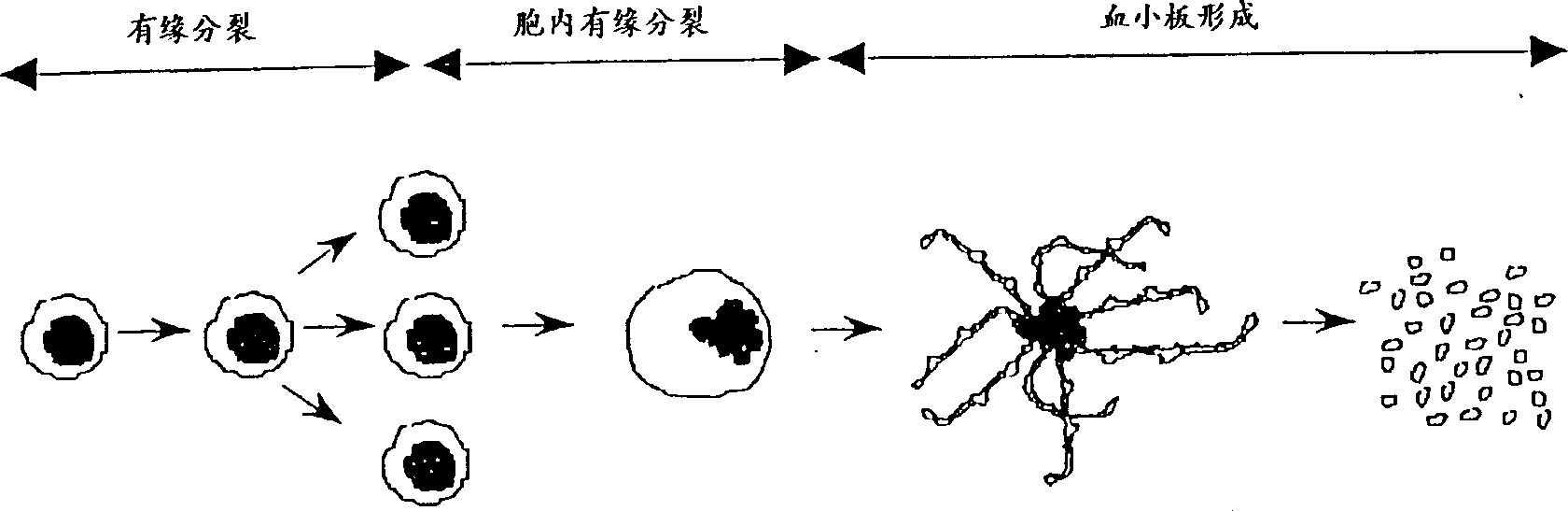
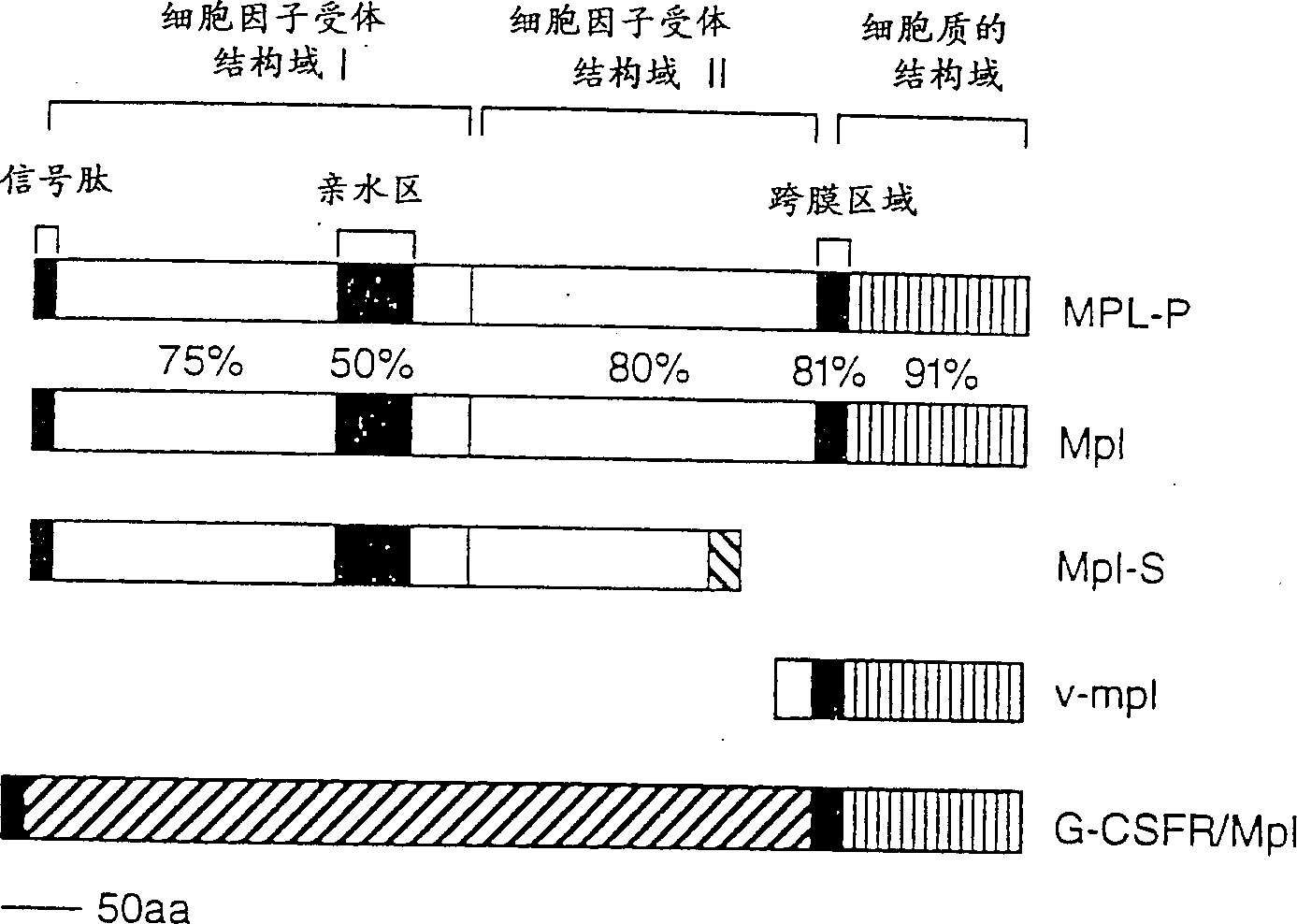
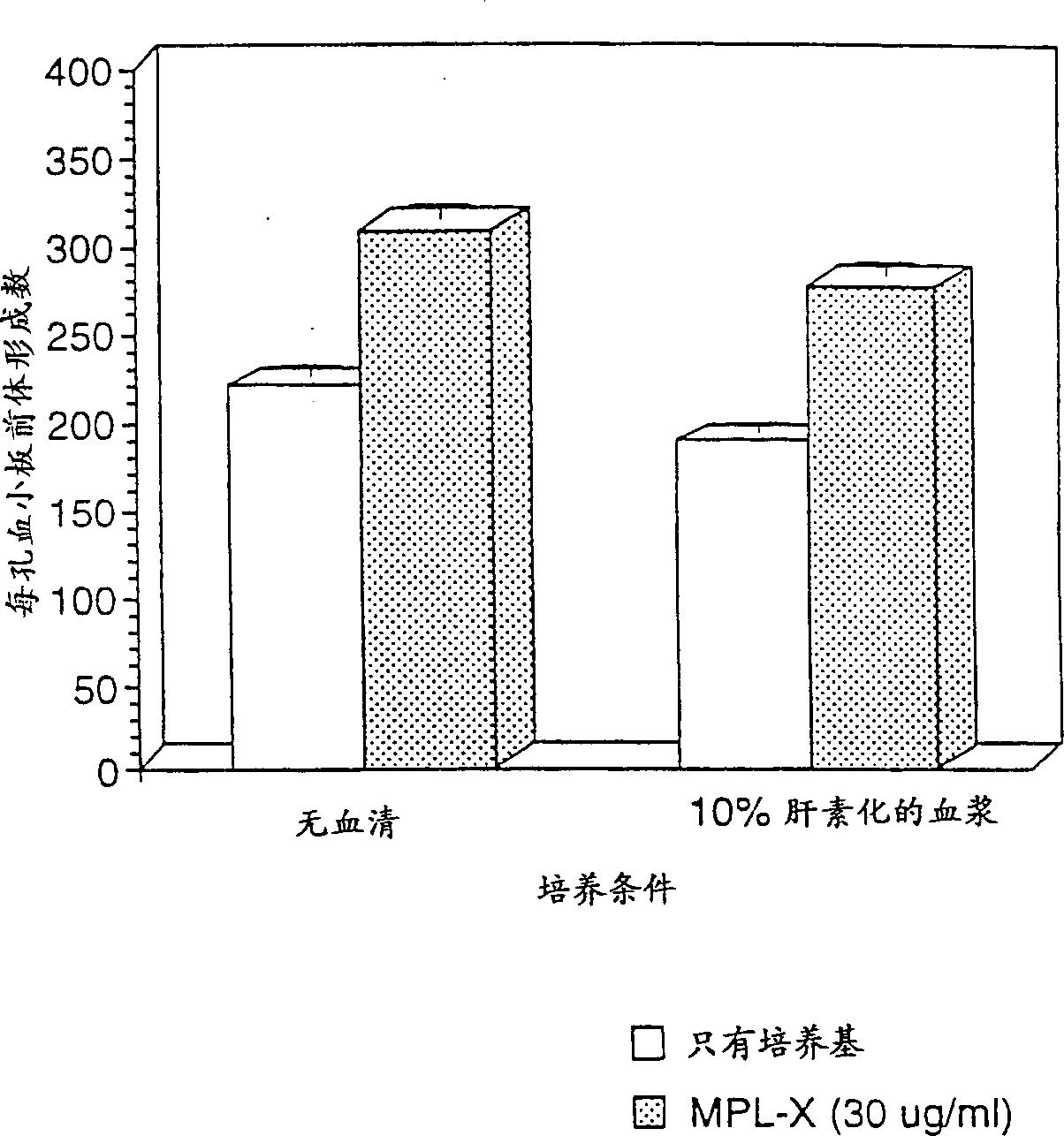
Compositions and methods using unbound mpl receptor for stimulating platelet production
A technology of platelets and compositions, applied in drug combinations, biochemical equipment and methods, receptors of cytokines/lymphokines/interferons, etc., can solve problems such as increased medical expenses and expensive platelets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0087] The following examples will illustrate the present invention in more detail. In addition, these Examples provide preferred specific examples of the present invention. It is not intended to limit the scope of the invention unless otherwise indicated. Standard methods for many of the experiments described in the following examples, or appropriate alternative procedures, are mentioned in well-known molecular biology handbooks, such as Sambrook et al., "Molecular Cloning," Second Edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press ( 1987) and Ausubel et al., (Eds), "Current Protocols in Molecular Biology," Greeneassociates / Wiley Interscience, New York (1990).
example 1
[0089] Isolation of Nucleic Acid Sequences Encoding MPL Receptor
[0090] Encodes murine (Vigon et al., Oncogene 8:2607-2615 (1993)) and (Skoda et al., EMBO) 12(7):2645-2653 (1993)) and human (Vigon et al., DNAS89:5640 -5644 (1992)) isolation of a clone of the MPL receptor isotype has been published. These DNA sequences can be obtained from the GenBank database. The codes of the murine receptors are X73677 and 222657, and the codes of the human receptors K and P are M90102 and M90103, respectively. It has been reported that the mRNA of MPL can be expressed in spleen, bone marrow, placenta and fetal liver and other tissues. Tissue strains expressing MPL include HEL. Thus, it is clear to those skilled in the art how to isolate the gene encoding MPL. The cDNA can be produced from the above-mentioned tissue sources or cell lines or from other sources, and the expression of MPL in these sources can be confirmed by RNA Northern blot analysis or Western blot analysis.
[0091] Th...
example 2
[0094] Isolation of clones expressing soluble murine MPL
[0095] Using the above-mentioned clones confirmed to contain MPL, or cDNA obtained from a source capable of expressing MPL, a clone capable of expressing soluble MPL was obtained by PCR. The primers used for murine MPL PCR amplification may be in the following form: 5' end primer: TAC AAG CTT GCC GTC ATC ATG CCC TCT TGGGCC CTC (SEQ ID NO. 5); and 3' end primer: ACT TCT AGA CTA TCA AGC AGT CTC GGA GCTGGA (serial number 6)
[0096] The PCR reaction includes the following components: 1 microliter of cDNA reaction mixture, the above-mentioned various oligonucleotides containing Tris-HCl (pH8.3) at a concentration of 5 picomolar and 10 millimolar, and potassium chloride at a concentration of 50 millimolar. , magnesium chloride at a concentration of 1.5 millimolar, and each dNTP at a concentration of 200 micromolar and 1 unit of Taq polymerase, respectively. DNA amplification was set at 94°C for 30 seconds, at 50°C for 30 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com