Substance, kit and method used for detecting systemic infection
A systemic infection and kit technology, applied in the material field of systemic infection detection, can solve problems such as high cost, low ratio, and insufficient sequencing depth, and achieve high detection sensitivity and specificity, and good severity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
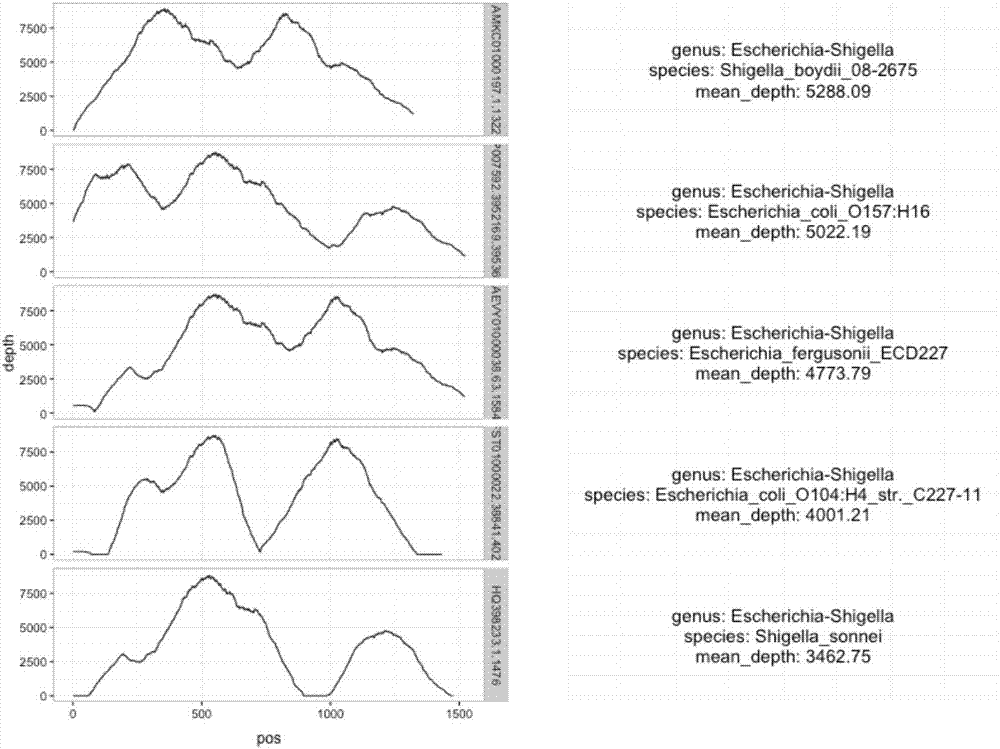
[0041] The source of the sample is a middle-aged male patient, who was clinically diagnosed with laryngeal cancer surgery, severe pneumonia, and septic shock. Sputum and blood cultures showed Escherichia coli.
[0042] 1. Collect peripheral blood and centrifuge to separate plasma
[0043] Use cfDNA-specific blood collection tubes to routinely collect 6ml of peripheral blood and store it as required; centrifuge at 2500g for 10 minutes, then extract the supernatant plasma, centrifuge at 20000g for 10 minutes, and extract 3ml of supernatant plasma.
[0044] 2. Use the kit QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit to extract plasma circulating DNA as required
[0045]1. Add 3ml plasma, 300μl Proteinase K, and 2.4ml Buffer ACL (containing 1.0μg carrier RNA) to a 50ml centrifuge tube, vortex for 30s, and incubate at 60°C for 30min.
[0046] 2. Take out the centrifuge tube, add 5.4ml Buffer ACB, vortex for 30s, and incubate on ice for 5min.
[0047] 3. Connect the negative pressure extr...
Embodiment 2
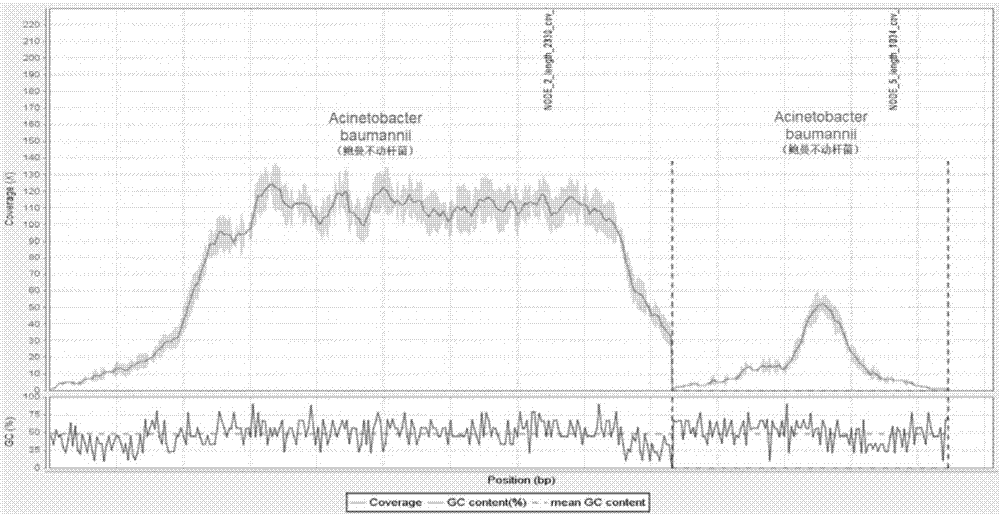
[0119] The source of the sample was an elderly male patient who was clinically diagnosed with severe pneumonia. The sputum culture was Acinetobacter baumannii, and the blood culture result was negative.
[0120] 1. Collect peripheral blood and centrifuge to separate plasma
[0121] Use cfDNA-specific blood collection tubes to routinely collect 6ml of peripheral blood and store it as required; centrifuge at 2500g for 10 minutes, then extract the supernatant plasma, centrifuge at 20000g for 10 minutes, and extract 3ml of supernatant plasma.
[0122] 2. Use the kit QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit to extract plasma circulating DNA as required
[0123] 1. Add 3ml plasma, 300μl Proteinase K, and 2.4ml Buffer ACL (containing 1.0μg carrier RNA) to a 50ml centrifuge tube, vortex for 30s, and incubate at 60°C for 30min.
[0124] 2. Take out the centrifuge tube, add 5.4ml Buffer ACB, vortex for 30s, and incubate on ice for 5min.
[0125] 3. Connect the negative pressure extractor Q...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com