Construction of a recombinant expression strain of nitrilase and its high-density fermentation method
A technology of nitrilase and concentration, applied in the direction of hydrolase, microorganism-based methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of bacterial poisoning, increase process steps and production costs, etc., to ensure rapid growth, avoid inhibitory effects, and widely used foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Construction of Escherichia coli CGMCC No.14254 producing constitutive recombinant nitrilase
[0027] In the following examples, the experimental methods of specific molecular construction conditions are not indicated, usually according to the conditions described in Sambrook et al.'s "Molecular Cloning Experiment Handbook" (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989), or according to the manufacturing conditions recommended by the manufacturer.
[0028] 1) Amplification of the NIT sequence of the nitrilase gene: Genomic DNA was extracted from Pseudomonas putida CGMCC3830 and used as a template to design upstream and downstream primers 2PU, 3bD and restriction sites for PCR amplification. Primers:
[0029]2PU: 5'-GGAATTCCATATGATGGTTACGTACACGAATAAGTT-3'
[0030] 3bD: 5'-ATTGCTCAGCTCAGCCTCTCTTCATGGACCTTAAC-3'
[0031] PCR amplification system:
[0032]
[0033] PCR reaction process: cycle after pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 minutes, denaturation...
Embodiment 2
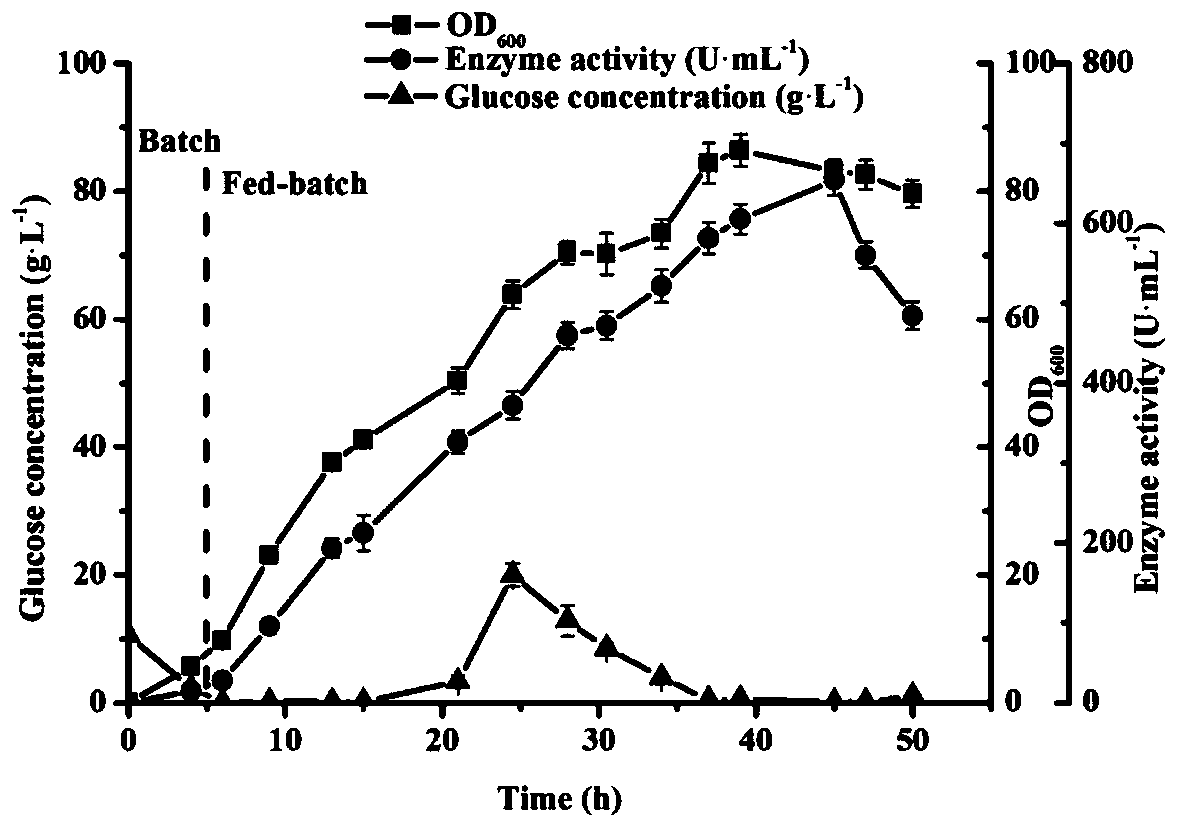
[0041] Embodiment 2: Application of high-density fermentation technology in recombinant nitrilase fermentation
[0042] The slant strain CGMCC No.14254 was activated, transferred to a fresh seed medium with a 2% inoculation amount, and cultured at 37° C. for 8 hours. According to the 10% inoculation amount, transfer to the fermenter, use the pH electrode and the dissolved oxygen electrode to monitor the pH and dissolved oxygen value of the fermentation broth in real time, and maintain the dissolved oxygen at 10% by adjusting the rotation speed and ventilation. From the batch fermentation stage, adjust the pH by feeding ammonia water to make it not lower than 6.8; in the feeding stage, set the pH to be stable at 6.8, (1) In the early stage of feeding, start feeding the feeding medium when the pH changes by 0.01 (2) In the mid-feeding period, when the pH changes by 0.03, the feed medium or ammonia water is fed; (3) In the late feeding period, when the pH changes by 0.05, the fee...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Preparation and continuous conversion of free cell catalyst
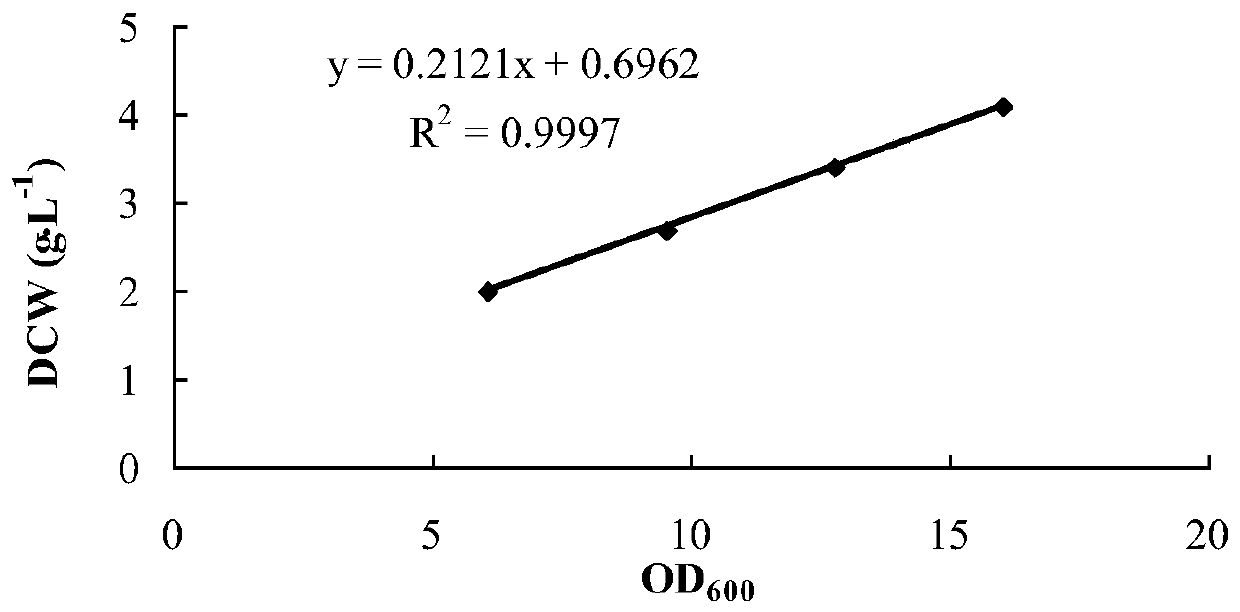
[0044] CGMCC No.14254 was cultured in the fermentation medium for 8-10 hours, centrifuged at 12000×g for 1 min, discarded the supernatant, then resuspended the cells with sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2, 100 mM) and washed for 2- 3 times to obtain the cells after removal of the medium residue, and finally resuspend the cells with the same sodium phosphate buffer to obtain a resting cell suspension, measure the cell concentration and store in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
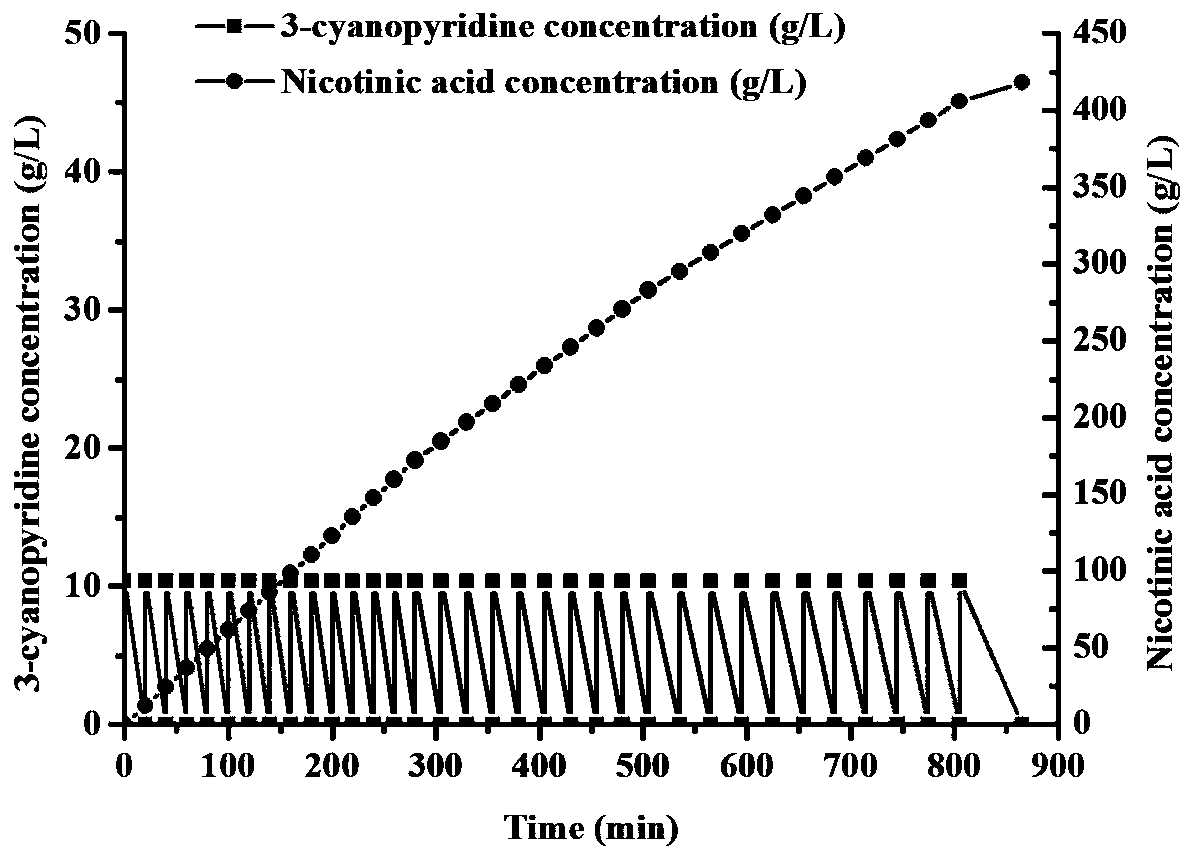
[0045] Mix the prepared cell suspension (100mL, the dry weight of the bacteria is 2.26g / L) with 1.04g 3-cyanopyridine (the initial concentration of 3-cyanopyridine is 100mM), and transform at 30°C and 220rpm For the reaction, detect the remaining substrate in the conversion solution by HPLC, and when the substrate is completely converted, continue to add the next batch of substrate.
[0046] When the final concentration o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com