A lightweight RFID security authentication method based on present algorithm
A security authentication and lightweight technology, applied in the field of RFID system information security, can solve problems such as desynchronization attacks, achieve the effects of fewer interaction rounds, improved trustworthiness and real-time performance, and low key length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] (1) Implementation steps
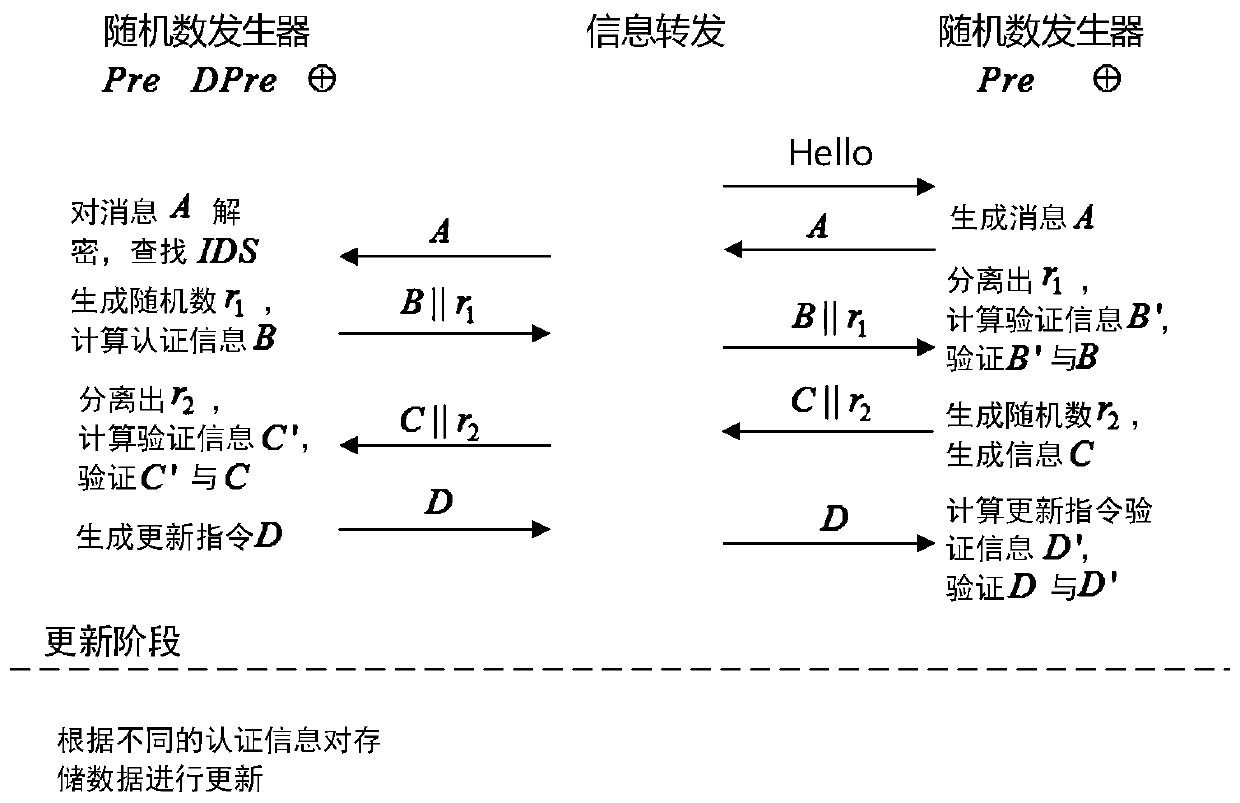
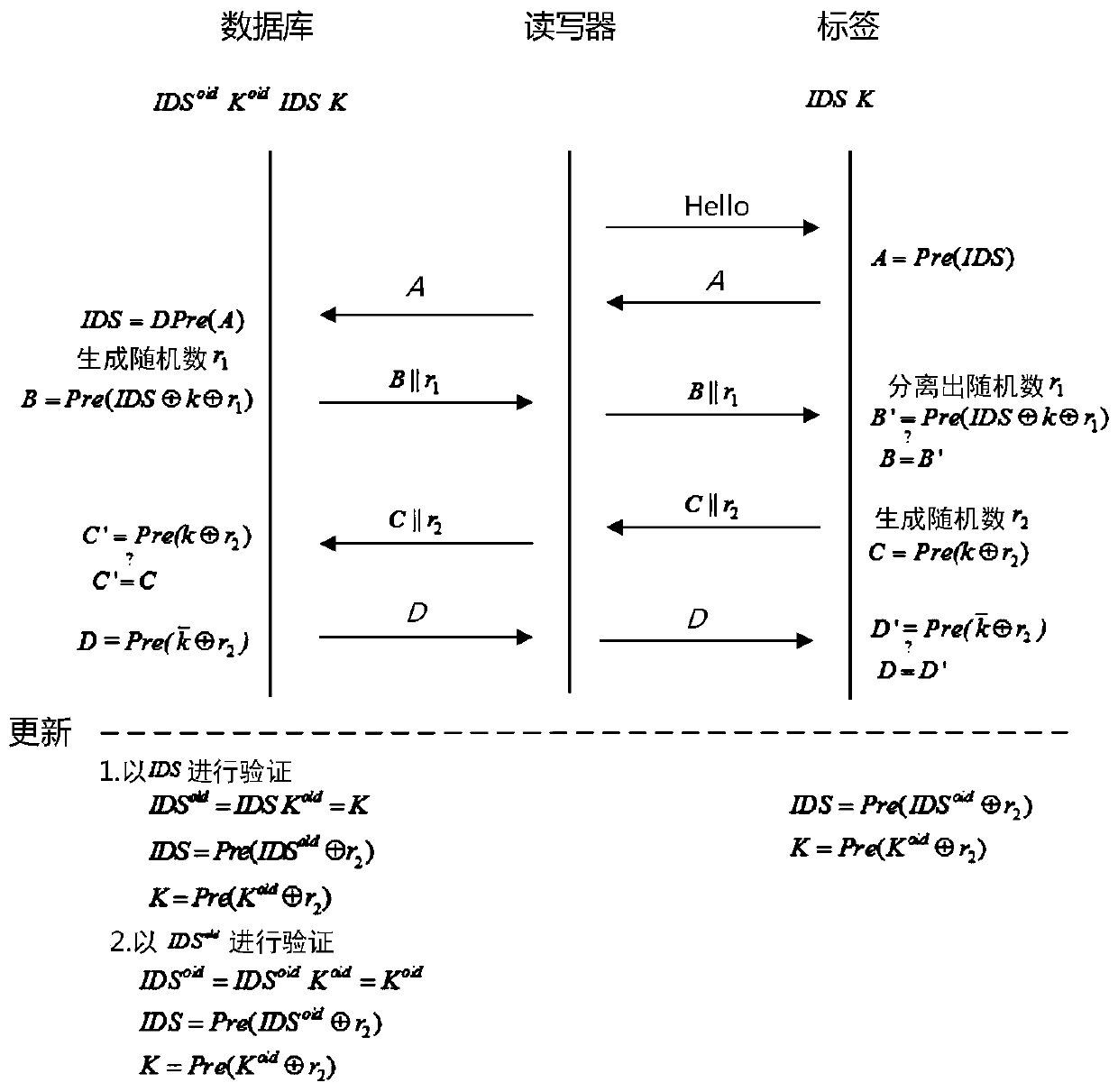
[0012] The authentication method includes three stages of initialization, authentication, and update. The specific interaction process between the background database, reader, and tag in the protocol is described as follows:
[0013] 1. Initialization phase
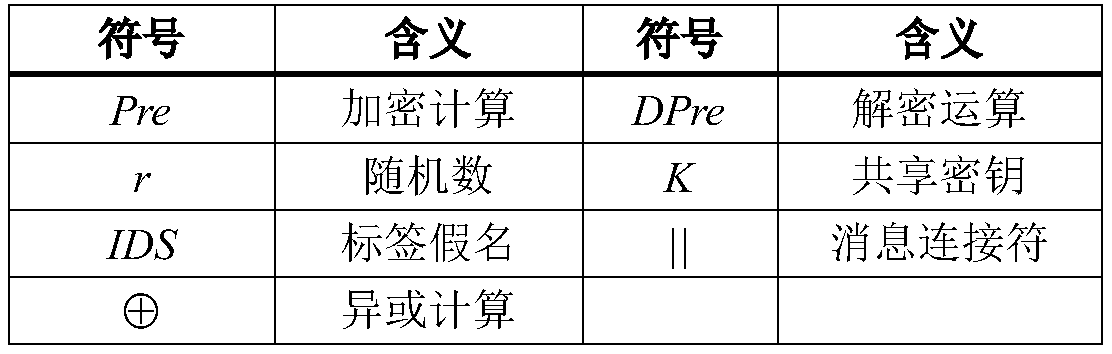
[0014] The RFID system generates a unique search name IDS (tag pseudonym) for each tag, and shares the key (K) with the database. The tag party saves its unique search name and key, and the storage unit is (IDS, K); the background database storage directory (IDS old ,K old ;IDS,K), where the key unit (IDS,K) of the database is the same as the (IDS,K) of the tag.
[0015] 2. Authentication stage
[0016] 2.1) Step 1Reader→Tag(Challenge Message):Hello
[0017] The reader sends a request response message (Hello) to the tag.
[0018] 2.2) Step 2Tag→Reader→Back-End Server(Responding Message): A
[0019] After the tag receives the request message, it takes out the current unique index na...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com