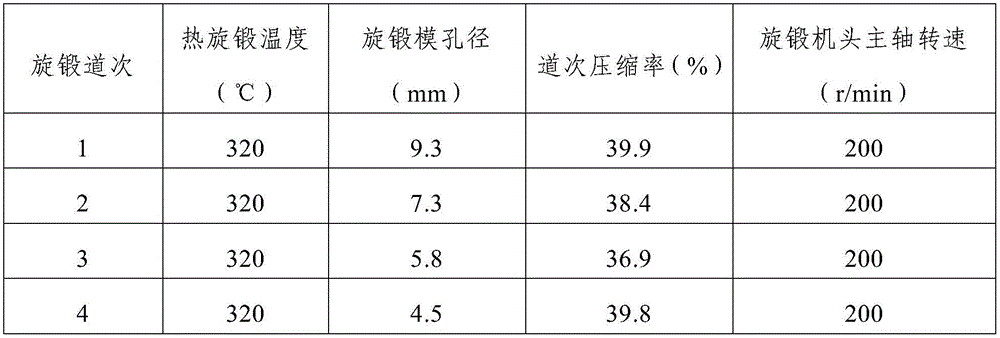
[0021] Taking the AZ61 magnesium alloy bar with a diameter of 4.5mm processed by hot swaging as an example, the method is as follows:
[0022] The AZ61 magnesium alloy billet with a diameter of 12mm is subjected to 4 passes of hot swaging to obtain an AZ61 magnesium alloy rod with a diameter of 4.5mm. The cumulative compression rate of the AZ61 magnesium alloy rod after 4 passes of hot swaging is 85.9%. Before each hot swaging pass, evenly apply a lubricant mixed with graphite powder, molybdenum disulfide and butter according to the mass ratio of 2:1:12.5 on the outside of the magnesium alloy billet, and the feeding speed of hot swaging is 0.2m / min ~1m / min, hot swaging process parameters are shown in Table 1;
[0023] The hot swaging process parameter of table 1 embodiment 1
[0024]
[0025] After the 1st to 4th passes of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is mechanically polished; after the 3rd pass of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is subjected to an inter...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Taking the hot swaging method to process Mg-2Zn-0.1Ca rods with a diameter of 10mm as an example, the method is as follows:
[0029] The Mg-2Zn-0.1Ca billet with a diameter of 30 mm is subjected to 7 passes of hot swaging to obtain a Mg-2Zn-0.1Ca bar with a diameter of 10 mm. The Mg-2Zn-0.1 after 7 passes of hot swaging The accumulative compression rate of the Ca bar is 88.9%. Before each pass of hot swaging, a lubricant mixed with graphite powder, molybdenum disulfide and butter in a mass ratio of 2:1:15 is evenly applied on the outside of the magnesium alloy billet. The feeding speed of swaging is 0.8m / min~2m / min, and the technical parameters of hot swaging are shown in Table 2;
[0030] The hot swaging process parameter of table 2 embodiment 2
[0031]
[0032]
[0033] After the 1st to 7th passes of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is mechanically polished; after the 4th pass of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is subjected to an intermediate an...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Taking the processing of Mg-5Zn rods with a diameter of 8mm by hot swaging as an example, the method is as follows:
[0037] A Mg-5Zn billet with a diameter of 50 mm is hot swaged 6 times to obtain a Mg-5Zn rod with a diameter of 8 mm. The cumulative compression ratio of the Mg-5Zn rod after 6 times of hot swaging is 84 %, before each pass of hot swaging, evenly apply a lubricant mixed with graphite powder, molybdenum disulfide and butter in a mass ratio of 2:1:15 on the outside of the magnesium alloy billet, and the feeding speed of hot swaging is 0.2m / min~2m / min, hot swaging process parameters are shown in Table 3;
[0038] The hot swaging process parameter of table 3 embodiment 3
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] After the 1st to 11th passes of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is mechanically polished; after the 4th pass of hot swaging, the magnesium alloy billet is subjected to an intermediate annealing treatment at 250 ° C for 60 minutes, and then the surfa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com