Method for synchronously removing heavy metals and organic matters from wastewater
A technology for organic matter and heavy metals, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of improving degradation efficiency, mild reaction conditions, and reducing chemical dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Take a certain electroplating wastewater, pH=6.3, the initial concentration and removal rate of pollutants in this water sample are shown in Table 1.
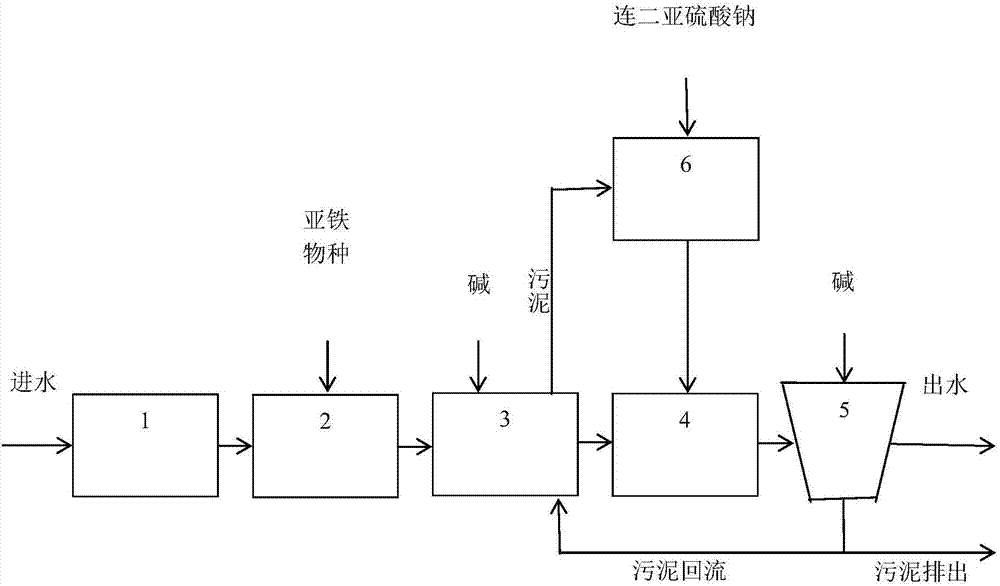
[0039] (1) Anoxic reaction: take 1L of the industrial wastewater, add FeSO to it 4 ·7H 2 O 2.78g, then the molar concentration of Fe is 10mmol / L. The sum of the molar concentrations M of heavy metal ions in the wastewater is 4.0mmol / L, then the molar ratio of Fe to M is 2.5:1, which meets the technical characteristics of greater than 2:1; the COD concentration in the wastewater is 120mg / L, and the Fe mass concentration and COD concentration The ratio is 4.7:1, which meets the technical characteristics of greater than 3:1. Add the adjusted wastewater to the anoxic tank, control the dissolved oxygen concentration of the wastewater to less than 1.0 mg / L, adjust the pH to 7.0, and react for 10 minutes to generate FeM catalyst with high activity in situ.
[0040] (2) Incubation reaction: After the reaction in the anoxic ta...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Take a certain electroplating wastewater, pH=2.1, the initial concentration and removal rate of pollutants in this water sample are shown in Table 2.
[0047] (1) Anoxic reaction: take 1L of the industrial wastewater, add FeSO to it 4 ·7H 2 O 3.34g, then the molar concentration of Fe is 12mmol / L. The total molar concentration M of heavy metal ions in the wastewater is 4.7mmol / L, then the molar ratio of Fe to M is 2.5:1, which meets the technical characteristics of greater than 2:1; the COD concentration in the wastewater is 60mg / L, and the Fe mass concentration and COD concentration The ratio is 11.2:1, which meets the technical characteristics of greater than 3:1. Add the adjusted wastewater to the anoxic tank, control the dissolved oxygen concentration of the wastewater to less than 1.0 mg / L, adjust the pH to 7.0, and react for 20 minutes to generate FeM catalyst with high activity in situ.
[0048] (2) Incubation reaction: After the reaction in the anoxic tank, th...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Take a certain titanium dioxide production wastewater, pH = 1.2, the initial concentration and removal rate of pollutants in this water sample are shown in Table 3.
[0055] (1) Anoxic reaction: Take 1L of this industrial wastewater, because the mass concentration of Fe in the wastewater is 3148mg / L, that is, the molar concentration is 56mmol / L. And the molar concentration sum M of heavy metal ions in the waste water is 2.1mmol / L, then the molar ratio of Fe and M is 26.2:1, accords with the technical feature greater than 2:1; COD concentration is 447mg / L in the waste water, Fe mass concentration and COD The concentration ratio is 7.0:1, which meets the technical characteristics of greater than 3:1, so Fe ions are no longer added to the wastewater. Add the adjusted wastewater to the anoxic tank, control the dissolved oxygen concentration of the wastewater to less than 1.0 mg / L, adjust the pH to 7.0, and react for 30 minutes to generate FeM catalyst with high activity in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com