Method for detecting escherichia coli O157 based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology
A technology of Escherichia coli and O157, which is applied in the field of biosensing and detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome experimental operations, difficult analysis results of molecular biological methods, and cumbersome operations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Method for detecting Escherichia coli O157 based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology
[0049] 1. Experimental materials
[0050] See Table 1 for information on Escherichia coli O157 and non-Escherichia coli O157 strains used in this example.
[0051] Information on E. coli O157 and non-E. coli O157 used in Table 1
[0052]
[0053] E. coli O157 and other bacterial strains were used to determine the specificity of the nanozyme sensor. All strains were stored at -80°C in 20% (v / v) glycerol solution until use. They were then cultured overnight in LB medium for activation. E. coli O157 concentration was determined by spectrophotometry.
[0054] 2. Genome extraction of Escherichia coli O157
[0055] The bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit from New Industry Company was used, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0056] (1) Take 1.5 mL of bacterial culture solution, centrifuge at 12,000 g for 1 min, and absorb the supernatant as much as...
Embodiment 2
[0093] The optimization of embodiment 2 nanozyme nucleic acid test strips
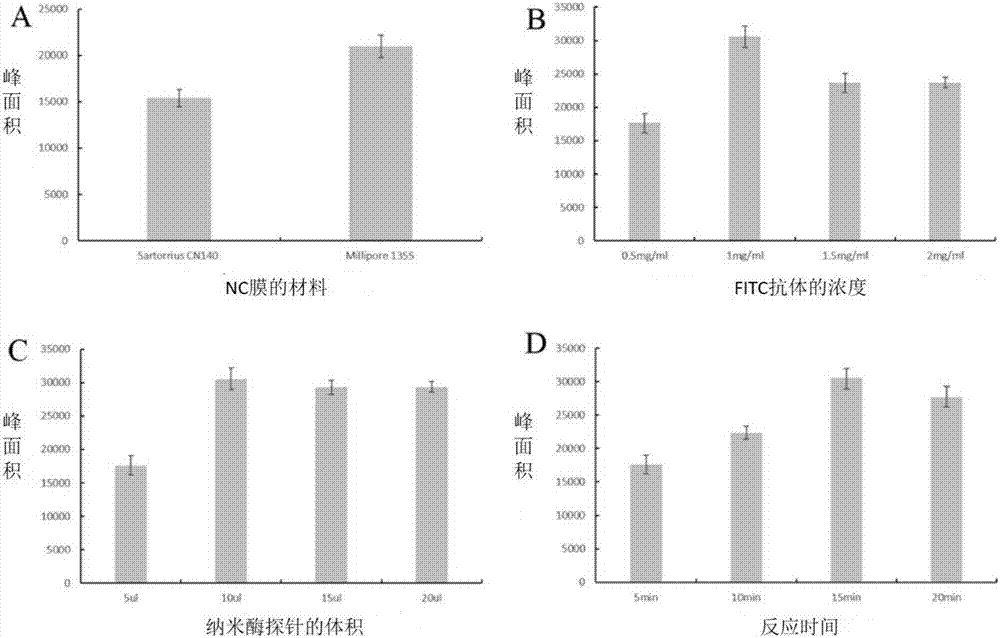
[0094] Synthesis of Fe by hydrothermal method 3 o 4 Magnetic particles, and then the magnetic particles were incubated with biotin secondary antibody (goat anti-mouse IgG) to prepare nanozyme probes. Use FITC antibody and biotin antibody to draw lines on the T-line and C-line positions on the NC membrane, and assemble them into nanozyme nucleic acid test strips after drying. In order to improve the sensitivity of the nanozyme sensor, it was systematically analyzed by comparing the performance of membrane materials, the concentration of FITC antibody in the detection area, the amount of nanozyme probe, and the reaction time. The results prove that the performance of the nano-enzyme sensor using Millipore135S nitrocellulose membrane is better ( figure 2 A). Using 1 mg / mL FITC antibody and 1 mg / mL goat anti-mouse IgG, the signal peak area was the highest ( figure 2 B). In addition, the amount of n...
Embodiment 3
[0095] The performance detection of embodiment 3 nano-enzyme sensor
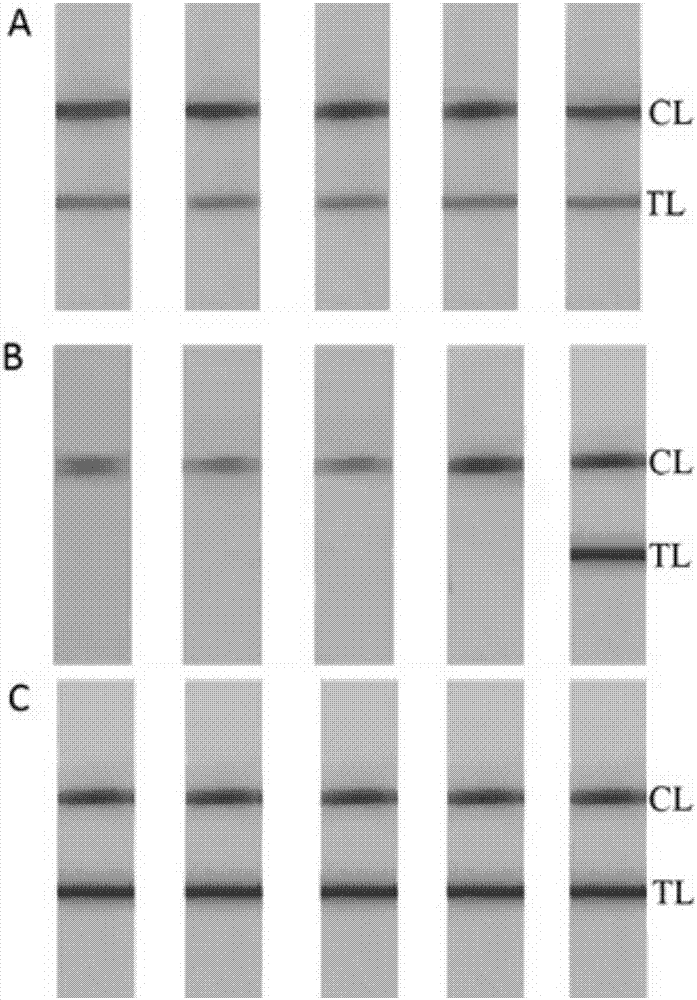
[0096] The principle of the nanozyme sensor is as follows. First, the samples were treated with PMA (step 1). PMA can selectively penetrate the damaged cell membrane of dead cells, bind to the DNA in the cell, and make it unavailable for subsequent LAMP amplification, but if it is the intact cell membrane of living cells, PMA cannot enter the cell. Then, many BIO- and FITC-linked duplex DNAs were generated in a short time using LAMP (step 2). In the presence of the target rfb E specific sequence, it is recognized and amplified by four primers. The third is the visual interpretation of the nanozyme nucleic acid test paper (step 3). The FITC antibody and goat anti-mouse IgG were immobilized on the nitrocellulose membrane by physical adsorption to form the detection zone (TL) and quality control zone (CL), respectively. If the sample is positive, after LAMP amplification, the 5' end of the target substance ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com