Method for Screening Molecular Markers Related to Leaf Growth
A technology of molecular markers and duckweed, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe measurement/inspection, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the efficiency of biological treatment and fast detection speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
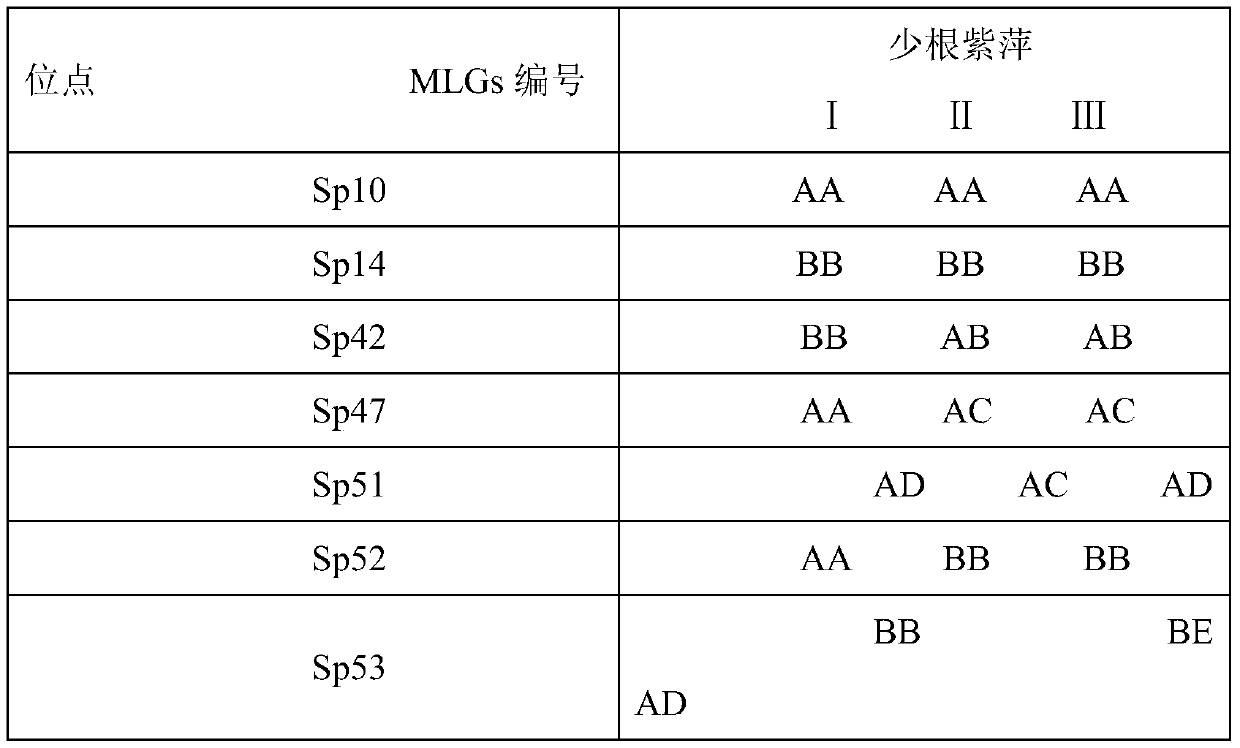
[0015] The method for screening the molecular markers related to the growth of the leaves of P. fruticosa includes clone culture, genomic DNA extraction, design of microsatellite primers, PCR amplification, and data statistics and analysis.
[0016] The composition and concentration of the nutrient solution for plant clone cultivation are: nitrogen 0.3-0.4g / L, phosphoric anhydride 0.1-0.15g / L, potassium oxide 0.16-0.23g / L, magnesium oxide 0.01-0.015g / L and sulfur 0.012 ~0.02g / L. The above-mentioned nutrient solution can comprehensively provide the macroelements and trace elements required for the growth of P. chinensis, the asexual reproduction speed is fast, the probability of gene mutation is low, and a large number of plants with the same gene can be obtained, and the sample size is sufficient.
[0017] The plant clones were cultured indoors in a light incubator for 50-70 days, the culture conditions were 22.5-23.5°C, the humidity was 73-83%, the light intensity was 1800-22...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The method for screening the molecular markers related to the growth of the leaves of P. fruticosa includes clone culture, genomic DNA extraction, design of microsatellite primers, PCR amplification, and data statistics and analysis.
[0023] The composition and concentration of the nutrient solution for plant clone cultivation are: nitrogen 0.32g / L, phosphoric anhydride 0.12g / L, potassium oxide 0.19g / L, magnesium oxide 0.012g / L and sulfur 0.016g / L. The above-mentioned nutrient solution can comprehensively provide the macroelements and trace elements required for the growth of P. chinensis, the asexual reproduction speed is fast, the probability of gene mutation is low, and a large number of plants with the same gene can be obtained, and the sample size is sufficient.
[0024] The plant clones were cultured indoors for 60 days in a light incubator, the culture conditions were 23° C., humidity 78%, light intensity 2000 lux, light and dark time 16:8 hours. Under the above...
Embodiment 3
[0029] The method for screening the molecular markers related to the growth of the leaves of P. fruticosa includes clone culture, genomic DNA extraction, design of microsatellite primers, PCR amplification, and data statistics and analysis.
[0030] The composition and concentration of the nutrient solution for plant clone cultivation are: nitrogen 0.32g / L, phosphoric anhydride 0.12g / L, potassium oxide 0.2g / L, magnesium oxide 0.013g / L and sulfur 0.017g / L. The above-mentioned nutrient solution can comprehensively provide the macroelements and trace elements required for the growth of P. chinensis, the asexual reproduction speed is fast, the probability of gene mutation is low, and a large number of plants with the same gene can be obtained, and the sample size is sufficient.
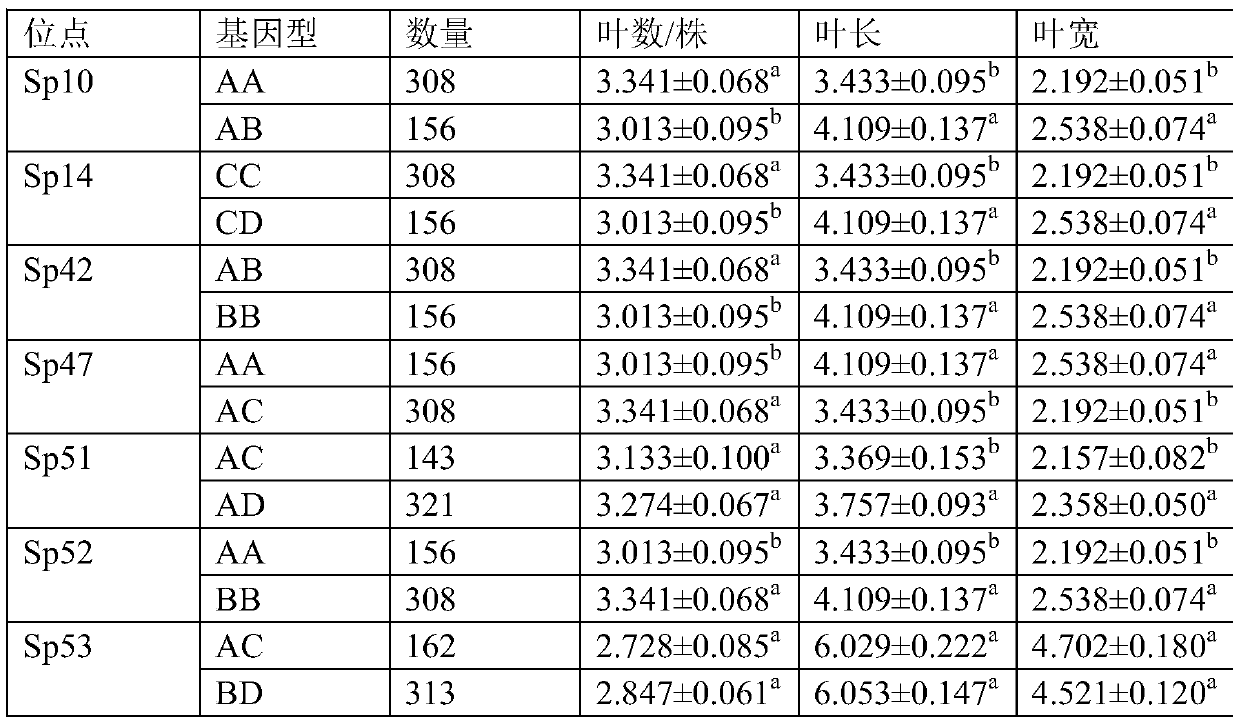
[0031] The number of leaves was counted for each plant (leaves connected) in different culture lines, and the leaf length (the longest length of the leaf), the width of the leaf (the shortest length of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com