Nanometer zero-valent iron-loaded lignin-grafted bentonite composite material and preparation method thereof
A nano-zero-valent iron and composite material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, processing wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of narrow application range, unsatisfactory treatment effect, inapplicability, etc. Improved stability, good treatment effect, good adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
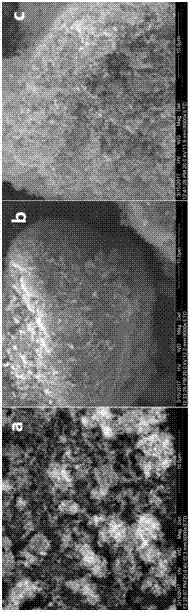
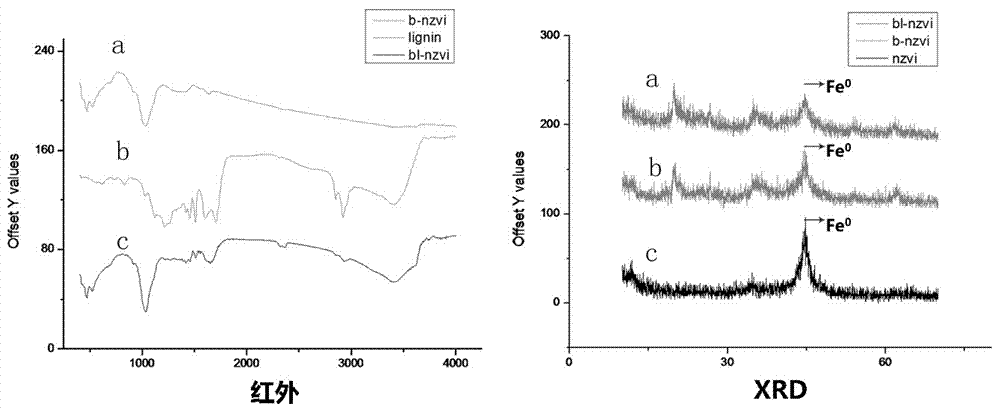
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] At 25°C, dissolve 9.66g of ferric chloride in 50ml of distilled water, transfer to a three-necked flask, blow nitrogen, and stir. Subsequently, 2 g of bentonite and 2 g of lignin were added to the three-necked flask, and vigorously stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring is completed, dissolve 3.54g of sodium borohydride in 100ml of distilled water, and add it into the three-neck flask at a rate of 1-2 drops per second, and stir for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition is completed. Then, 2 g of acrylamide was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, and 0.4 g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide was dissolved in 20 ml of distilled water, which were successively added into a three-necked flask and stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring was completed, 0.2 g of potassium persulfate was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, added into a three-necked flask, and 100 microliters of N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine was added, and stirred for 30 minutes. The product was va...
Embodiment 2
[0031] At 30°C, dissolve 9.66g of ferric chloride in 50ml of distilled water, transfer to a three-necked flask, blow nitrogen, and stir. Subsequently, 2 g of bentonite and 2 g of lignin were added to the three-necked flask, and vigorously stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring is completed, dissolve 3.54g of sodium borohydride in 100ml of distilled water, and add it into the three-neck flask at a rate of 1-2 drops per second, and stir for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition is completed. Subsequently, 3 g of acrylamide was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, and 0.3 g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide was dissolved in 20 ml of distilled water, which were successively added into a three-necked flask and stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring was completed, 0.3 g of potassium persulfate was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, and added to a three-neck flask, and 100 microliters of N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine was added, and stirred for 30 minutes. The produc...
Embodiment 3
[0033] At 30°C, dissolve 9.66g of ferric chloride in 50ml of distilled water, transfer to a three-necked flask, blow nitrogen, and stir. Subsequently, 2 g of bentonite and 2 g of lignin were added to the three-necked flask, and vigorously stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring is completed, dissolve 3.54g of sodium borohydride in 100ml of distilled water, and add it into the three-neck flask at a rate of 1-2 drops per second, and stir for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition is completed. Then, 4 g of acrylamide was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, and 0.2 g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide was dissolved in 20 ml of distilled water, which were successively added into a three-necked flask and stirred for 30 minutes. After the stirring was completed, 0.5 g of potassium persulfate was dissolved in 10 ml of distilled water, and added to a three-neck flask, and 100 microliters of N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine was added, and stirred for 1 h. The product was vacuum fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com