A protective cement concrete curing agent and its preparation method and application
A technology of cement concrete and curing agent, which is applied in the field of chemical building materials to achieve the effects of reducing carbonization, improving water retention rate and protection effect, and reducing transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
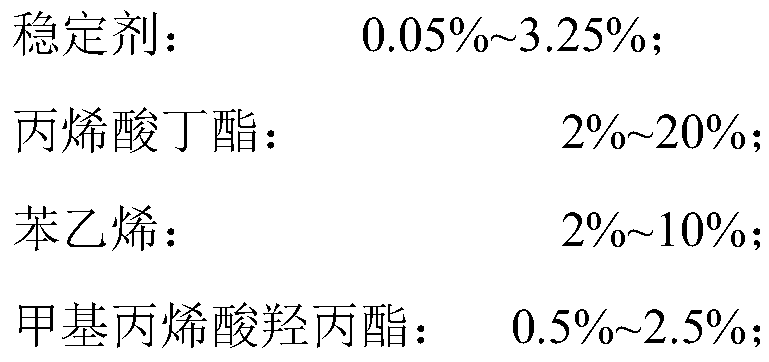
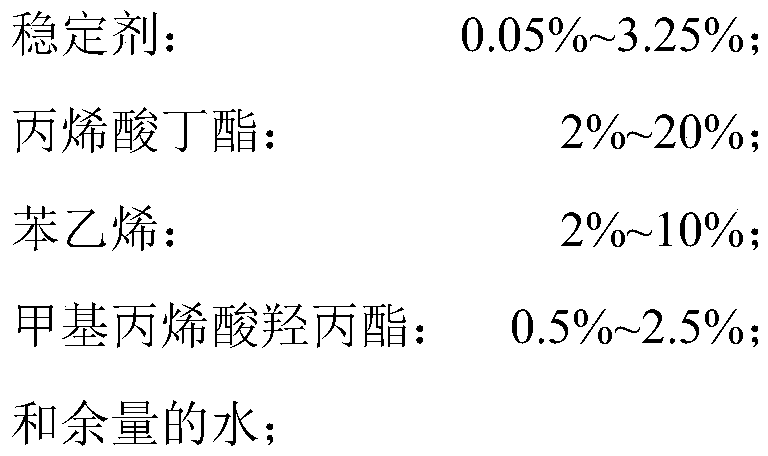
[0028] Raw material ratio: 0.1g sulfonated graphene, 2g butyl acrylate, 1g hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 5g styrene, 0.04g ammonium persulfate and appropriate amount of water.
[0029] Prepare the mixed liquid of ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and three monomers of butyl acrylate, styrene and hydroxypropyl methacrylate. Under stirring conditions, raise the temperature of the sulfonated graphene and the remaining water to 75°C, and drop the ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and the mixture of the three monomers at the same time; control the dropping speed so that the two are added at the same time. , the temperature of the reaction liquid was raised to 85° C. and continued to keep warm and stirred for 2 hours, cooled, and discharged to obtain protective curing agent 1.
[0030] According to the building material industry standard (JC 901-2002) and the construction industry standard (JG 335-2011), the water retention rate of curing agent 1 is 92%, and the carbonization dep...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Raw material ratio: 0.27g sulfonated graphene, 20g butyl acrylate, 2g hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 5g styrene, 0.135g ammonium persulfate and appropriate amount of water.
[0037] Prepare the mixed liquid of ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and three monomers of butyl acrylate, styrene and hydroxypropyl methacrylate. Under stirring conditions, raise the temperature of the sulfonated graphene and the remaining water to 80°C, and drop the ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and the mixture of the three monomers at the same time; , the temperature of the reaction solution was raised to 90° C. and continued to heat and stir for 4 hours, cooled, and discharged to obtain protective curing agent 2.
[0038] According to the building material industry standard (JC 901-2002) and the construction industry standard (JG 335-2011), the water retention rate of curing agent 1 is 89%, and the carbonization depth ratio is 18%.
[0039] As a comparison, the ratio of raw materials in ...
Embodiment 3
[0042]Raw material ratio: 0.2g sulfonated graphene, 2g butyl acrylate, 0.5g hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2g styrene, 0.0225g ammonium persulfate and appropriate amount of water.
[0043] Prepare the mixed liquid of ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and three monomers of butyl acrylate, styrene and hydroxypropyl methacrylate. Under stirring conditions, raise the temperature of the sulfonated graphene and the remaining water to 70°C, and drop the ammonium persulfate aqueous solution and the mixture of the three monomers at the same time; , the temperature of the reaction solution was raised to 80° C. and continued to keep warm and stirred for 4 hours, cooled, and discharged to obtain protective curing agent 3.
[0044] According to the building material industry standard (JC 901-2002) and the construction engineering industry standard (JG 335-2011), the water retention rate of curing agent 1 is 85%, and the carbonization depth ratio is 25%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com