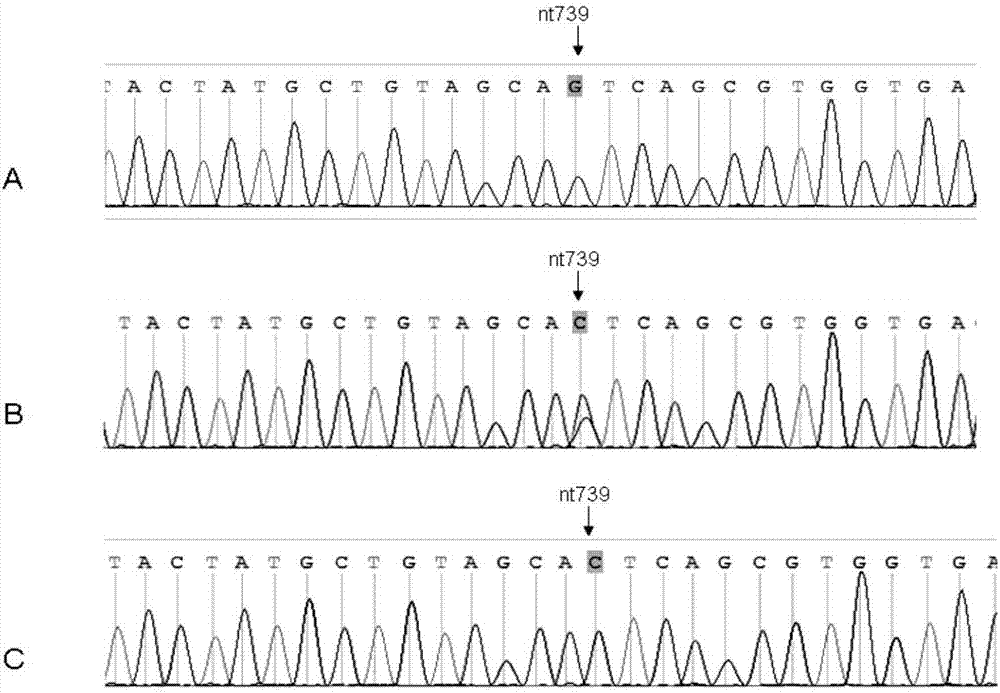
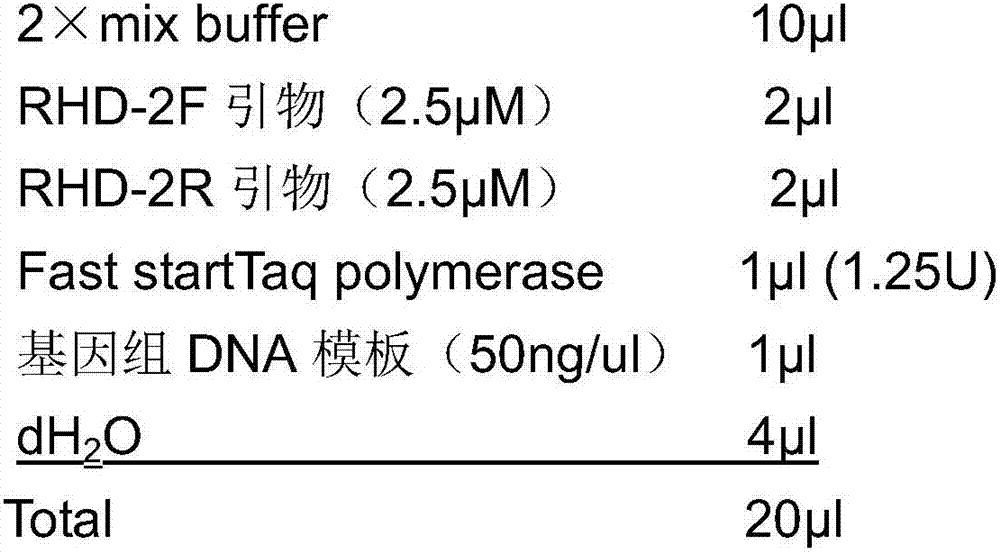
SNP mark applied to detecting RhD variation phenotype
A labeling and mutation technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as inability to judge, sample quality interference, easy missed detection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Screening of SNP markers
[0021] 1. Extraction of peripheral blood genomic DNA:
[0022] In compliance with the relevant national policies and regulations, and on the basis of the consent of the sampling subjects, draw 2-5mL of peripheral venous blood from RhD-negative or mutant blood donors, put them into EDTA anticoagulant tubes, and store them at -80°C for later use; frozen EDTA anticoagulant blood After the coagulated blood melts at room temperature, take 500 μL and put it in a centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of TE (pH 8.0), mix well, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes, and discard the supernatant.
[0023] Add 180 μL TE, 20 μL SDS (10%), and 8 μL proteinase K (10 mg / ml) to mix well, and place in a 37° C. water bath overnight. Remove the sample from the water bath and briefly centrifuge to pellet the sample. Add an equal volume of Tris-saturated phenol (about 300 μL) to the reaction tube, mix thoroughly, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Genetic Validation of Parents of a Proband with a SNP Mutation
[0038] 1. Extraction of peripheral blood genomic DNA:
[0039] In compliance with the relevant national policies and regulations, and on the basis of the consent of the sampling subjects, draw 2-5mL of peripheral venous blood from RhD-negative or mutant blood donors, put them into EDTA anticoagulant tubes, and store them at -80°C for later use; frozen EDTA anticoagulant blood After the coagulated blood melts at room temperature, take 500 μL and put it in a centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of TE (pH 8.0), mix well, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes, and discard the supernatant.
[0040] Add 180 μL TE, 20 μL SDS (10%), and 8 μL proteinase K (10 mg / ml) to mix well, and place in a 37° C. water bath overnight. Remove the sample from the water bath and briefly centrifuge to pellet the sample. Add an equal volume of Tris-saturated phenol (about 300 μL) to the reaction tube, mix thoro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com