Method for in-situ determination of activity of drinking water biological activated carbon TTC-dehydrogenase
A technology of biological activated carbon and dehydrogenase, applied in the direction of color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of destruction, microbial poisoning, damage, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation method, low operation cost and wide application prospect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
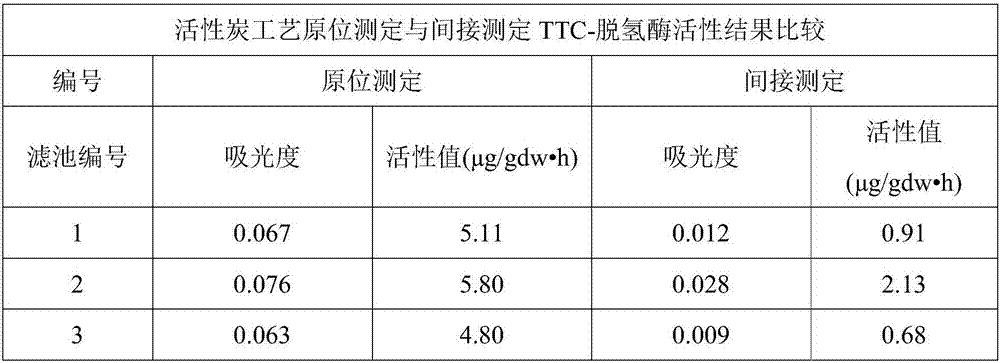
[0032] Specific embodiment one: the present embodiment is a kind of method for in situ determination of drinking water biological activated carbon TTC-dehydrogenase activity is carried out according to the following steps:
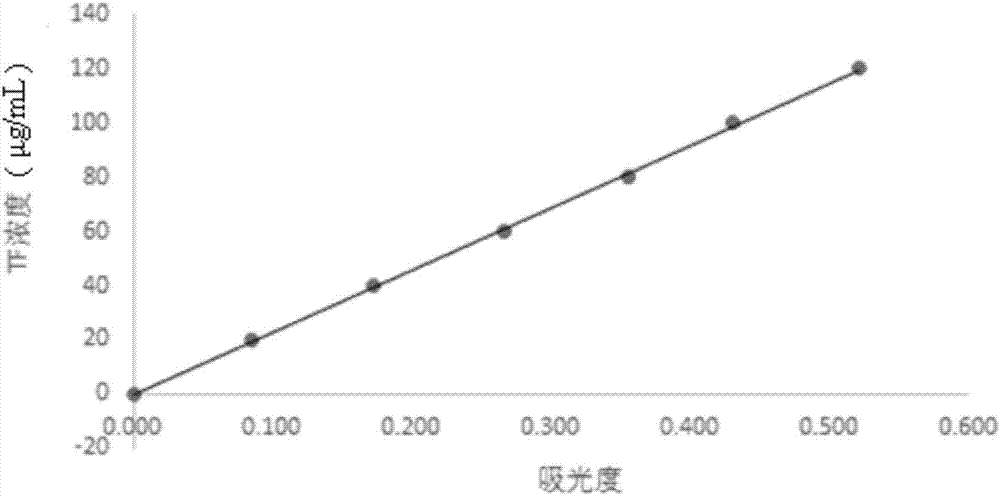
[0033] 1. Use the absorbance value as the abscissa and the TF concentration as the ordinate to draw the TF standard curve;
[0034] 2. Sample treatment: Take out the activated carbon filter material to be tested from the water, wash it repeatedly with distilled water for 3 to 4 times, then divide the washed activated carbon filter material into 2 parts according to the mass, and put them into two plugged colorimetric tubes respectively. middle;
[0035] 3. Add Tris-HCL buffer solution and 0.36% Na in the two stoppered colorimetric tubes in step 2. 2 SO 3 Solution, glucose solution with a concentration of 0.1mol / L and TTC solution with a mass concentration of 0.4% until the activated carbon filter material is completely submerged, then add formaldehyde so...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0046] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: draw TF standard curve in step one and carry out according to the following steps:
[0047] 1) Pipette 1mL, 2mL, 3mL, 4mL, 5mL and 6mL of TTC standard use solution into six 50mL volumetric flasks, dilute to volume with water, and prepare 20μg / mL, 40μg / mL, 60μg / mL, 80μg / mL respectively mL, 100 μg / mL and 120 μg / mL TTC solutions; the preparation method of the TTC standard use solution is as follows: Weigh 100 mg of TTC solid, dissolve and set the volume to a 100 m volumetric flask to obtain the TTC standard use solution;
[0048] 2) Take 7 test tubes, add 2mL of Tris-HCL buffer respectively, then add 1mL of TTC solution of different concentrations in step (1) to 6 of them, and add 1mL of anaerobic water to the 7th test tube as a control , and then add 1mL of 10% sodium sulfide solution to the 7 test tubes, put the 7 test tubes into a 37°C constant temperature shaker and shake fo...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 4, the stoppered colorimetric tubes of the test group and the blank group were placed in a constant temperature water bath shaker with a temperature of 37° C. for 20 hours. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com