Quantitative evaluation method for water and sand reduction effect of erosion and torrent control work
A quantitative evaluation and evaluation method technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate calculation or simulation, affecting the accuracy of calculation or simulation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
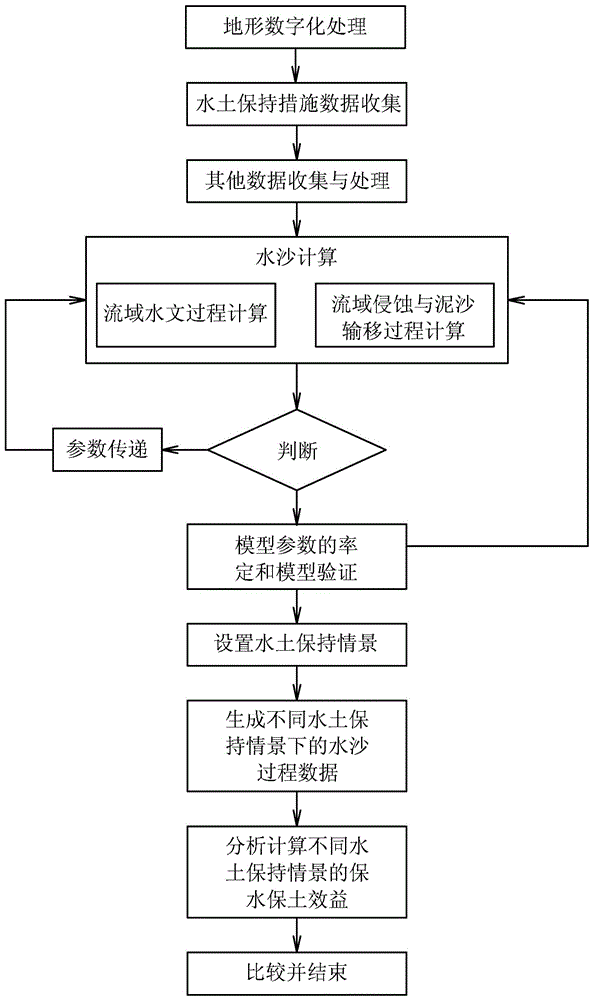
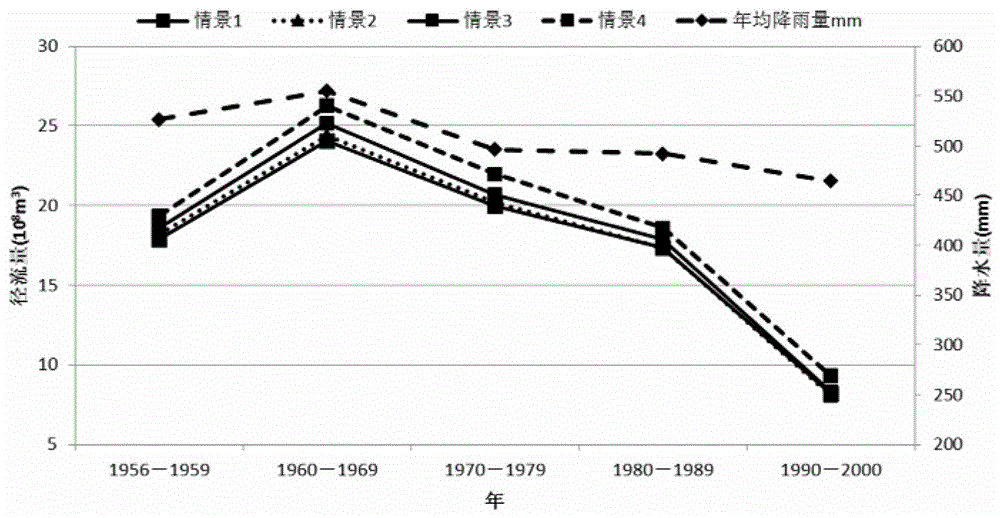
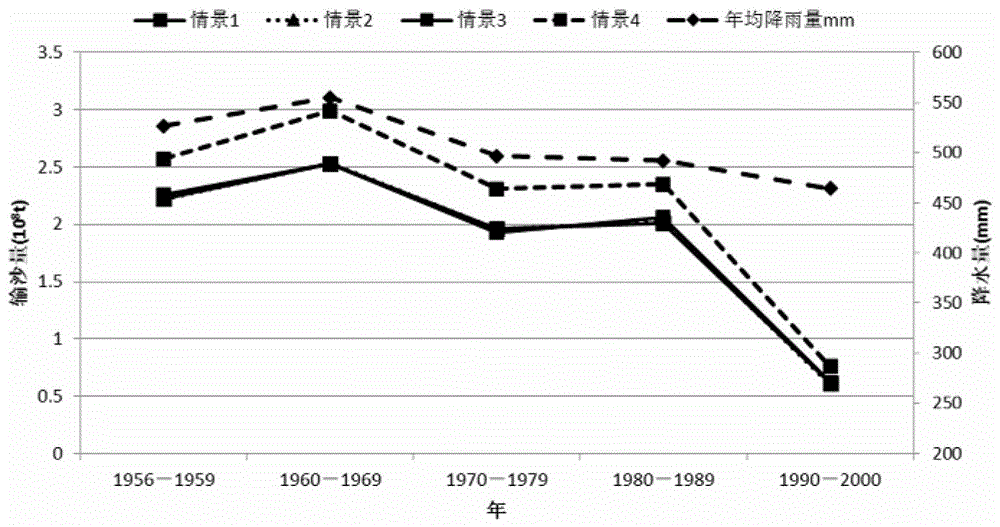
[0084] This embodiment is a quantitative evaluation method for water and sediment reduction benefits of soil and water conservation projects. In this example, based on the process-based hydrological simulation, through the systematic identification of the coupling relationship between topographic features and hydrodynamic features, the establishment of soil erosion based on terrain "surface (sheet) erosion - rill erosion - shallow gully erosion - gully erosion" The simulation method of soil erosion and sediment transport process is based on the chain as the platform and the typical hydrodynamic conditions are "thin-layer water flow-stream flow". In this embodiment, firstly, the topological relationship of the slope calculation unit and the confluence channel network are formed by processing the DEM data, and then this is the platform for hydrometeorology, water and soil conservation measures (water and soil conservation forest grass, terraced fields, horizontal ditches, fish sc...
Embodiment 2
[0161] This embodiment is an improvement of the embodiment, and is a refinement of the calculation of evapotranspiration in the first embodiment. The evapotranspiration calculation described in this embodiment:
[0162] The evapotranspiration within the calculation unit (grid or contour zone) includes evaporation from the wet leaf surface of the vegetation (vegetation intercepted water), water, soil, urban ground surface, urban buildings, etc., and transpiration from the dry leaf surface of the vegetation . The average evapotranspiration model of the calculation unit is calculated by the following formula:
[0163] (1)
[0164] In the formula, F W , F U , F SV , F IR , F NI are the area ratios (%) of water area, impermeable water area, bare land-vegetation area, irrigated farmland and non-irrigated farmland in the calculation unit; E W , E SV , E U , E IR , E NI They are the evaporation or evapotranspiration of the water area, impermeable water area, b...
Embodiment 3
[0203] This embodiment is an improvement of the above embodiment, and is a refinement of the above embodiment regarding infiltration calculation. The infiltration calculation described in this embodiment uses the Green-Ampt vertical one-dimensional infiltration model to simulate rainfall infiltration and over-seepage slope runoff, and the general Green-Ampt model for calculation.
[0204] When the infiltration wetting front reaches the m The infiltration capacity of the soil layer is calculated by the following formula:
[0205] (twenty four)
[0206] In the formula, f is the infiltration capacity; F is the cumulative infiltration; k m , A m-1 , B m-1 See below. cumulative infiltration F The calculation method depends on whether there is water on the ground surface.
[0207] If the self-infiltration wetting front enters the first m-1 The surface of the soil has continuously accumulated water since the beginning of the soil layer, then the cumulative infiltratio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com