Endophytic fungi for improving salviae miltiorrhizae yield and content of effective components and application thereof
An endophytic fungus and Salvia miltiorrhiza technology is applied in the field of microorganisms to achieve the effects of promoting biosynthesis, increasing the area of a single leaf, and increasing biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
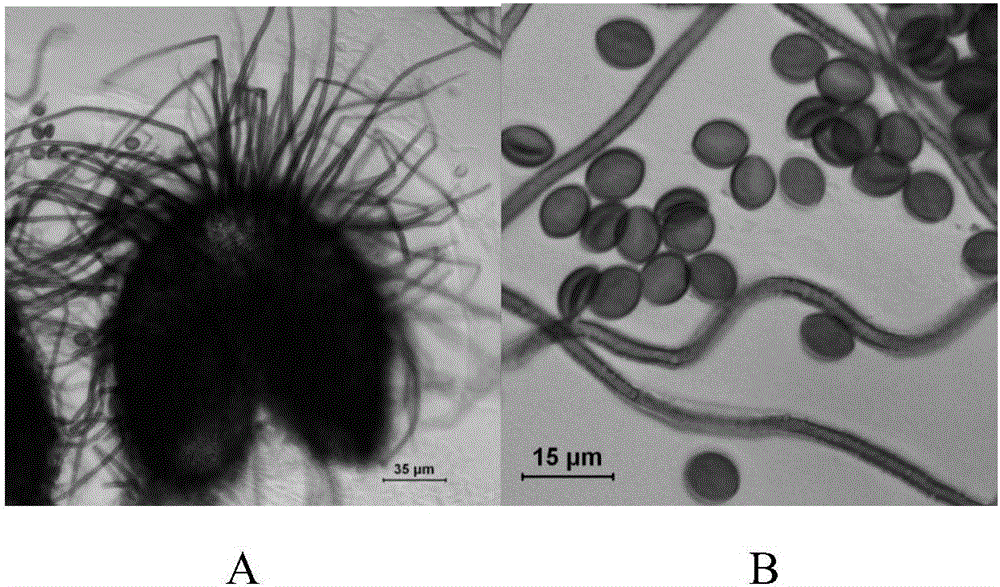
[0055] Example 1: Isolation and purification of endophytic fungi from Salvia miltiorrhiza
[0056] The endophytic fungus of Salvia miltiorrhiza of the present invention is a strain obtained from leaves of Danshen root in Ruicheng, Shanxi.
[0057] The endophytic fungus of Salvia miltiorrhiza of the present invention is separated and obtained according to the following steps: washing with tap water for 30 minutes to remove sediment, and then washing with deionized water for 3 times. Surface disinfection of leaves was carried out according to the following procedure: 75% ethanol, 30s→1.3M sodium hypochlorite (3-5% available chlorine), 1min→75% ethanol, 30s→sterile deionized water washing 3 times. After the filter paper was blotted to dry the residual moisture, the leaves were cut into 1cm×1cm tissue pieces with a sterilized scalpel, and placed in PDA containing 100mg / L penicillin (potato 200g / L, glucose 20g / L, agar, 15g / L) culture medium at 28°C. The samples were observed for...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: the cultivation of the aseptic seedling of Salvia miltiorrhiza
[0061] The salvia miltiorrhiza seed of the present invention is purchased from Shanxi Shangluo Tianshili Danshen planting base.
[0062] The aseptic seedlings of Salvia miltiorrhiza of the present invention are cultivated according to the following steps: soak the seeds of Salvia miltiorrhiza in hot water at 40-50°C for 2 hours, wipe off the sticky matter on the surface of the seeds with sterile gauze; then carry out disinfection treatment by conventional disinfection method: 75% Ethanol 30s, 2% NaClO 3 min, 75% ethanol for 30 seconds, rinsed with sterile water for 10 times, and finally inoculated on MS medium at 25°C, 16h light / 8h dark culture, and transferred to new MS medium after seed germination to obtain sterile seedlings.
Embodiment 3
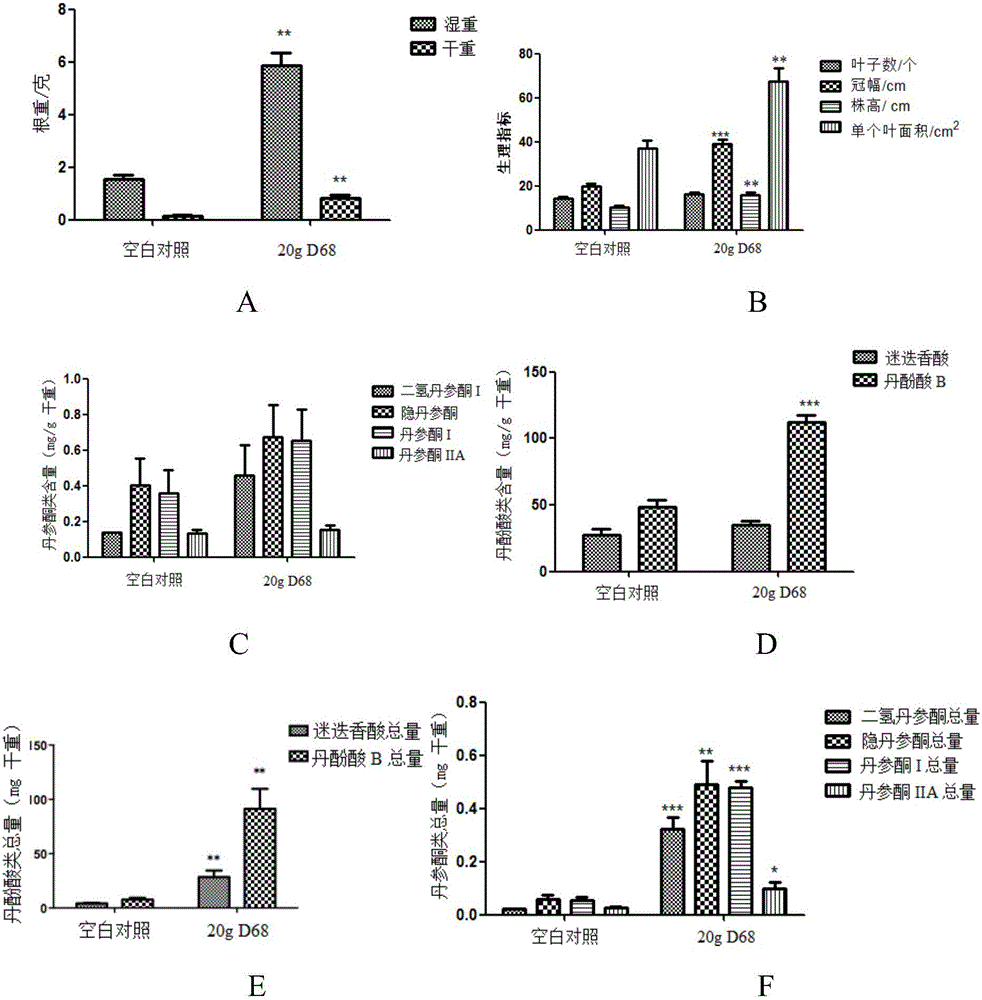
[0063] Example 3: Determination of the content of active components of tanshinones and salvianolic acids in the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza
[0064] When preparing the seed root of the Salvia miltiorrhiza plant and harvesting, the soil on the root of the Salvia miltiorrhiza root was washed off, washed with distilled water for 3 times, and the residual water was blotted with filter paper. After drying at 50°C to constant weight, determine the content of active ingredients of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the ingredients according to the following method.
[0065] High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to analyze the content of active ingredients of tanshinone and salvianolic acid, mainly to quantitatively detect the content of rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid B, tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone I . Specific steps are as follows:
[0066] Preparation of samples for HPLC injection of Salvia miltiorrhiza root: Precisely ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com