Reversible double enzyme co-immobilization method capable of regulating and controlling enzyme ratio
A technology for regulating the ratio of enzymes, which is applied to biochemical equipment and methods, and enzymes immobilized on or in inorganic carriers, can solve the problem of affecting the performance and stability of immobilized enzyme systems, difficult to control different enzyme ratios, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of saving preparation costs, maintaining activity, and mild immobilization reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Establishment of a multi-enzyme immobilization system with adjustable enzyme ratio
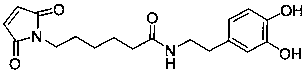
[0032] (1) 25 mg of magnetic nanoparticles (MP) with a particle size of 12-18 nm were ultrasonically dispersed in 5 mL of anhydrous methanol, and 5.3 mM dopamine (DA) and dopamine maleimide derivatives (MA) were added. , the mixture was sonicated for 1 h at room temperature; after the reaction, the product (DM@MP) was washed three times with deionized water, soaked in deionized water, and stored at 4 °C for subsequent use.
[0033] (2) 0.5 OD 5' carboxyl-modified single-stranded DNA (P1) was dissolved in 25 mM MES (pH 6.0) buffer solution, followed by adding 500 μL of 20 mg mL -1 of NHS and 40 mg mL -1 After the reaction was completed, the above reaction solution was added to 5 mL DM@MP (5 mg mL -1 ) dispersion, placed on a shaker for reaction at 29°C for 6 h; after the reaction, washed 3 times with 10 mM PBS (0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.4), and added 0.5 OD 5' thiol-modified single-s...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Regulating the ratio of enzymes in the multi-enzyme immobilization system.
[0040] (1) Preparation of immobilized multi-enzyme systems with different enzyme ratios: the specific steps are the same as those in Example 1. Adjust the molar ratios of DA and MA, P1 and P2, C1-GOx and C2-HRP to prepare GOx:HRP molar ratios of 1:4, 3:4, 5:4, 8:4, 10:4, 13: 4 GOx-HRP@DM@MP.
[0041] (2) Prepare a 5 mM β-Glucose substrate solution, 0.5 mg of GOx-HRP@DM@MP synthesized in Example 1, add 1 mL of β-Glucose solution (containing 1 mM TMB), and react at 37 °C with a shaker for 5 min . After the reaction, the GOx-HRP@DM@MP was separated by a magnetic field, 20 μL of 2 M sulfuric acid solution was added to the supernatant, and its absorbance at 450 nm was detected with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and the relative enzyme relative enzymes were compared according to the absorbance. active.
[0042] After investigation, the GOx-HRP multi-enzyme immobilization system pre...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Enzymatic properties of the multi-enzyme immobilization system
[0044] (1) Preparation of immobilized multi-enzyme system: Same as Example 1.
[0045] (2) Prepare a series of concentrations of β-Glucose substrate solution, 0.5 mg of GOx-HRP@DM@MP synthesized in Example 1, add 1 mL of β-Glucose solution (containing 1 mM TMB), and shake at 37 °C. bed reaction for 5 min. 20 μL of 2 M sulfuric acid solution was added to the supernatant, and its absorbance at 450 nm was detected. The enzymatic properties of free GOx-HRP and GOx-HRP@APTES@MP were determined by the same method and compared with GOx-HRP@DM@MP.
[0046] The analysis results show that the Michaelis constant of GOx-HRP@DM@MP is 1.41 mM, the Michaelis constant of free GOx-HRP is 2.63 mM, and the Michaelis constant of GOx-HRP@APTES@MP is 1.92 mM. Compared with other GOx-HRP multi-enzyme immobilization systems and free GOx-HRP, the Michaelis constant value of the GOx-HRP multi-enzyme immobilization sys...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com