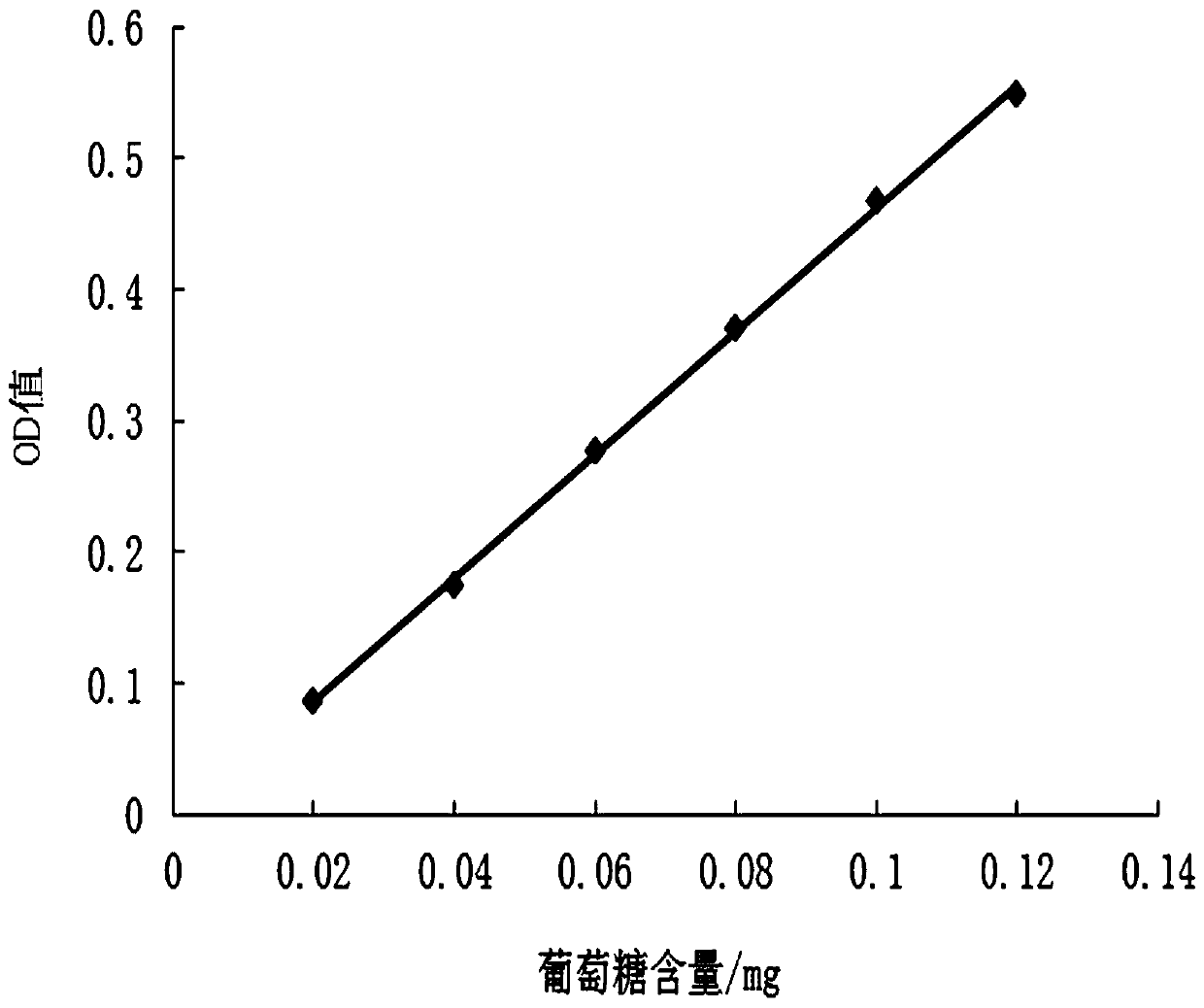
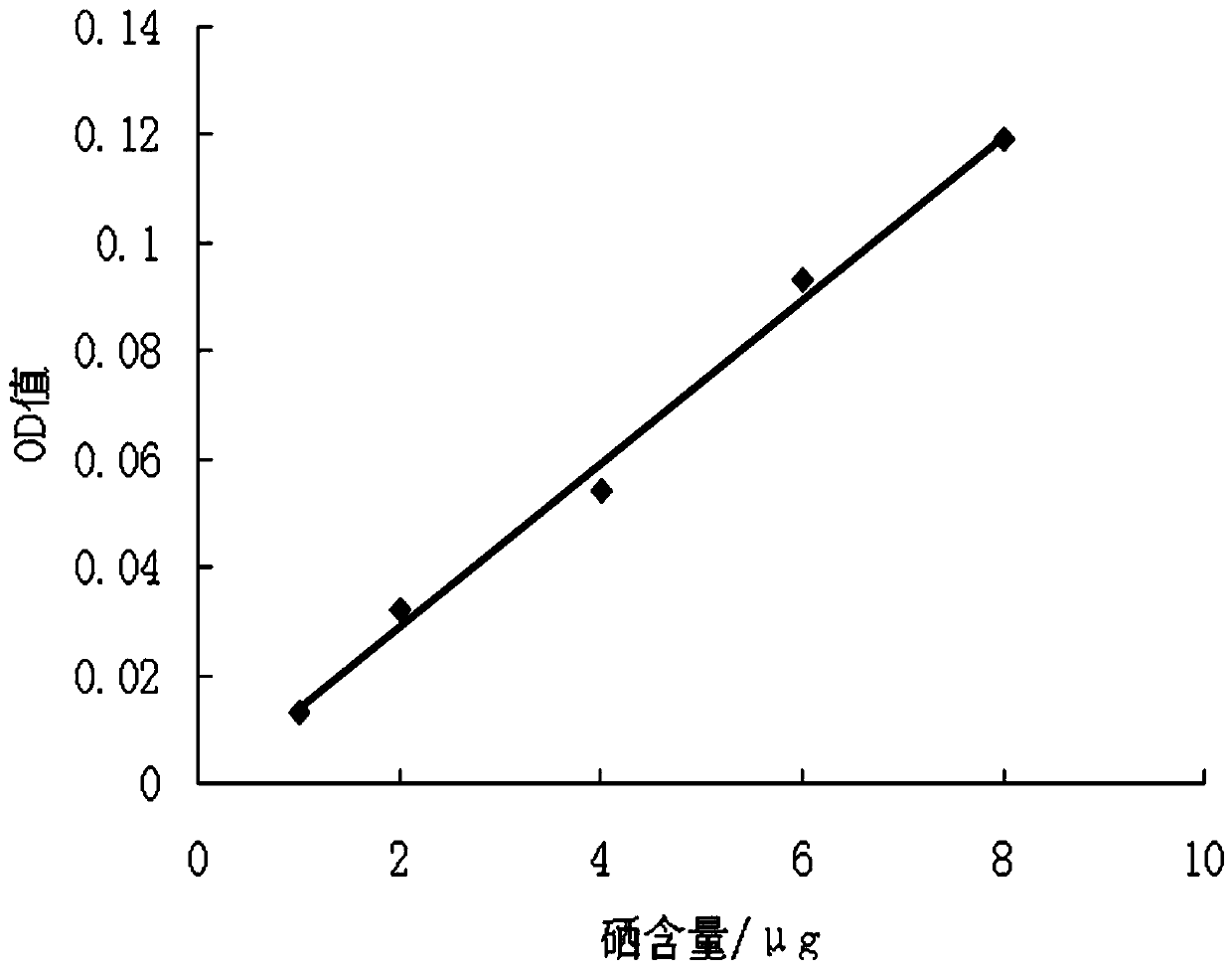
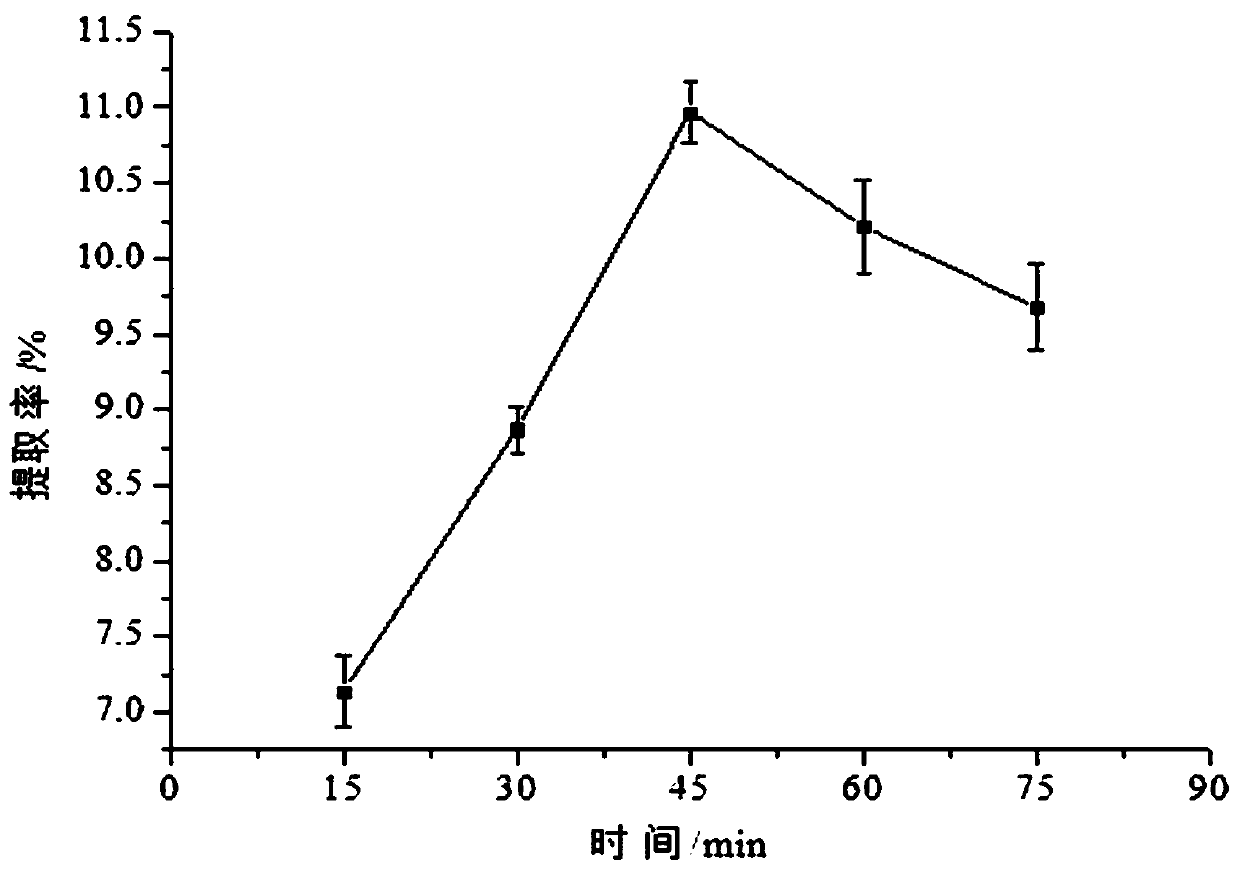
Method for extracting and testing selenium polysaccharide from selenium-enriched lotus leaf lyophyllum mycelia
A technology of lotus leaves and selenium polysaccharides, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of selenium polysaccharide molecular biology research and insufficient structure-activity relationship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] A method for extracting selenium polysaccharides from the mycelium of the selenium-enriched lotus leaf Agrocybe, specifically including the following steps;
[0091] Step (1) Put the selenium-enriched lotus leaf licheniformis mycelium fermented in a 20L biological tank into a vacuum drying oven for drying, and grind through a 100-mesh sieve to prepare a sample;
[0092] Step (2) Accurately weigh 0.5000 g of the sample, and perform ultrasonic extraction once at an extraction time of 15 minutes, an extraction temperature of 50°C, and a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:40;
[0093] Step (3) After extraction, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min, combine the supernatant and concentrate under reduced pressure into a concentrated solution ≤50mL;
[0094] Step (4) Add 3 times the volume of 95% ethanol to the concentrated solution and let it stand overnight in a refrigerator at 4°C to obtain selenium polysaccharide precipitate. After repeated washing with ethanol, the selenium polysaccharide ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] A method for extracting selenium polysaccharides from the mycelium of the selenium-enriched lotus leaf Agrocybe, specifically including the following steps;
[0098] Step (1) Put the selenium-enriched lotus leaf licheniformis mycelium fermented in a 20L biological tank into a vacuum drying oven for drying, and grind through a 100-mesh sieve to prepare a sample;
[0099] Step (2) Accurately weigh 0.5000 g of the sample, and perform ultrasonic extraction twice under the conditions of extraction time of 50 minutes, extraction temperature of 83°C, and material-to-liquid ratio of 1:130;
[0100] Step (3) After extraction, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min, combine the supernatant and concentrate under reduced pressure into a concentrated solution ≤50mL;
[0101] Step (4) Add 3 times the volume of 95% ethanol to the concentrated solution and let it stand overnight in a refrigerator at 4°C to obtain selenium polysaccharide precipitate. After repeated washing with ethanol, the selenium ...
Embodiment 3
[0104] A method for extracting selenium polysaccharides from the mycelium of the selenium-enriched lotus leaf Agrocybe, specifically including the following steps;
[0105] Step (1) Put the selenium-enriched lotus leaf licheniformis mycelium fermented in a 20L biological tank into a vacuum drying oven for drying, and grind through a 100-mesh sieve to prepare a sample;
[0106] Step (2) Accurately weigh 0.5000g of the sample, and perform ultrasonic extraction 4 times under the conditions of extraction time 75min, extraction temperature 90°C, and material-to-liquid ratio 1:200;
[0107] Step (3) After extraction, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min, combine the supernatant and concentrate under reduced pressure into a concentrated solution ≤50mL;
[0108] Step (4) Add 3 times the volume of 95% ethanol to the concentrated solution and let it stand overnight in a refrigerator at 4°C to obtain selenium polysaccharide precipitate. After repeated washing with ethanol, the selenium polysaccharid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com