Method for simultaneously removing USEPA PAHs in plant bodies by utilizing compound PAHs degrading bacteria
A technology of plants and degrading bacteria, applied in botany equipment and methods, preservation of human or animal bodies, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve secondary soil pollution, PAHs removal and degradation technology is rarely involved, The repair process is not easy to control and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy operation and high removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
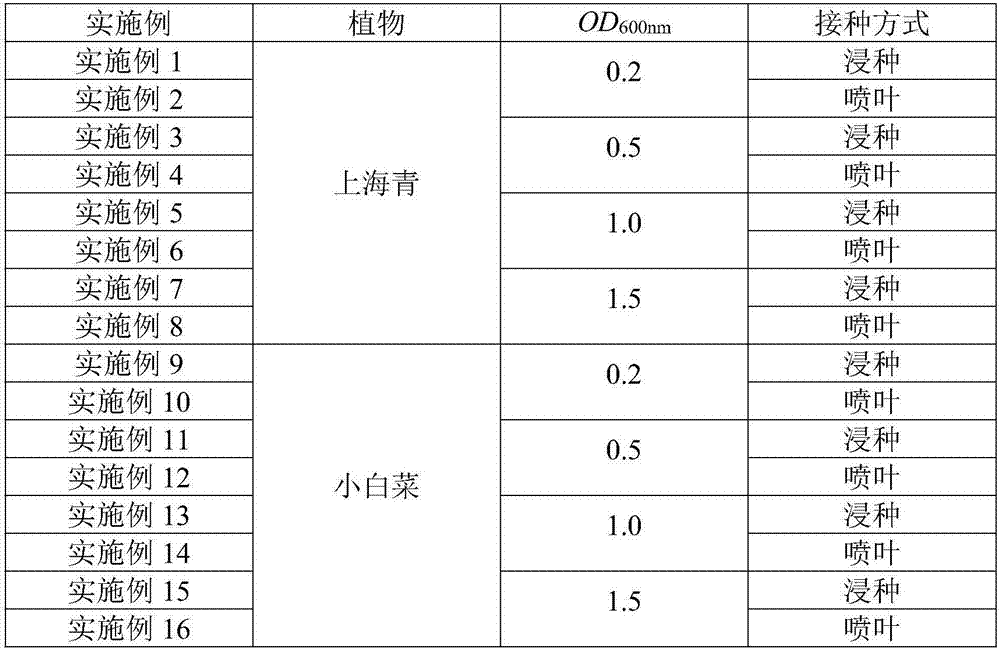
[0026] The Shanghai Qing seeds were inoculated with compound functional bacteria to reduce the PAHs content in the body.
[0027] Preparation of microbial composite functional bacteria agent:
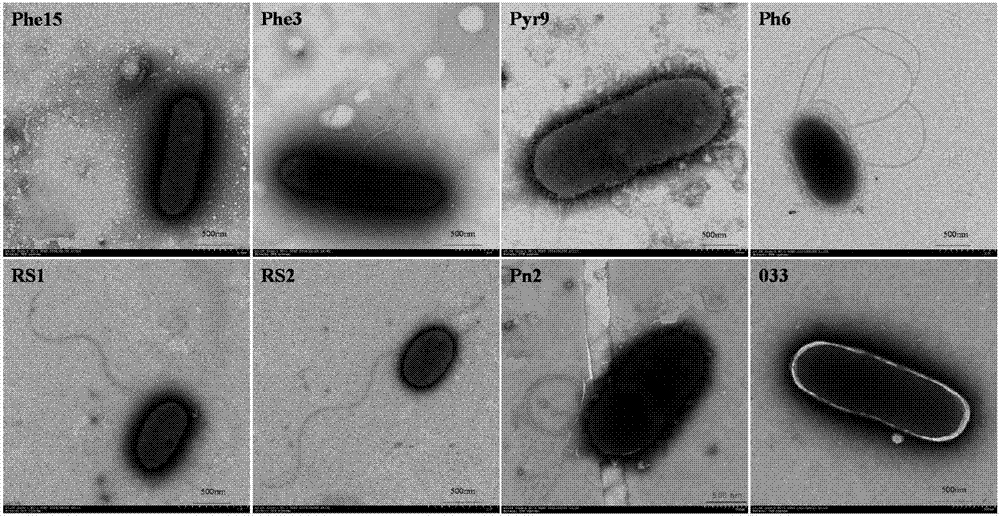
[0028] The composite functional bacteria is composed of 8 strains of PAHs degrading bacteria with different degradation spectrums, namely: Sphingobium sp. RS1, RS2), Mycobacterium sp. Pyr9, 033), (Diaphorobacter sp. Phe15), Massilia sp.Pn2, Paenibacillus sp.Phe3, Pseudomonas sp.Ph6;
[0029] Cultivate each strain separately, and then adjust the OD of each strain 600nm Mixing to make a microbial compound functional bacterial agent specifically includes the following steps:
[0030] (1) Preparation of bacterial suspension: 8 strains of PAHs-degrading bacteria were activated on LB solid plates, and each single colony was picked from the activated plate with an inoculation loop and inoculated in sterile LB liquid medium, placed at 30°C, 150r Centrifuge at 8000r / min at 4°C for 5 minutes a...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Inoculate the leaves of Shanghai green leaves with compound functional bacteria to reduce the PAHs content in the body.
[0036] Preparation of microbial composite functional bacteria agent:
[0037] The composite functional bacteria is composed of 8 strains of PAHs degrading bacteria with different degradation spectrums, namely: Sphingobium sp. RS1, RS2), Mycobacterium sp. Pyr9, 033), (Diaphorobacter sp. Phe15), Massilia sp.Pn2, Paenibacillus sp.Phe3, Pseudomonas sp.Ph6;
[0038] Cultivate each strain separately, and then adjust the OD of each strain 600nm Mixing to make a microbial compound functional bacterial agent specifically includes the following steps:
[0039] (1) Preparation of bacterial suspension: 8 strains of PAHs-degrading bacteria were activated on LB solid plates, and each single colony was picked from the activated plate with an inoculation loop and inoculated in sterile LB liquid medium, placed at 30°C, 150r Centrifuge at 8000r / min at 4°C for 5 min...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The Shanghai Qing seeds were inoculated with compound functional bacteria to reduce the PAHs content in the body.
[0045] Preparation of microbial composite functional bacteria agent:
[0046] The composite functional bacteria is composed of 8 strains of PAHs degrading bacteria with different degradation spectrums, namely: Sphingobium sp. RS1, RS2), Mycobacterium sp. Pyr9, 033), (Diaphorobacter sp. Phe15), Massilia sp.Pn2, Paenibacillus sp.Phe3, Pseudomonas sp.Ph6;
[0047] Cultivate each strain separately, and then adjust the OD of each strain 600nm Mixing to make a microbial compound functional bacterial agent specifically includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) Preparation of bacterial suspension: 8 strains of PAHs-degrading bacteria were activated on LB solid plates, and each single colony was picked from the activated plate with an inoculation loop and inoculated in sterile LB liquid medium, placed at 30°C, 150r Centrifuge at 8000r / min at 4°C for 5 minutes a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com