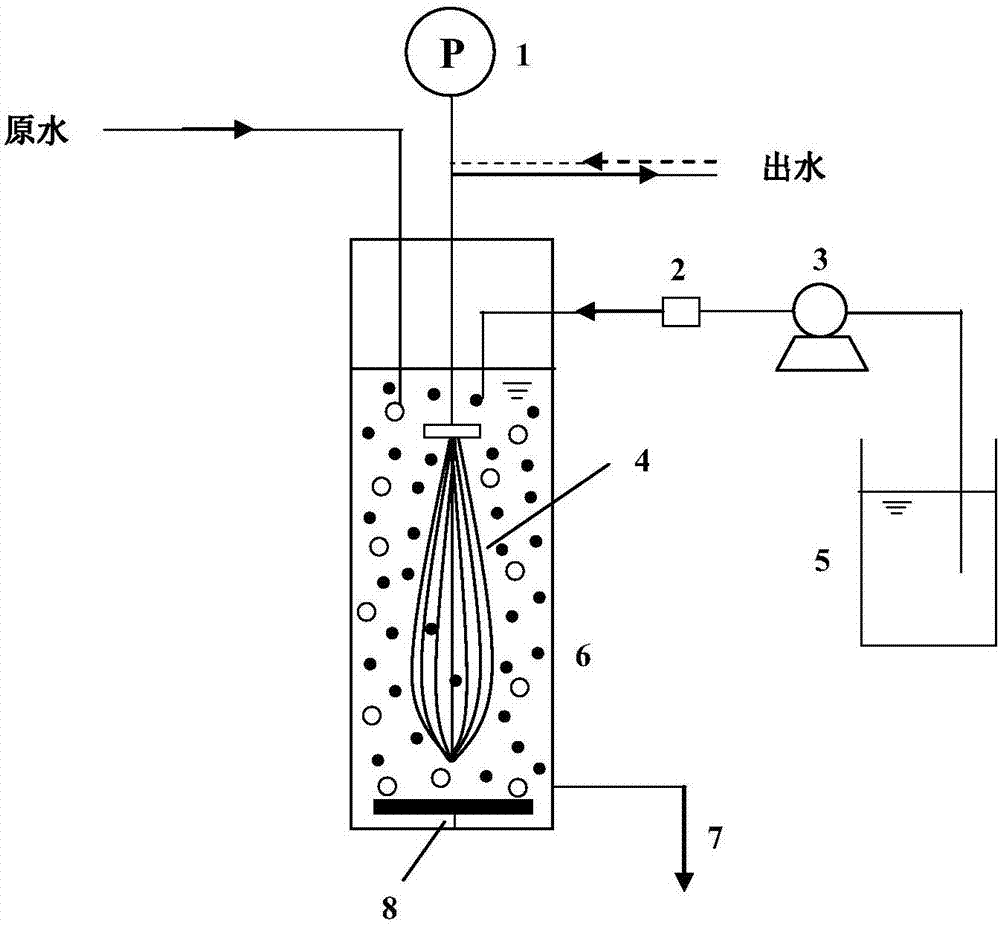
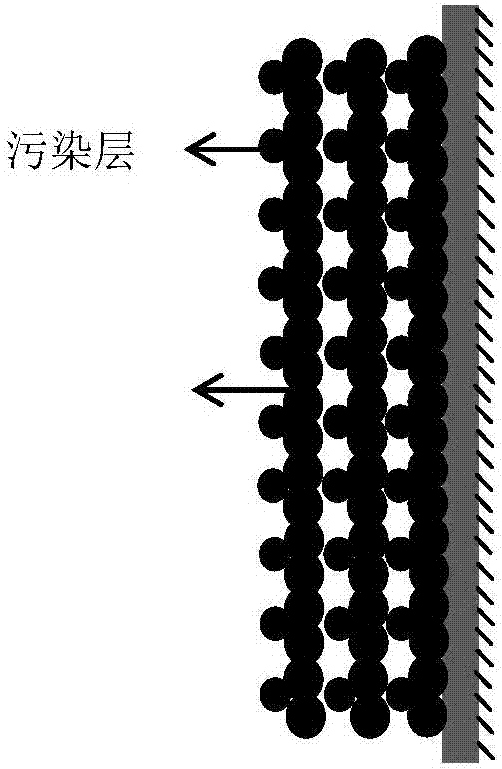
A low-pressure membrane water treatment technique based on a sandwich type loose floc protective layer
A low-pressure membrane and sandwich technology, applied in the field of water treatment and membrane fouling control, can solve the problems of easily scratched ultrafiltration membrane, high adsorbent price, aggravated membrane fouling, etc. small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment takes humic acid (HA) as an example. The total organic carbon content of humic acid in the water to be treated is 7.8mg / L. The integrated ultrafiltration membrane combination process is adopted, and no coagulant is added. The raw water enters the membrane tank at 1L / h, and the hydraulic retention time in the membrane tank is 2.2h. There is no sludge discharge in the membrane tank. After 8 days of continuous operation, the transmembrane pressure difference increased to 55.3kPa, and the removal rate of HA in the effluent was 32.3%, and the removal rate of small molecule HA (<3kDa) was 7.9%. After the operation, the ultrafiltration membrane was washed with water, and the transmembrane pressure dropped to 10.1kPa.
Embodiment 2
[0035]This embodiment takes humic acid (HA) as an example. The total organic carbon content of humic acid in the water to be treated is 7.8mg / L. Using the integrated ultrafiltration membrane combination process, dosing once every 48h, a total of 4 times, adding 1000mg of aluminum chloride (2.33mg / L as aluminum) each time. The raw water enters the membrane tank at 1L / h, and the hydraulic retention time in the membrane tank is 2.2h. There is no sludge discharge in the membrane tank. After 8 days of continuous operation, the transmembrane pressure difference increased to 15.2kPa, and the removal rate of HA in the effluent was 52.7%, among which the removal rate of small molecule HA (<3kDa) was 24.8%. After the operation, the ultrafiltration membrane was washed with water, and the transmembrane pressure dropped to 3.7kPa.
Embodiment 3
[0037] This embodiment takes humic acid (HA) as an example. The total organic carbon content of humic acid in the water to be treated is 7.8mg / L. Using the integrated ultrafiltration membrane combination process, dosing once every 24 hours, a total of 8 times, dosing 500mg of aluminum chloride (2.33mg / L as aluminum) each time. The raw water enters the membrane tank at 1L / h, and the hydraulic retention time in the membrane tank is 2.2h. There is no sludge discharge in the membrane tank. After 8 days of continuous operation, the transmembrane pressure difference increased to 14.6kPa, and the removal rate of HA in the effluent was 58.6%, and the removal rate of small molecule HA (<3kDa) was 30.7%. After the operation, the ultrafiltration membrane was washed with water, and the transmembrane pressure dropped to 3.2kPa.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com