Solvent resistant, transparent aromatic polyamide films with high refractive indices
An aromatic polyamide, high refractive index technology, applied in polyamide coatings, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in polymer production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
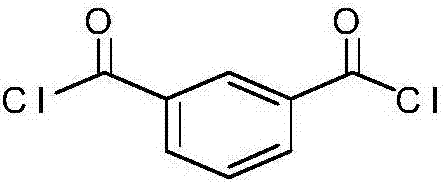
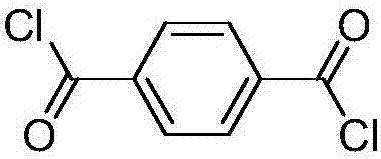
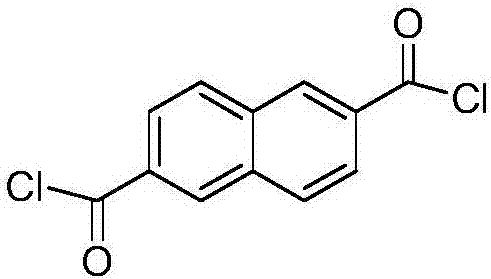
[0047] Example 1: This example illustrates a common method for preparing an aromatic polyamide solution from a mixture of diacid chlorides (TPC, IPC and / or NDC) and at least one diamine (FDA or TCB). Commonly used chemical reactions are as follows:
[0048]
[0049]In one experiment, about 87.11 g (0.25 mol) of 9,9-bis(4-aminophenyl) fluorine (FDA), 44 g (0.75 mol) of propylene oxide (PrO), and 1014 g of dimethylacetamide ( DMAc) was added to a 2 L three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen inlet and outlet and mechanical stirrer. Once the FDA is completely dissolved, cool the resulting solution in an ice-water bath. To the cooled resulting solution, about 15.23 g (0.075 mol) of isophthaloyl chloride (IPC) was added to the flask. Then, about 35.53 g (0.175 mol) of terephthaloyl chloride (TPC) were added in portions over 2 hours. The acid chloride / diamine solution was then stirred at room temperature for an additional 6 hours to form a polymer solution. The p...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: This example illustrates a common method for preparing a solution of a polyamide containing pendant carboxylic acid groups. Polymer solutions can be made from mixtures of dichlorides (TPC, IPC and / or NDC) and diamines, including at least one with free carboxylic acid pendant groups (FDA or TCB and DAB). Commonly used chemical reactions are as follows:
[0051]
[0052] In one experiment, about 3.3101 g (0.0095 mol) FDA, 0.0761 g (0.0005 mol) 3,5-diaminobenzoic acid (DAB), 4.4 g (0.075 mol) (PrO) and 38 g DMAc were added to a 250 ml A three-neck round bottom flask with nitrogen inlet and outlet and a mechanical stirrer. Once the diamine was completely dissolved, the solution was cooled in an ice-water bath. To this solution, approximately 0.2030 g (0.001 mol) of IPC was added to the flask. Then, about 1.8272 g (0.009 mol) of TPC was added in several portions over 2 hours. The acid chloride / diamine solution was then stirred at room temperature for a furt...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Examples 3 and 4: These examples illustrate the general procedure used to prepare polyamide solutions containing polyfunctional epoxy compounds (Example 3) and polyfunctional aromatic carboxylic acids (Example 4). The polymer solution was first prepared as described in Example 1, then TG or TA (an amount corresponding to 5 wt% of the polymer) was added. The polymer solution contained a total of about 10 wt% solids.
[0054] Membrane preparation
[0055] The polymer solution was spread on the glass substrate using a spatula. The solvent was evaporated at 60°C for 1 hour, and the film was dried under reduced pressure at 160°C for 12 hours. For films containing multifunctional epoxies, no further heating is required. However, films containing polyfunctional aromatic carboxylic acids and films prepared from polyamides containing pendant carboxyl groups were further heated at a high temperature close to the Tg of the polyamide for 30 minutes, and then taken out from the g...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transparency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com