Bacillus thuringiensis for killing mosquito larvae and application of bacillus thuringiensis
A technology of Bacillus aureus and spore thuringiensis, which can be used in applications, pesticides, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of natural environment biological chain and soil damage, and achieve the effect of reducing risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Collection of Soil Samples and Isolation and Culture of Bt Strains
[0024] The soil sampling time is selected in summer and autumn (May to October), and the sunny slope of Dawangling Nature Reserve in Guangxi is selected. In order to increase the probability of obtaining new strains, the sampling points should be selected with complete vegetation protection, no human intervention in the ecological environment, and rich soil humus. best place. Bt strain screening adopts sodium acetate + antibiotic + temperature screening method, weighs 1g of soil sample into 10mL of BPA culture solution, then adds penicillin sodium salt and gentamicin sulfate to 400μg / mL, and then cultures on a shaking table at 30°C and 220rpm 4h. Let it stand for 30 minutes, take 10mL of soil suspension, put it in a 75°C water bath for 20 minutes, and shake it every few minutes. Take 1mL of the supernatant and perform a 10-fold serial dilution operation, setting up 4 dilution gradients (10 -1 ,10 -...
Embodiment 2
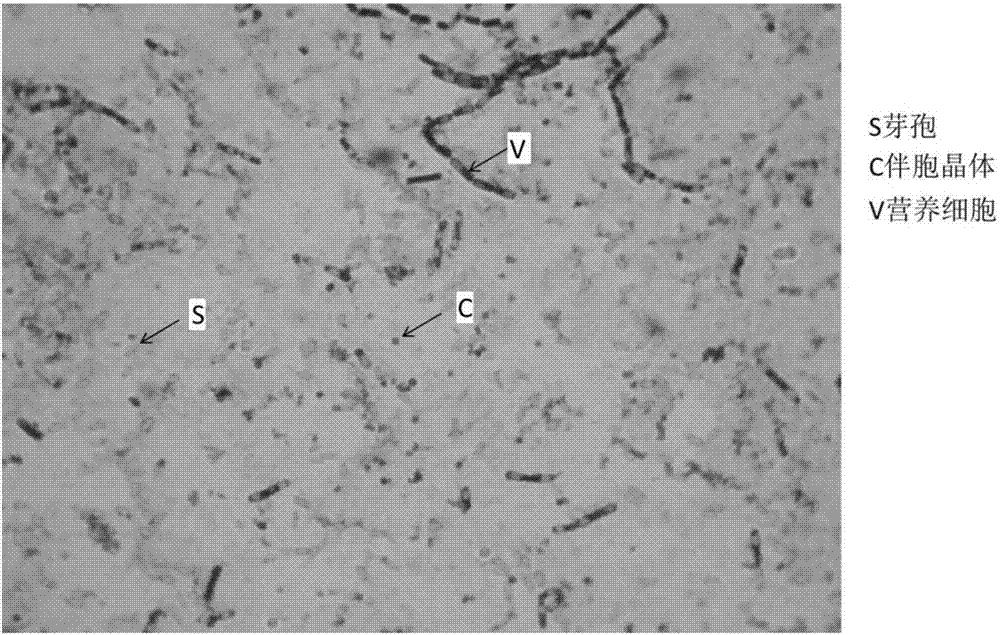
[0026] Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation of Crystal Protein of Bt S2160-1 Strain
[0027] The Bt strain was cultured in G-Tris medium at 30°C until the spores were completely formed, and 500 μL of bacteria were collected by centrifugation at 12,000 g for 10 minutes at 4°C, and then washed with 1M ice-cold NaCl for 3 times, and finally the bacteria were suspended in 500 μL of ice-cold ultrapure in the water. Take 10 μL of the mixture of spores and paraspore crystals and carefully spread it on a clean cover glass, then dry it in vacuum at 4 °C, and then wash it with 1% osmium tetroxide (OsO 4 ) to fix the sample, the sample is placed on a metal sample stage, and put into a vacuum evaporator to spray a metal film with a thickness of about 20nm. The prepared sample was placed in a S3-400N scanning electron microscope (HITACHI Ltd, Japan), and the image was observed and recorded under the voltage condition of 20kV.
Embodiment 3
[0029] SDS-PAGE electrophoresis analysis of crystal protein of Bt S2160-1 strain
[0030] The Bt strain was cultured in 200 mL of G-Tris medium for more than 3 days, and the culture conditions were 30° C. and 220 rpm shaking culture. Optical microscope observation confirmed that the spores were fully formed, and the paraspore crystals and spore mixture were collected by centrifugation at 12,000g for 10 minutes at 4°C. The precipitate was washed three times with an equal volume of ice-cold 1M NaCl, and then the cells were sonicated for 20 min (Model VC-130, Sonics and Materials Inc, USA). Centrifuge at 12,000g for 10min at 4°C, collect the precipitate, dissolve in 5mL of 50mM Na 2 CO 3 solution (PH=10.0). Generally, 7.5% or 12% SDS-PAGE can be used to analyze the crystal protein composition of Bt bacteria, 5uL prepared parasporal crystal protein and 5uL 2×SDS-PAGE sample Buffer [0.075M Tris Cl, (pH6.8); 0.020M EDTA; 2% SDS; 0.02% bromophenol blue; 0.25M dithiothreitol (DTT)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com