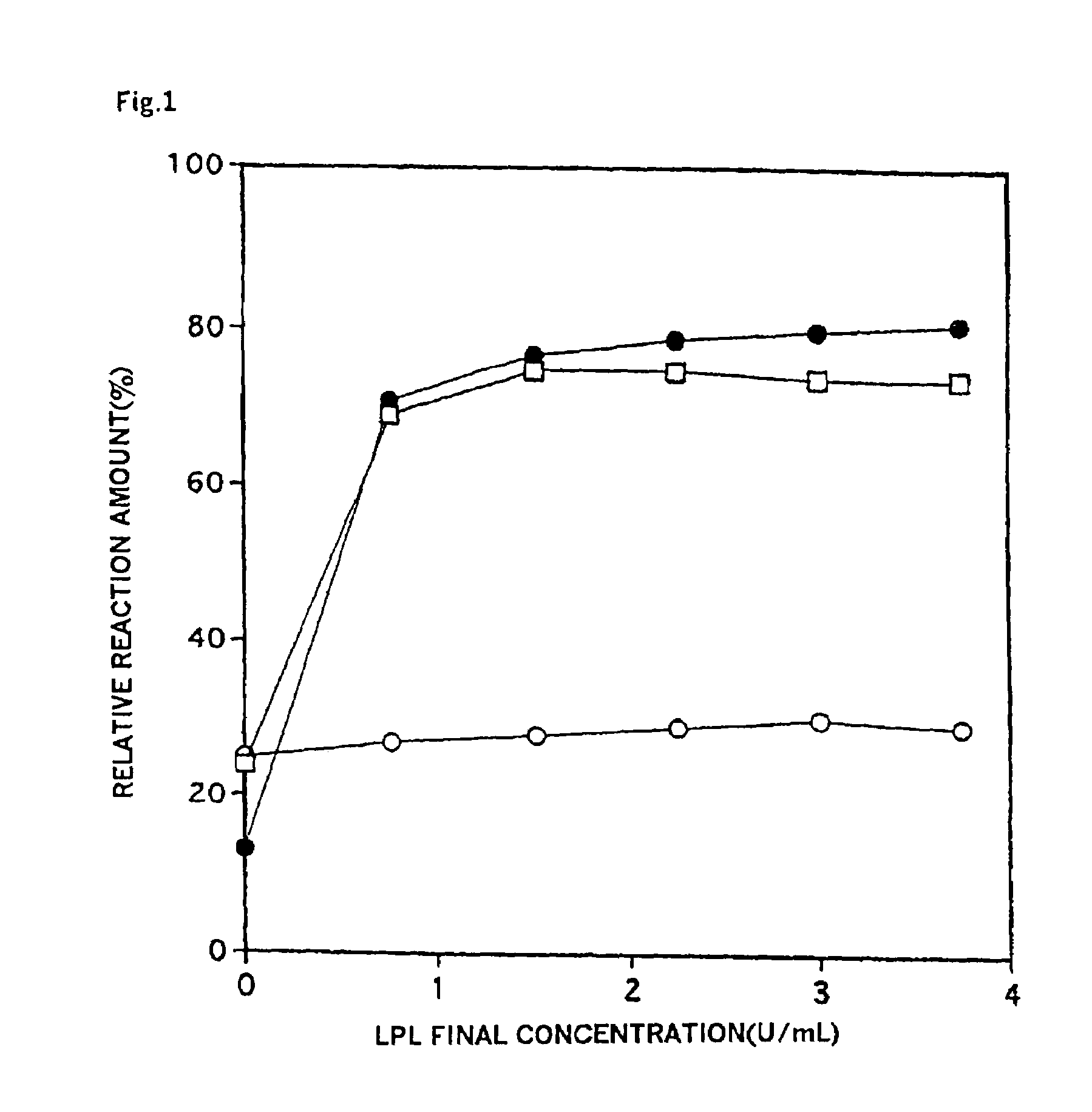
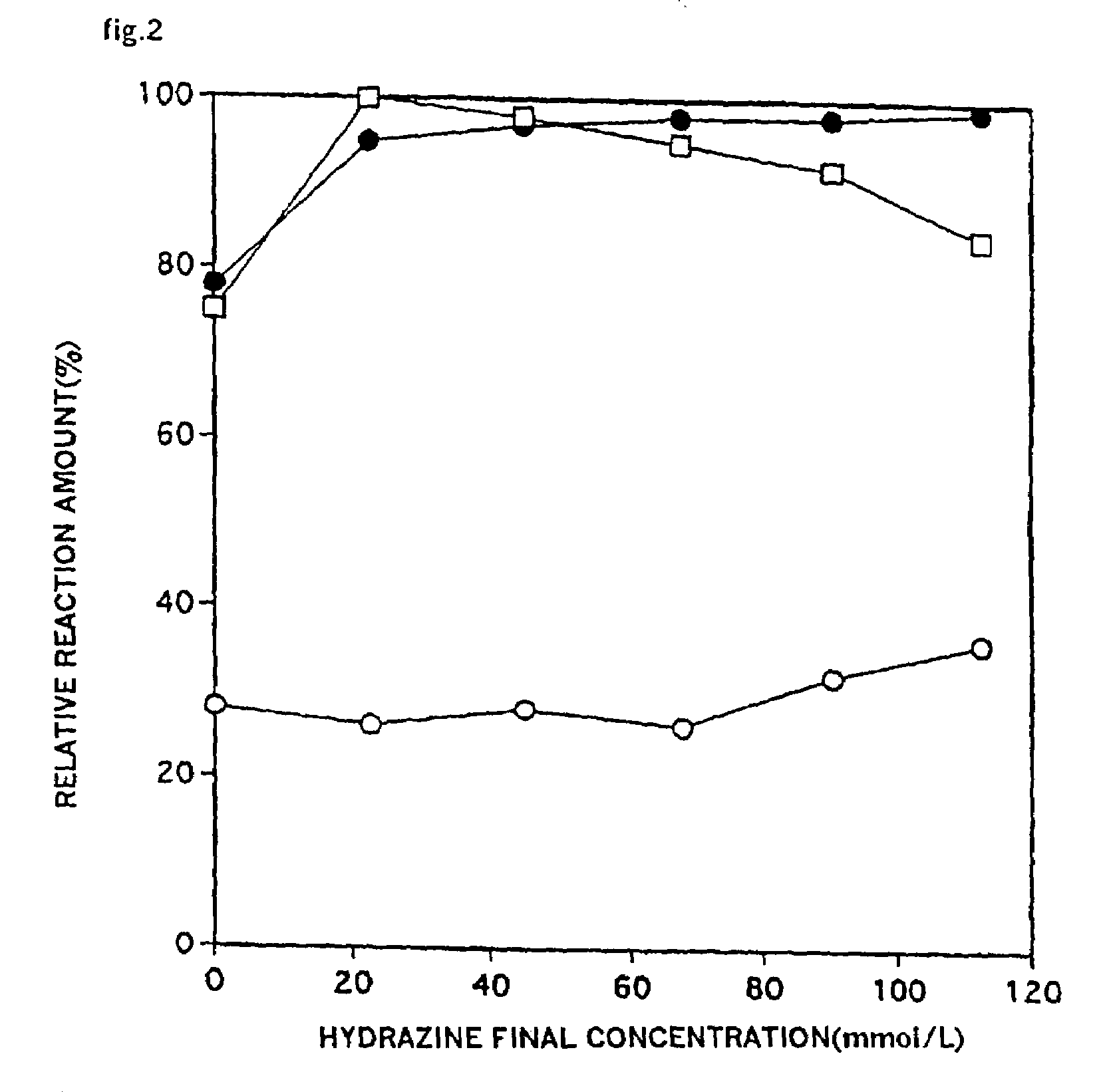
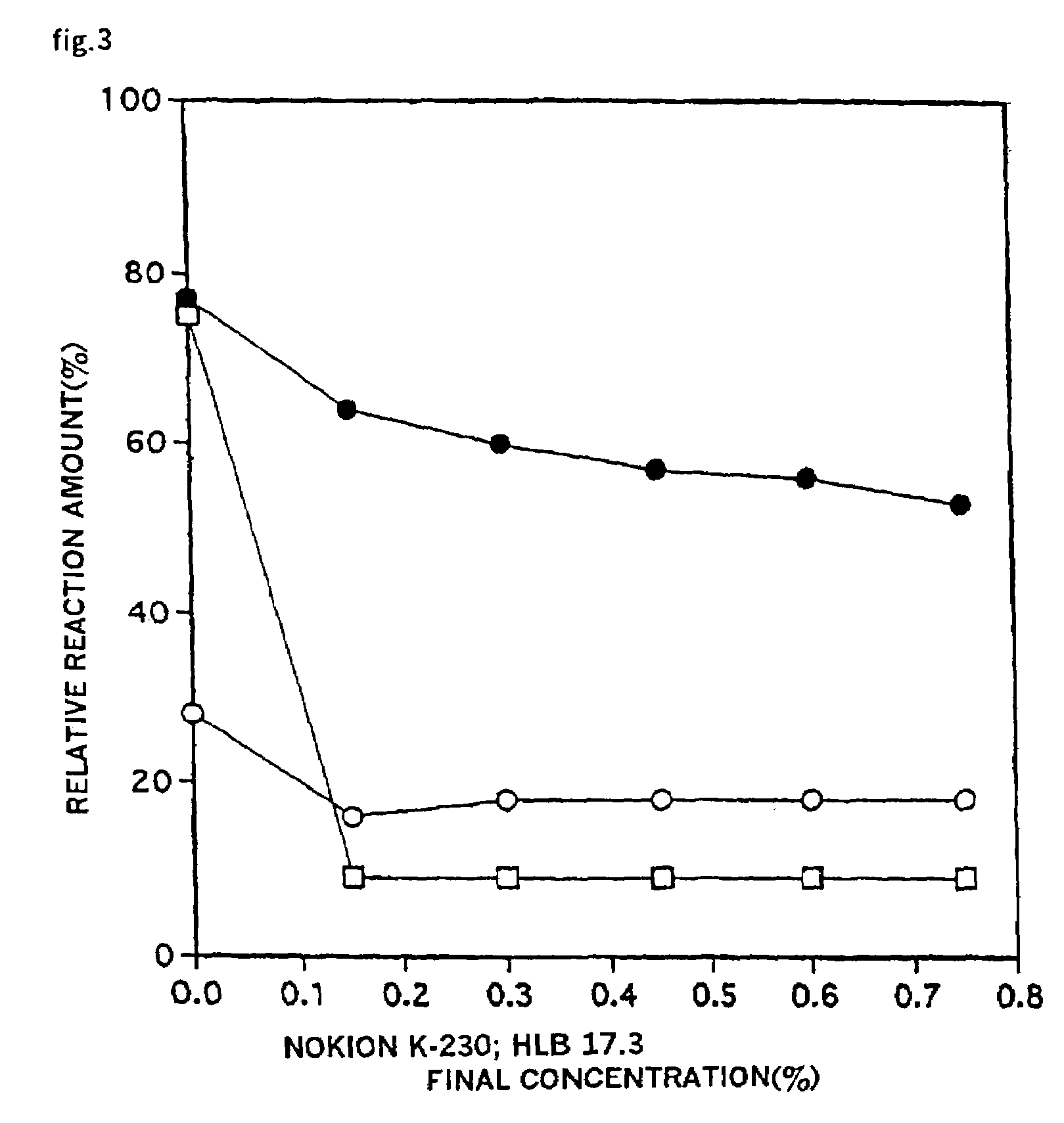
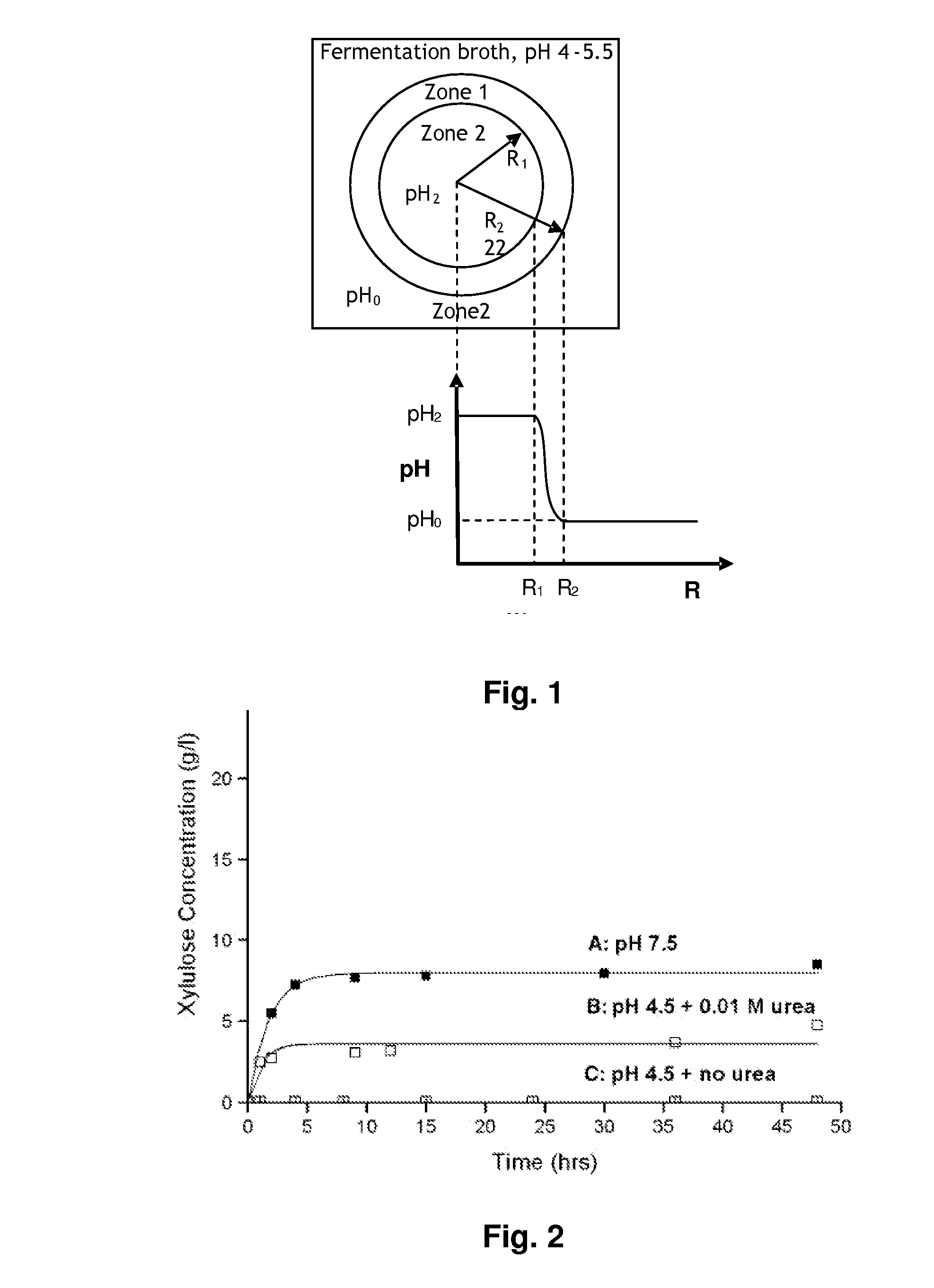
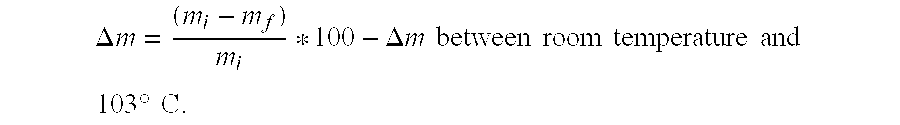Patents
Literature
206results about "Multi-enzyme systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer matrix containing catalase co-immobilized with analytic enzyme that generates hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS6858403B2Enhancing swelling kineticsLong useful lifePowder deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteHydrogen peroxide degradation
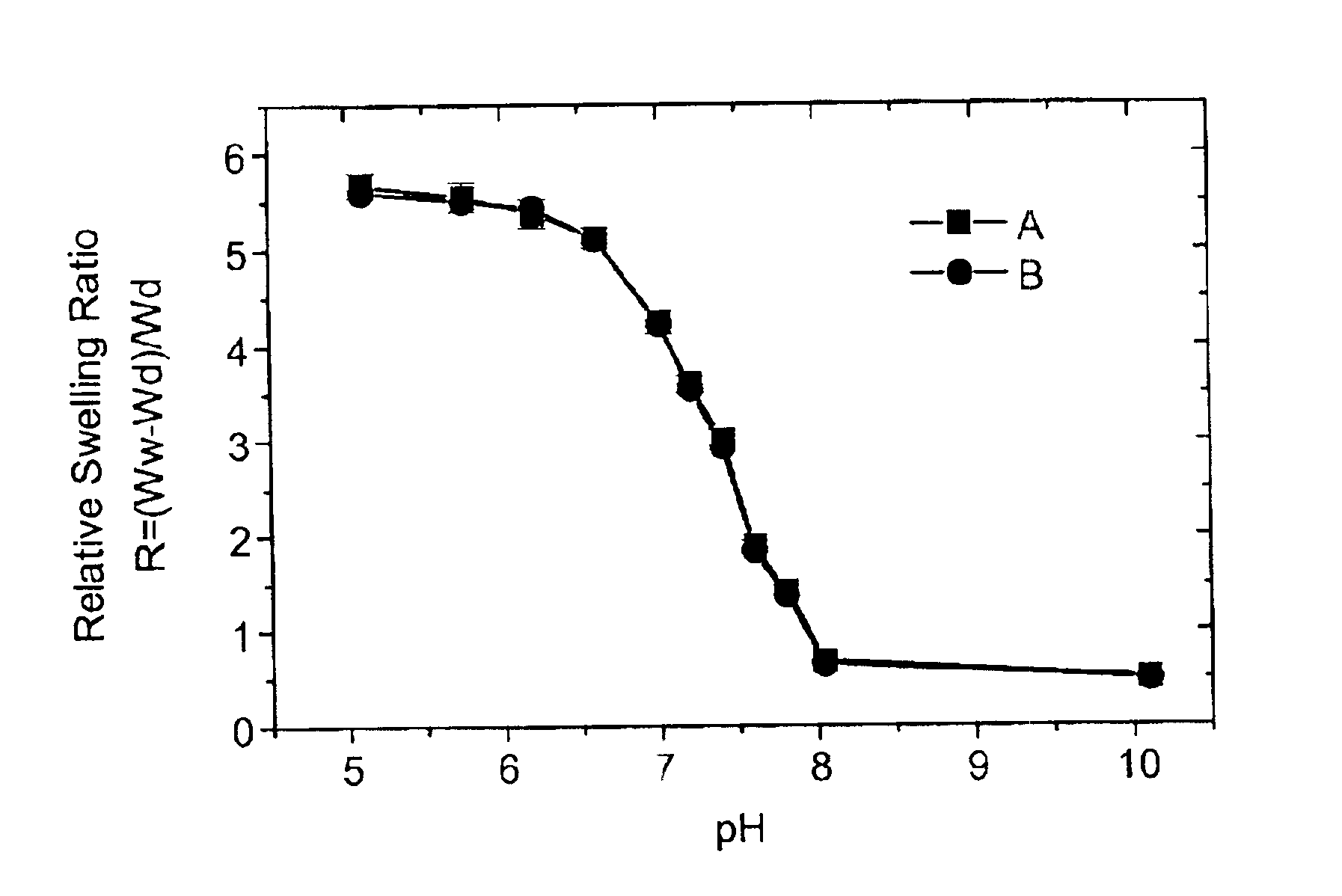
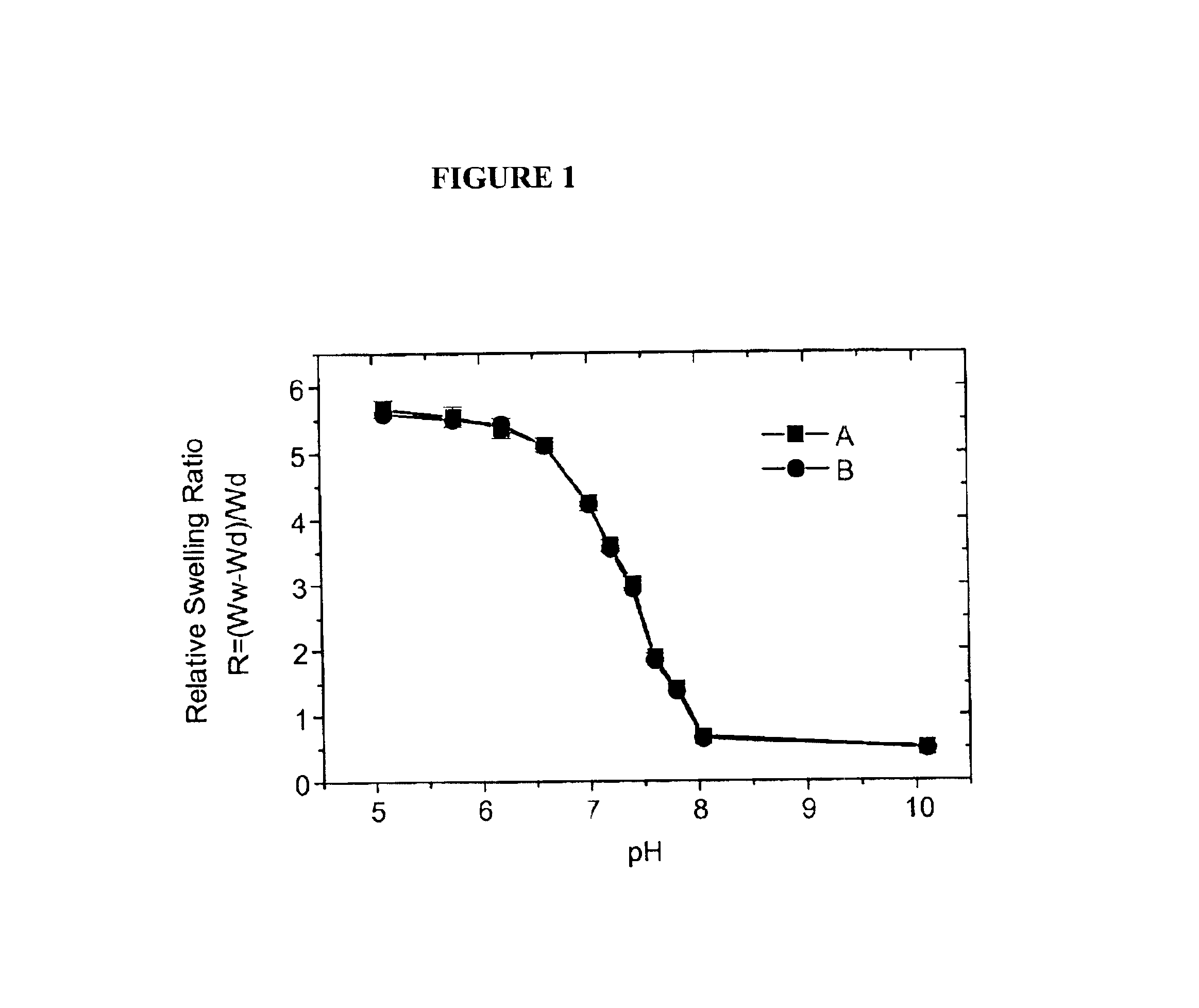
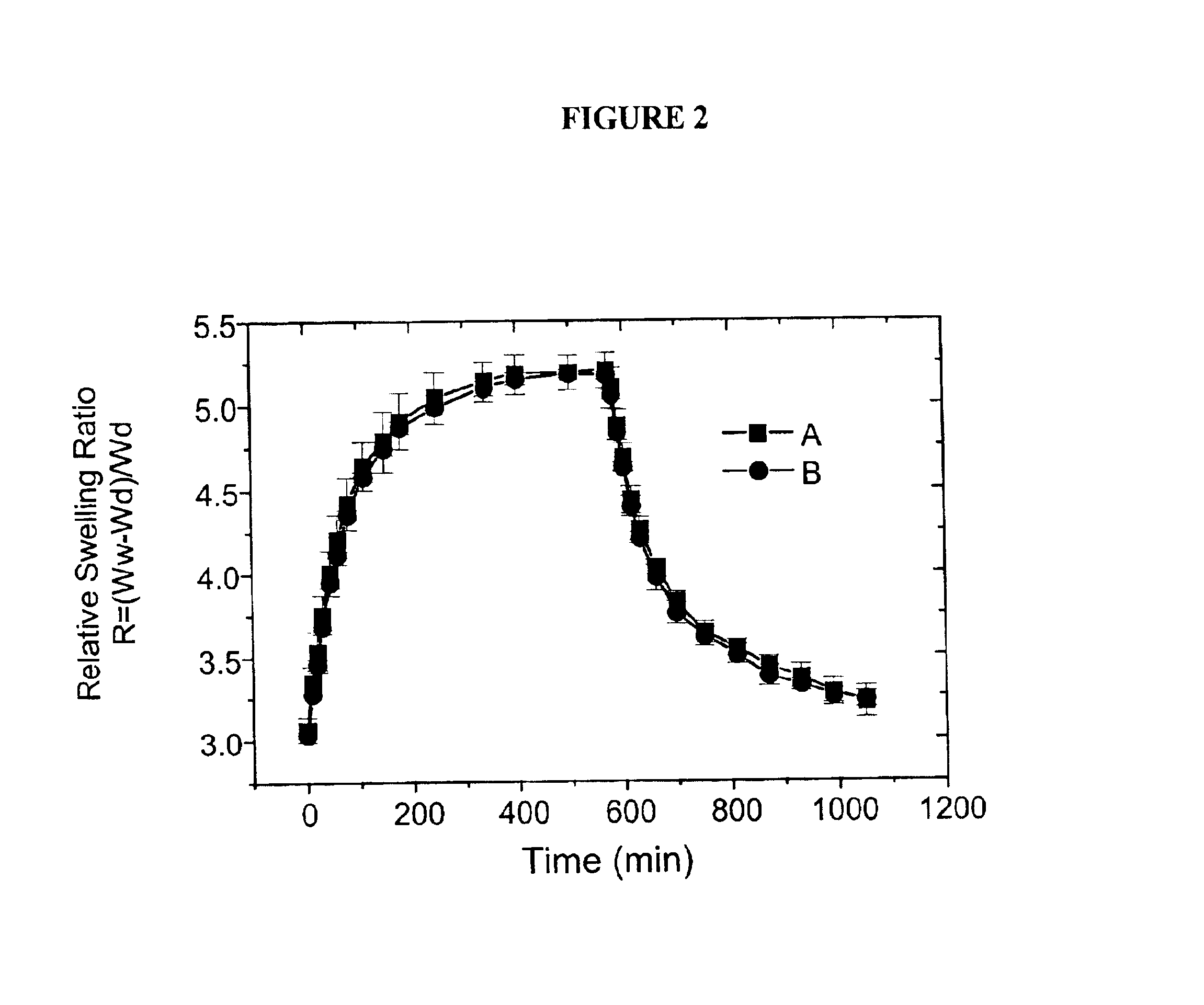
Hydrogels containing catalase co-immobilized with an analyte-sensitive enzyme such as glucose oxidase are disclosed. The hydrogels may be pH-sensitive, and preferably are thin and lightly crosslinked. The catalase is present in concentrations ranging generally from 100 units / ml to about 1000 units / ml. These hydrogels have much faster swelling response times as compared to hydrogels without catalase, and are useful in biosensors and analyte-responsive drug delivery devices. The hydrogels also have an increased useful life, due to protection of the immobilize analyte-sensitive enzyme from degradation by hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:M BIOTECH
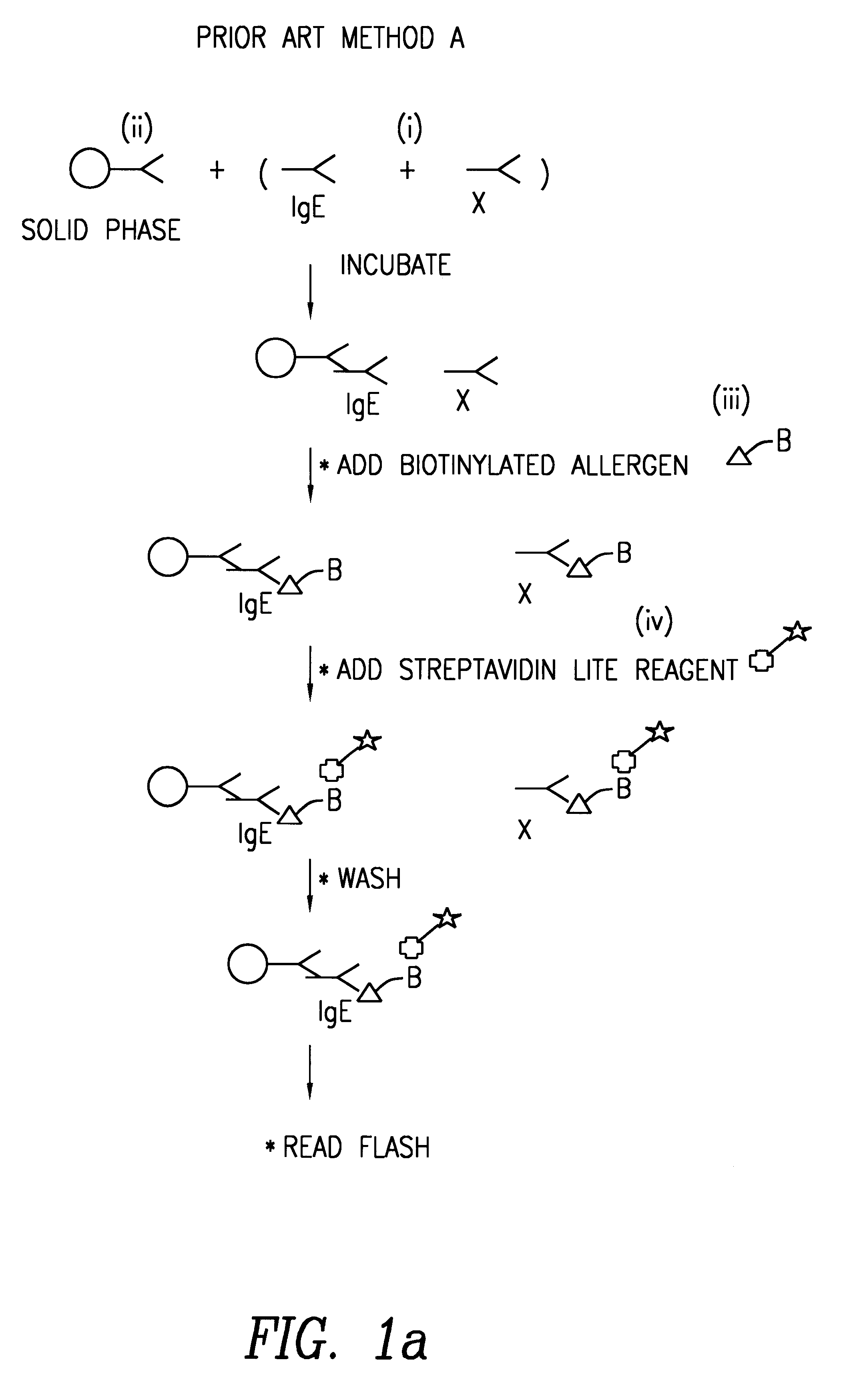
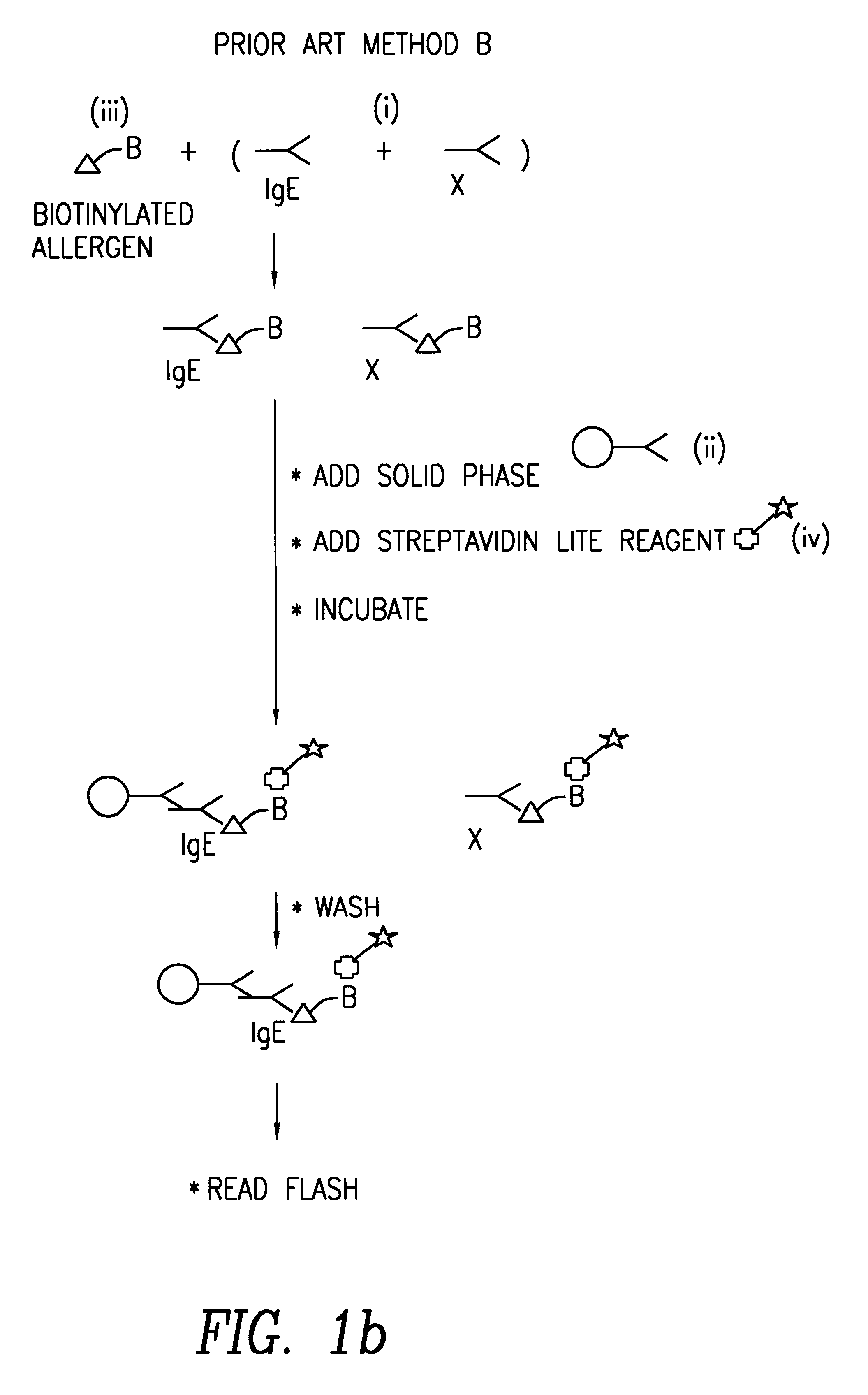
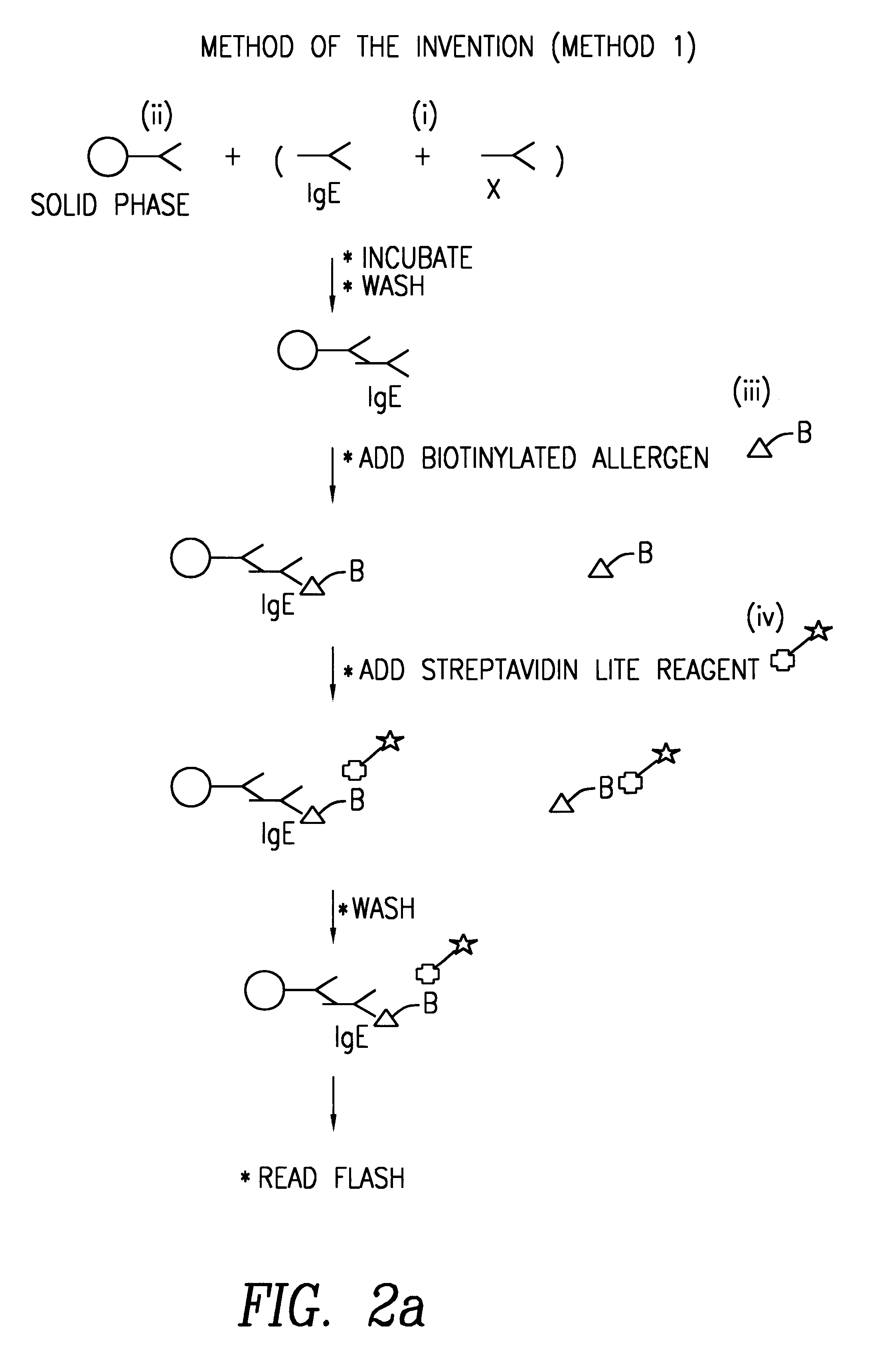
Reducing leukocyte interference in non-competitive immunoassays
ActiveUS20110117580A1Reducing and eliminating leukocyte interferenceReducing leukocyte interferenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteWhite blood cell
The invention is directed to methods and devices for reducing interference from leukocytes in an analyte immunoassay, and in particular in non-competitive immunoassays. In one embodiment, the invention is to a method comprising the steps of (a) amending a biological sample such as a whole blood sample with sacrificial beads; and (b) performing a non-competitive immunoassay on the amended sample to determine the concentration of said analyte in said sample. Preferably, the sample is amended with IgG-coated sacrificial beads.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
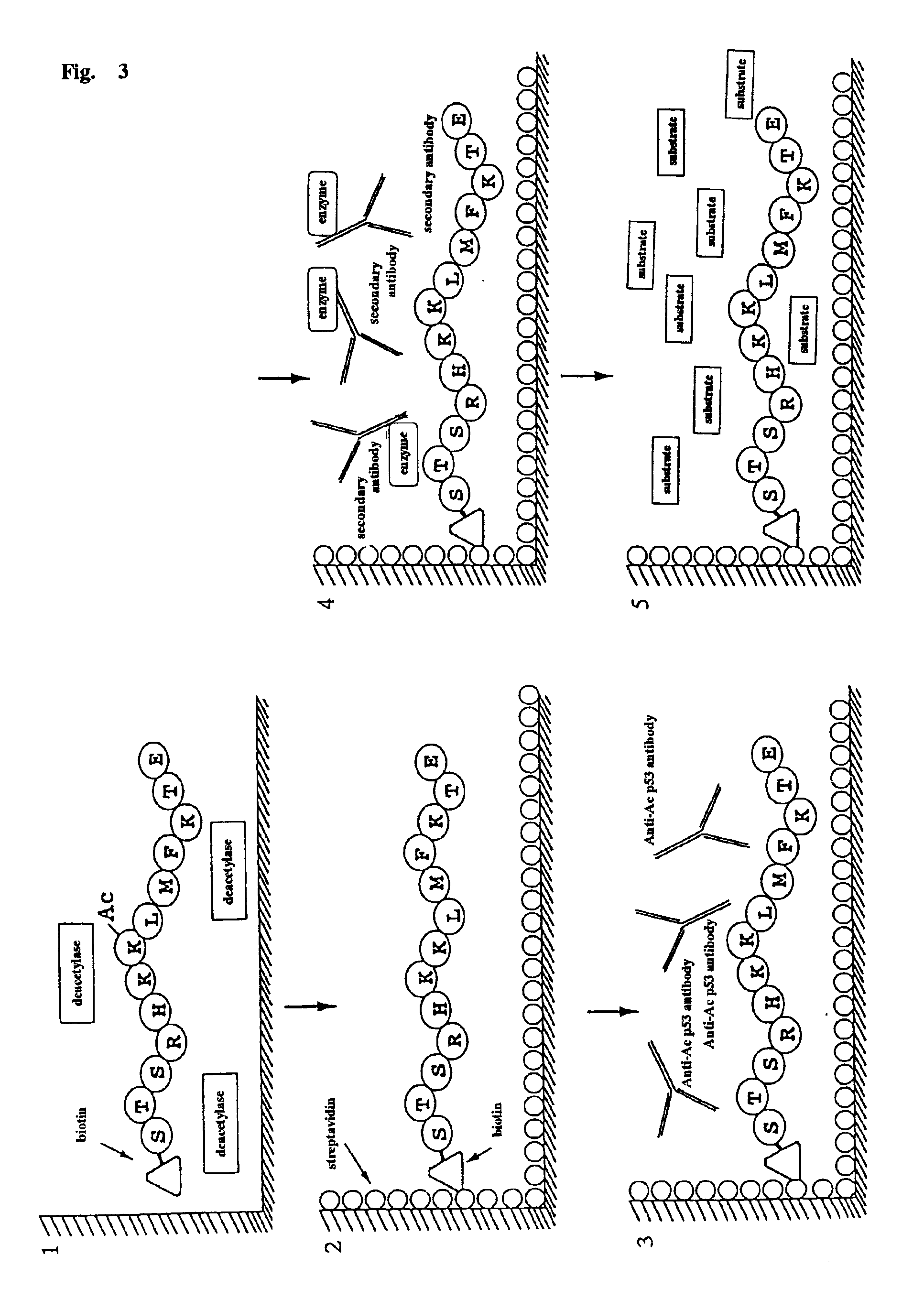
Method for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities and method for screening inhibitors or enhancers of these enzymes
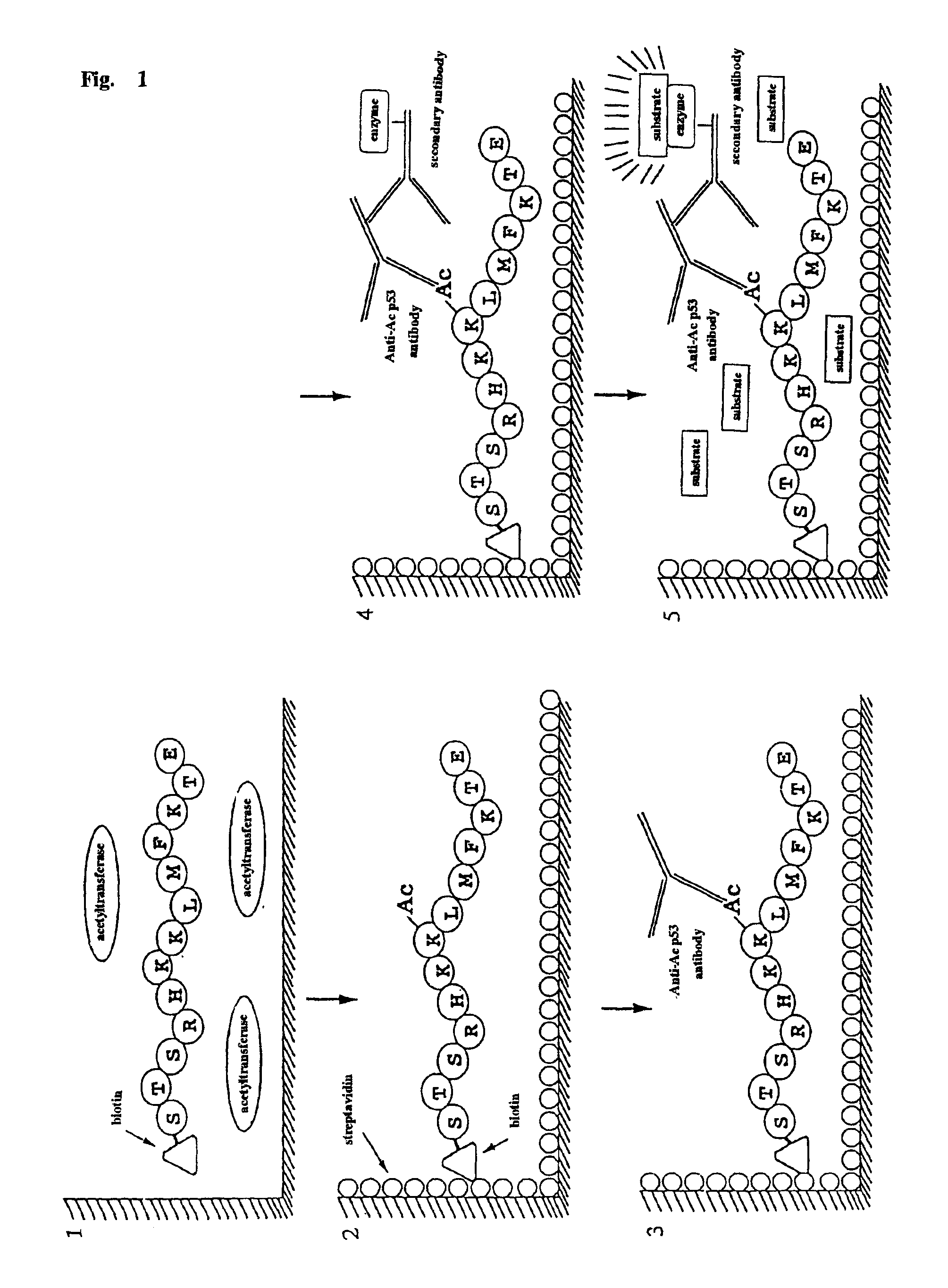
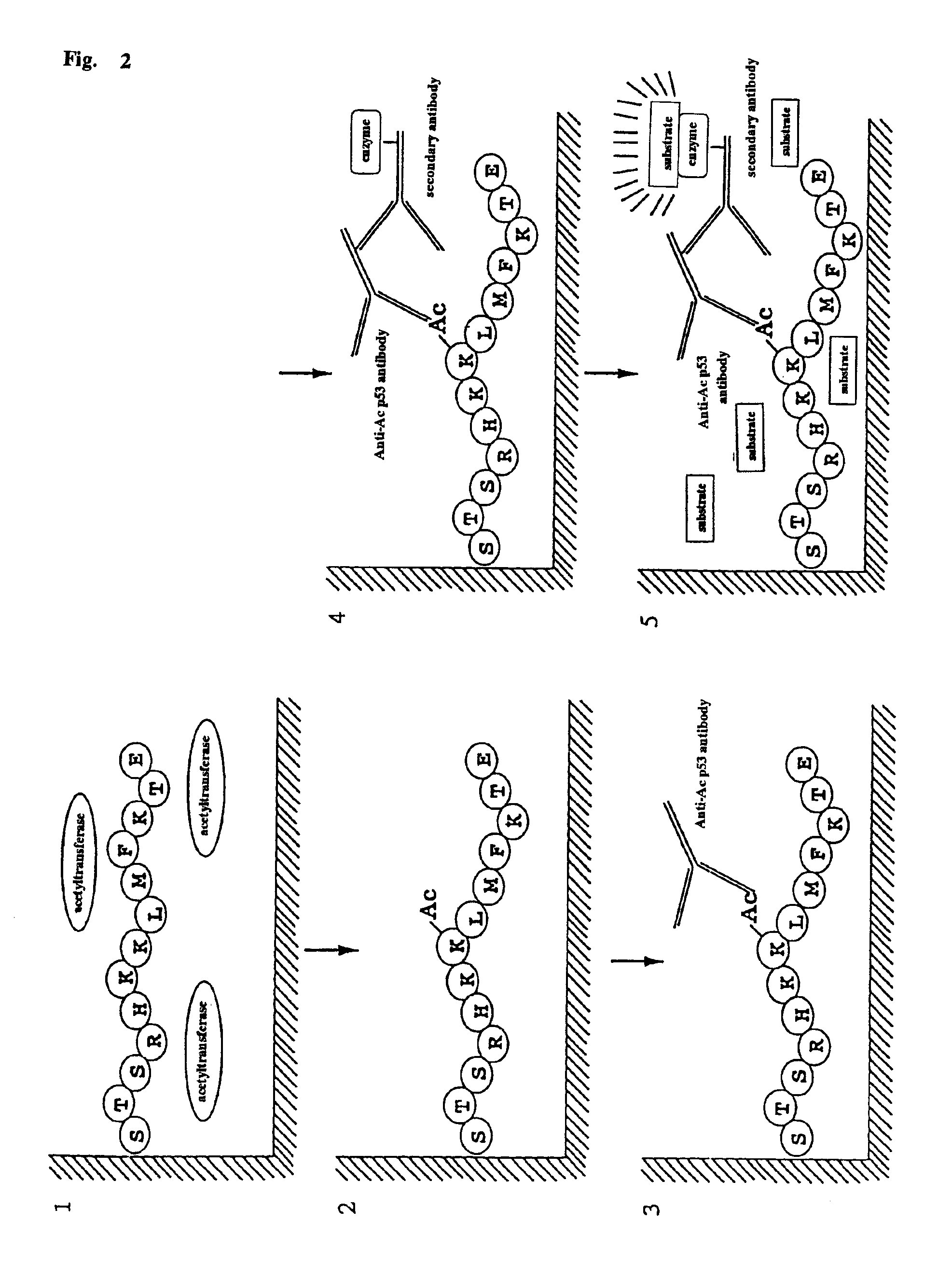
InactiveUS6884597B1Easy to detectConducive to screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide substrateAcetyltransferase
A method for simply and conveniently detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities of proteins by executing an acetylation reaction of a peptide substrate with an acetyltransferase, or a deacetylation reaction of an acetylated peptide substrate with a deacetylase, and after the completion of these reactions, detecting the acetyl group bound to the peptide substrate by using an anti-acetylated peptide antibody. This system for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities using the anti-acetylated peptide antibody enables screening inhibitors or enhancers of acetyltransferase and deacetylase. A system for screening deacetylase inhibitors or acetyltransferase enhancers using cultured cells is also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
Enzyme catalyst immobilized on porous fluoropolymer support
ActiveUS20120040395A1Maintain catalytic activityPretreated surfacesOn/in organic carrierHigh rateActive enzyme
Enzyme catalyst immobilized on porous flouropolymer supports. Catalytically active enzymes can be bound to a variety of fluoropolymer supports for use as a reaction catalyst. Moreover, consistently high rate of conversion during catalyst re-use over time is achieved. Furthermore, inactive enzyme catalyst can be stripped from the support and fresh enzyme can be bound to the support to achieve the original conversion rate. The immobilization of catalytic enzymes on porous fluoropolymers is a viable and novel technology for the preparation of advantaged catalysts.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
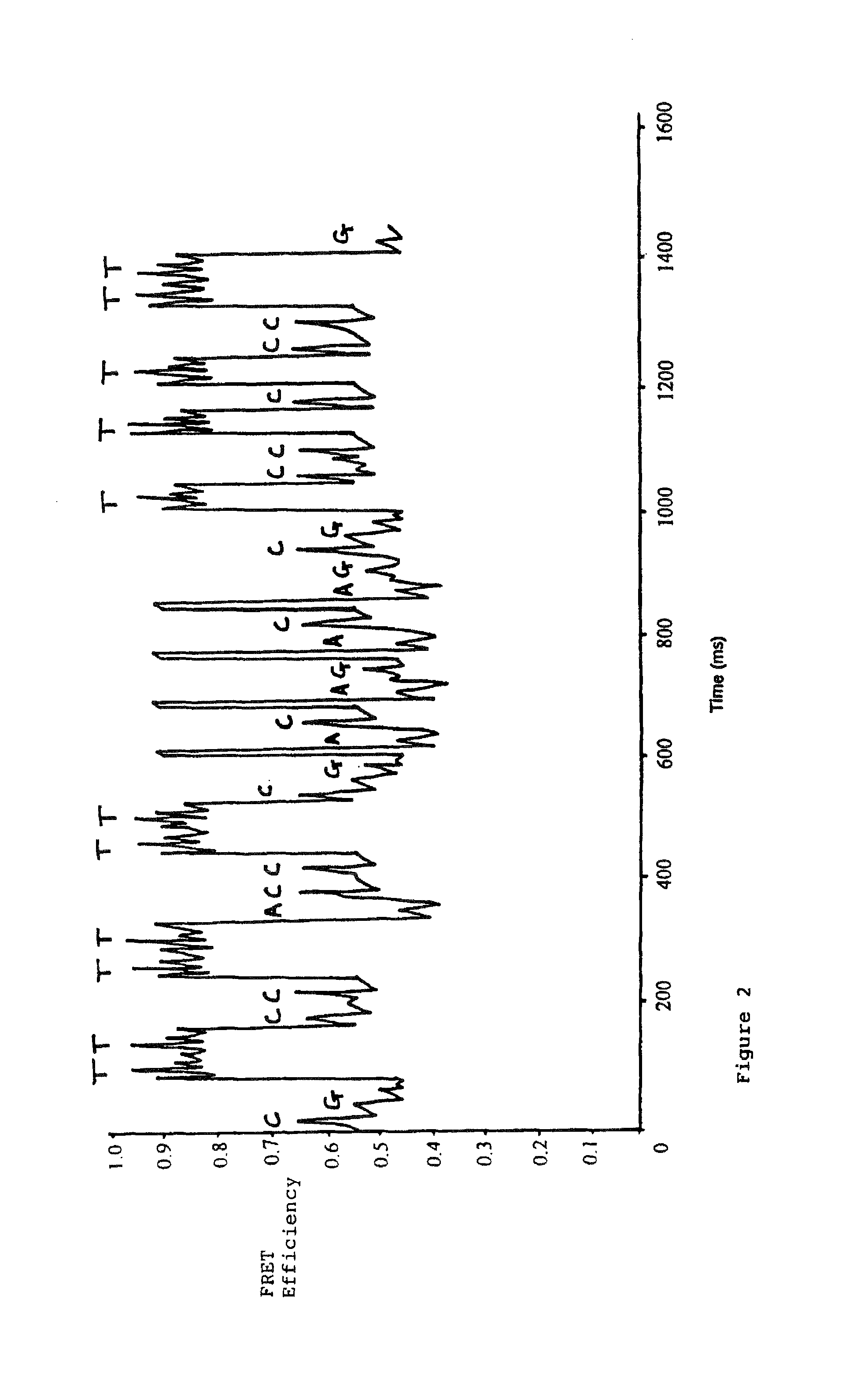
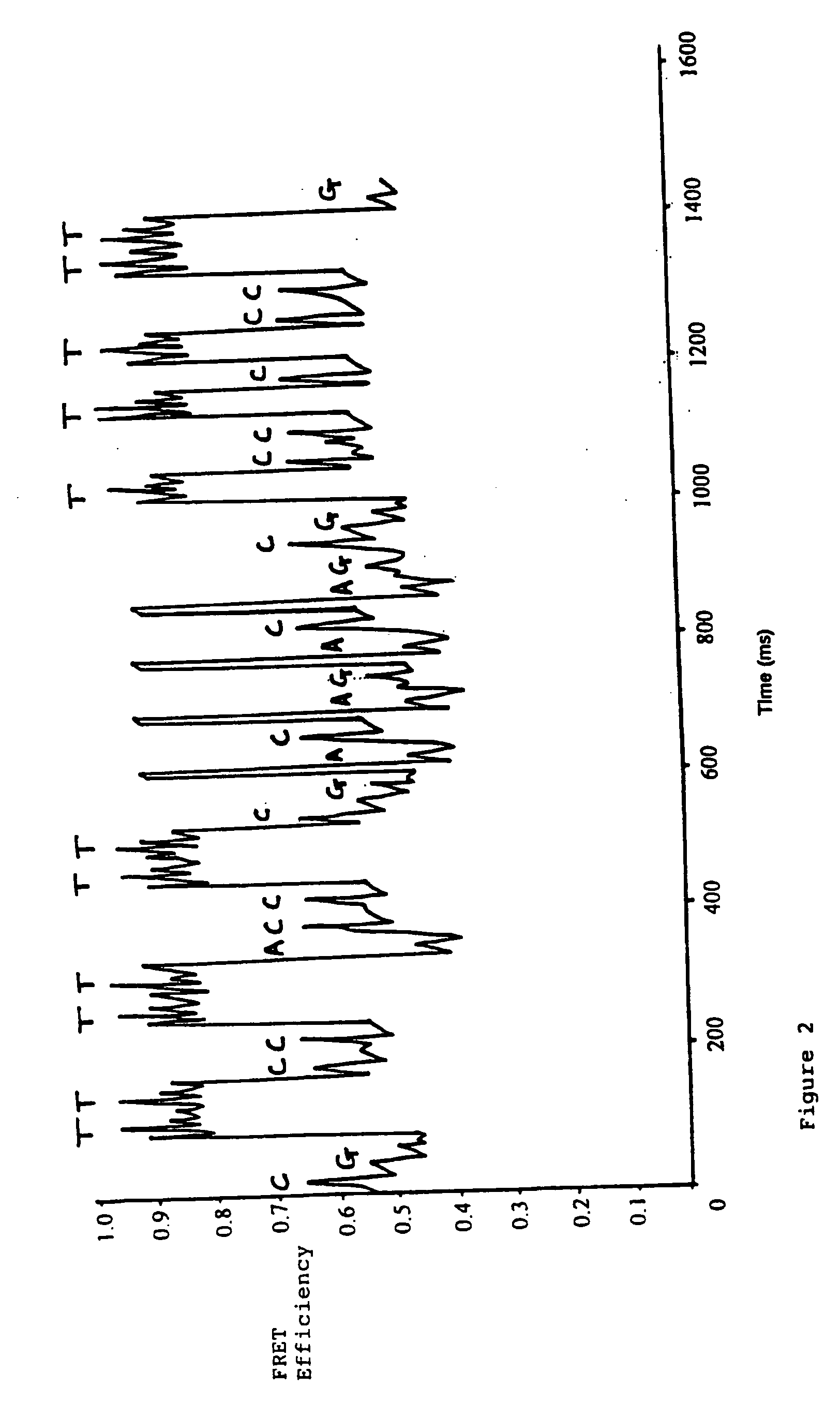
DNA sequencing method
InactiveUS7939264B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorescencePolynucleotide
The present invention pertains to a method for determining the sequence of a polynucleotide, the method relying on the detection of a conformational change in an enzyme that interacts with and processes along the polynucleotide. The detection of a conformational change may be carried out by measuring changes in a fluorophore bound to the enzyme.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
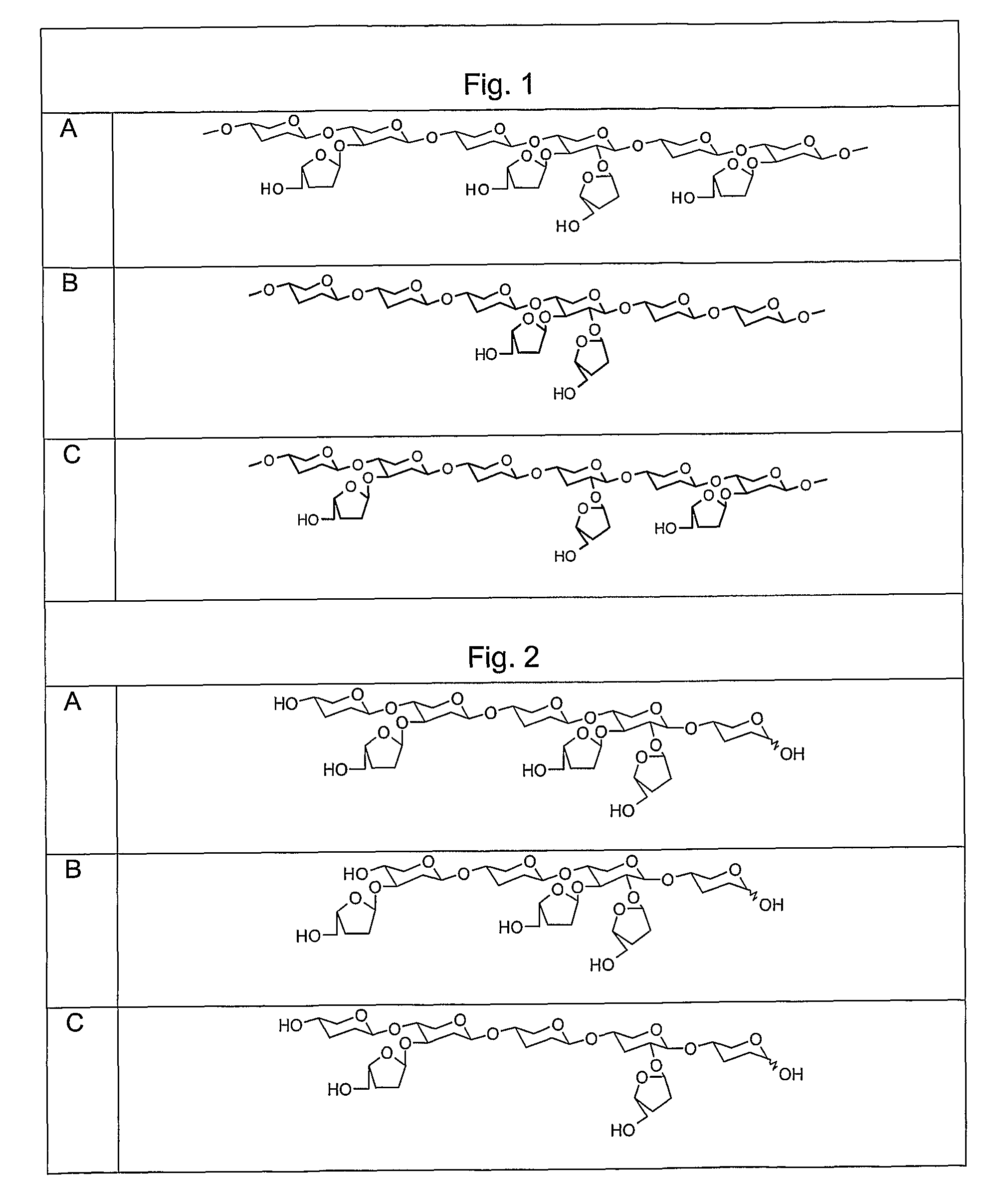
Dendrimer-like modular delivery vector
Various nucleic acid-based matrixes are provided, comprising nucleic acid monomers as building blocks, as well as nucleic acids encoding proteins, so as to produce novel biomaterials. The nucleic acids are used to form dendrimers that are useful as supports, vectors, carriers or delivery vehicles for a variety of compounds in biomedical and biotechnological applications. In particular, the macromolecules may be used for the delivery of drugs, genetic material, imaging components or other functional molecule to which they can be conjugated. An additional feature of the macromolecules is their ability to be targeted for certain organs, tumors, or types of tissues. Methods of utilizing such biomaterials include delivery of functional molecules to cells.
Owner:LUO DAN +1
Refolding method of thrombin
InactiveUS20020142369A1Peptide preparation methodsRecombinant DNA-technologyThrombin activityFoldase
A method for promoting the foling of a polypeptide selected from thrombin and a precursor thereof comprising contacting the polypeptide with a molecular chaperone and a foldase is provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Diagnostic device and method
InactiveUS7871813B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellLymphocyte
A method of separating a cell-containing sample into a substantially cell-depleted portion, and a cell-containing portion comprising at least one of a stem cell, a lymphocyte, and a leukocyte comprises a step in which the sample is received in a vessel with at least one flexible wall. In another step, an additive and particles are added to the sample, wherein the additive substantially binds to the at least one of the stem cell, lymphocyte, and leukocyte, and the particles and wherein the particles substantially bind to the at least one of the stem cell, lymphocyte, and leukocyte, and the additive, thereby producing a cell-containing network. In a further step, the network is separated from the substantially cell-depleted portion by applying a magnetic force.
Owner:QUALIGEN INC
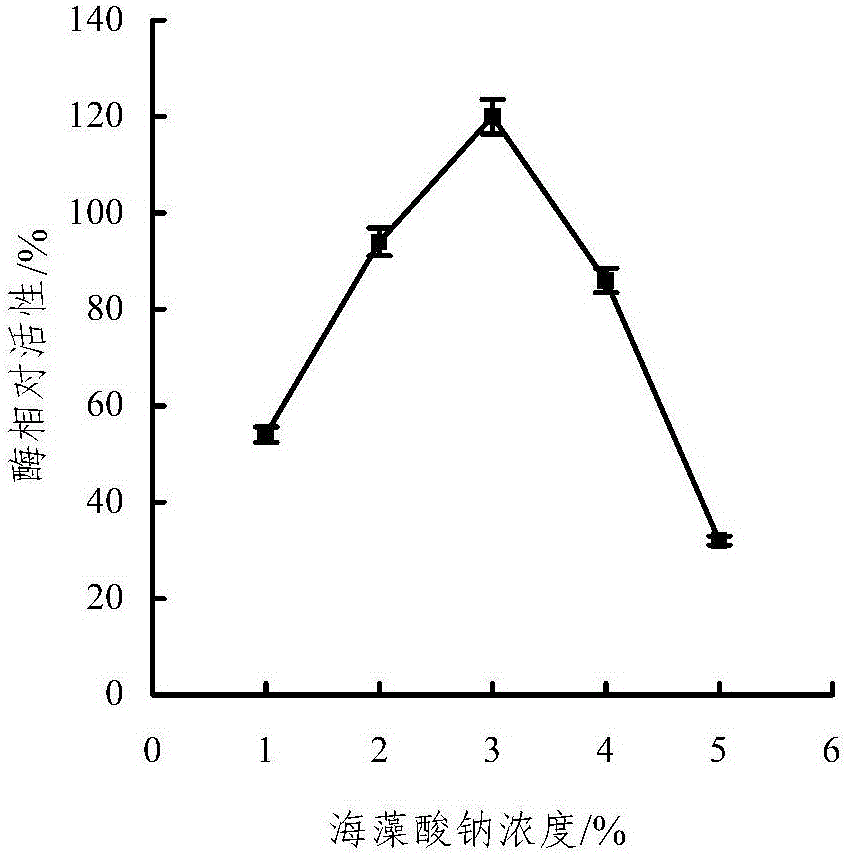
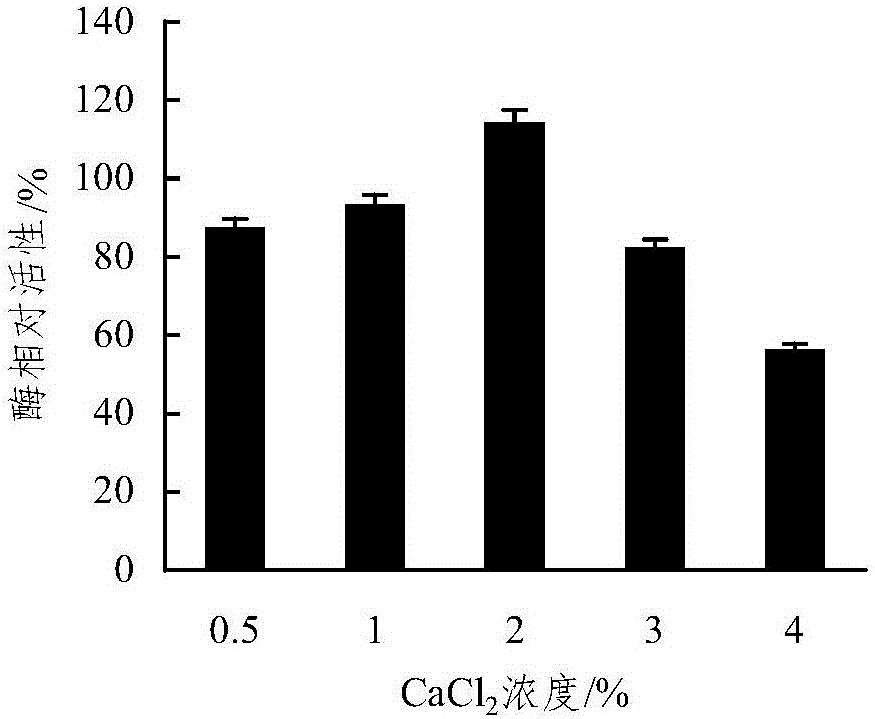
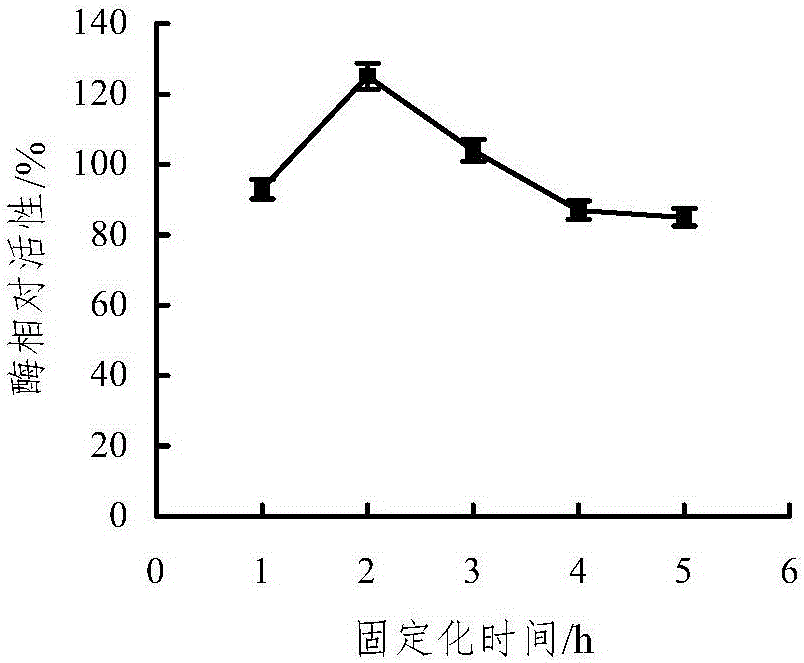
Method for preparing mixed immobilized glucose oxidase/catalase microspheres
InactiveCN102199592ACo-immobilizationReduce steric hindrance effectOn/in organic carrierMulti-enzyme systemsFreeze-dryingArginine
The invention provides a method for preparing mixed immobilized glucose oxidase (GOD) / catalase (CAT) microspheres and belongs to the technical field of immobilized enzyme. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of using chitosan-arginine anionic microspheres as carrier, adding a mixed solution of GOD and CAT and glutaraldehyde, performing crosslinking reaction, filtering, washing,and performing freeze drying to prepare mixed immobilized GOD / CAT microspheres. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, higher recovery rate of enzyme activity, long half-lifeof immobilized enzyme, simplicity in operation, low cost, cleanness, safety, and the like. The product prepared by the method can be widely used in the industries of medicines, food, water treatment,cement and the like. The product can also be used as a glucose-removing reagent, an anti-oxidation reagent, a bactericide, a glucose quantitative analysis reagent and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
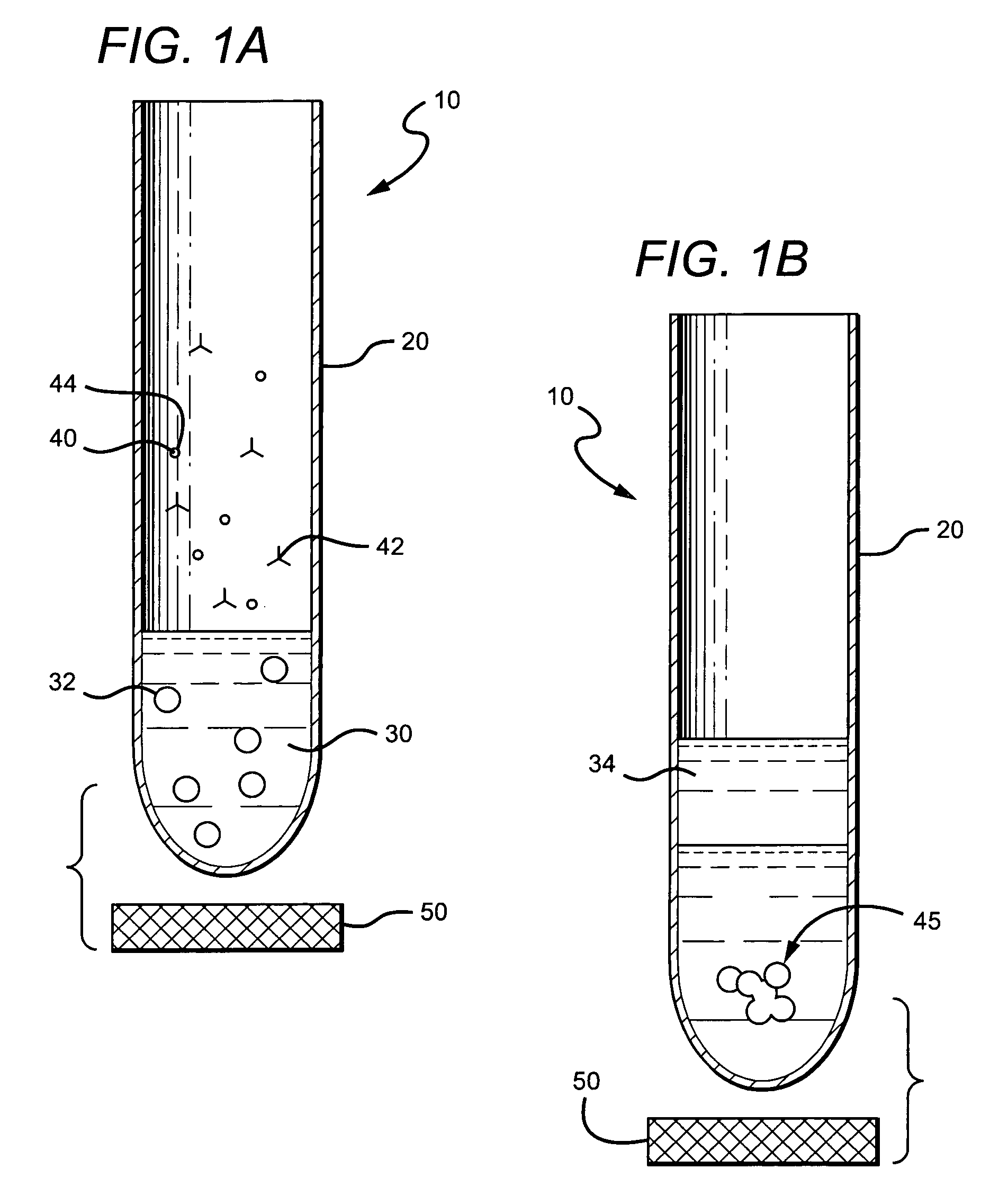
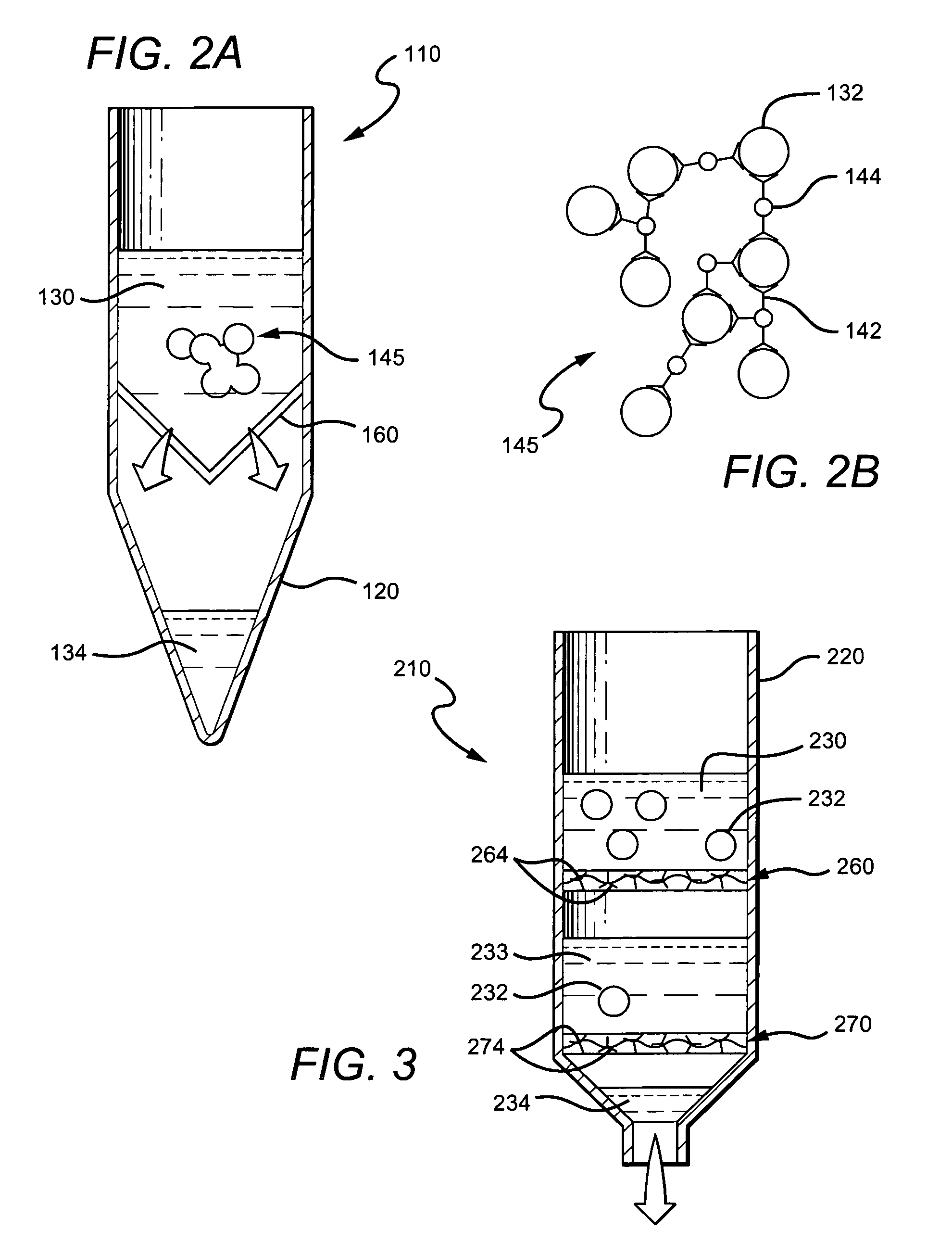
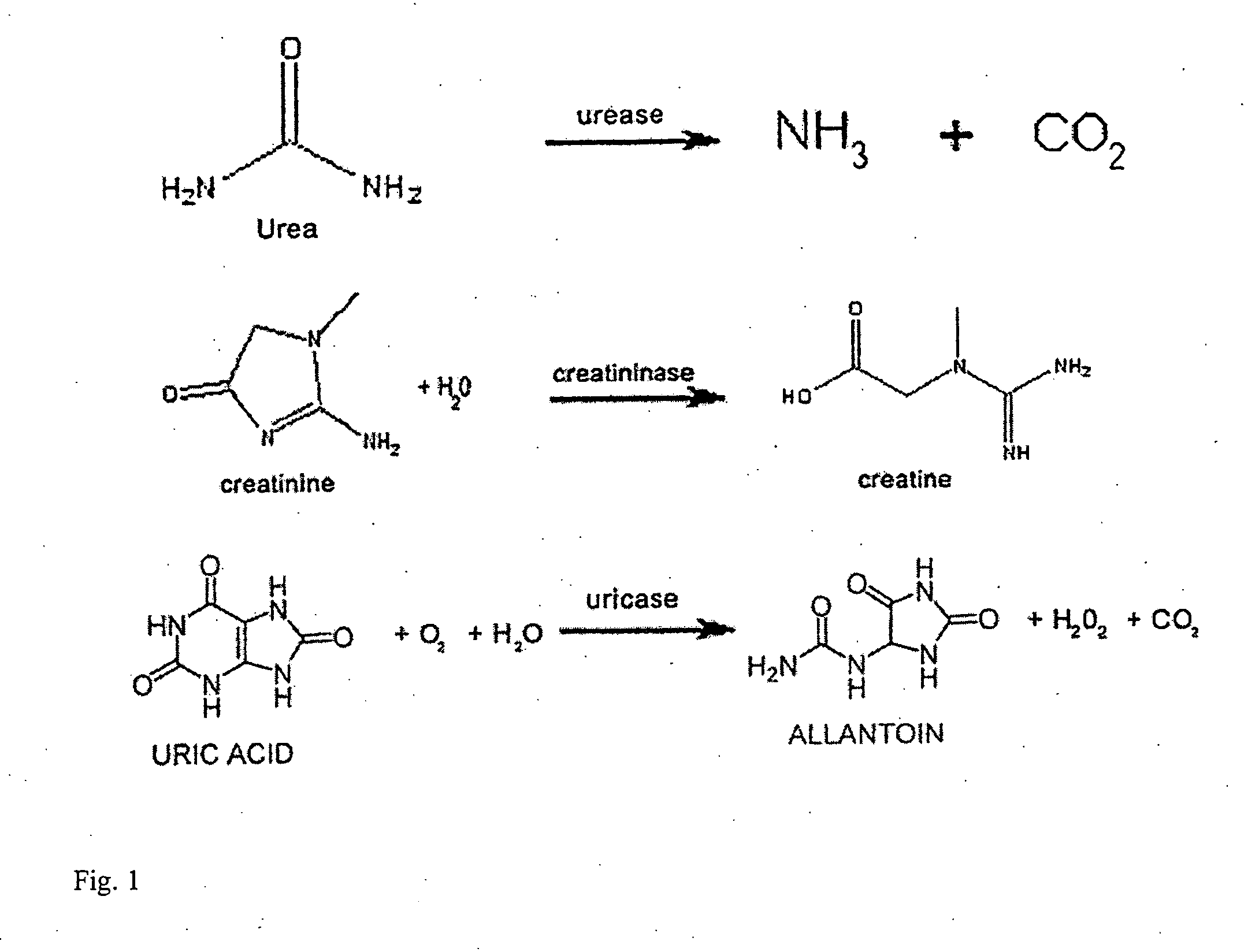
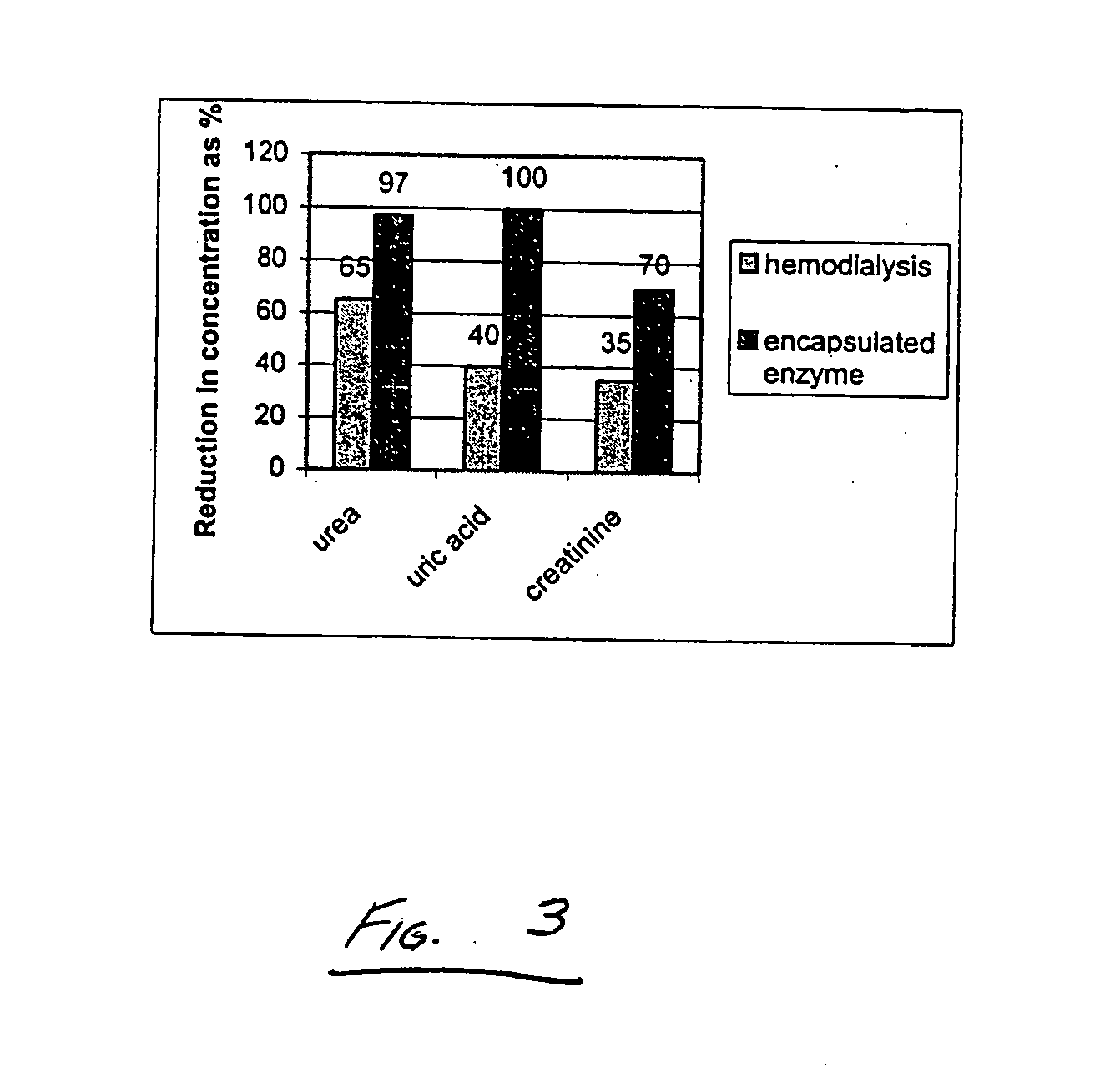
Systems and methods related to degradation of uremic toxins
The present invention generally relates to the treatment of uremic toxins in vivo using uremic toxin-treating enzymes, and / or cells capable of producing uremic toxin-treating enzymes or otherwise reacting with uremic toxins. Non-limiting examples of cases where the treatment of uremic toxins is desired include renal disease or dysfunction, gout, subjects receiving chemotherapy, or the like. In one aspect, the treatment includes an oral delivery composition able to reduce the blood concentration of one or more non-protein nitrogen compounds in vivo. The composition, in some cases, may comprise one, two, or more uremic toxin-treating enzymes, such as urease, uricase or creatininase. The oral delivery composition may be able to deliver the uremic toxin-treating enzymes, substantially undigested, to the intestines, where the enzymes can interact with uremic toxins transported to the intestines from the bloodstream. In another aspect, the treatment includes an oral delivery composition comprising a cell able to reduce the concentration of one or more uremic toxins in vivo. In some cases, the cell may be designed to overexpress one, two, or more uremic toxin-treating enzymes, such as urease, uricase or creatininase, for example, by transfecting the cell with a corresponding gene. In some embodiments, a species able to react with or otherwise sequester by-products of the uremic toxin-treating enzyme reactions may be included with the oral delivery composition. For example, if the by-product is ammonium, the species may be a sorbent able to adsorb ammonium, an enzyme able to react with the ammonium, or the like.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
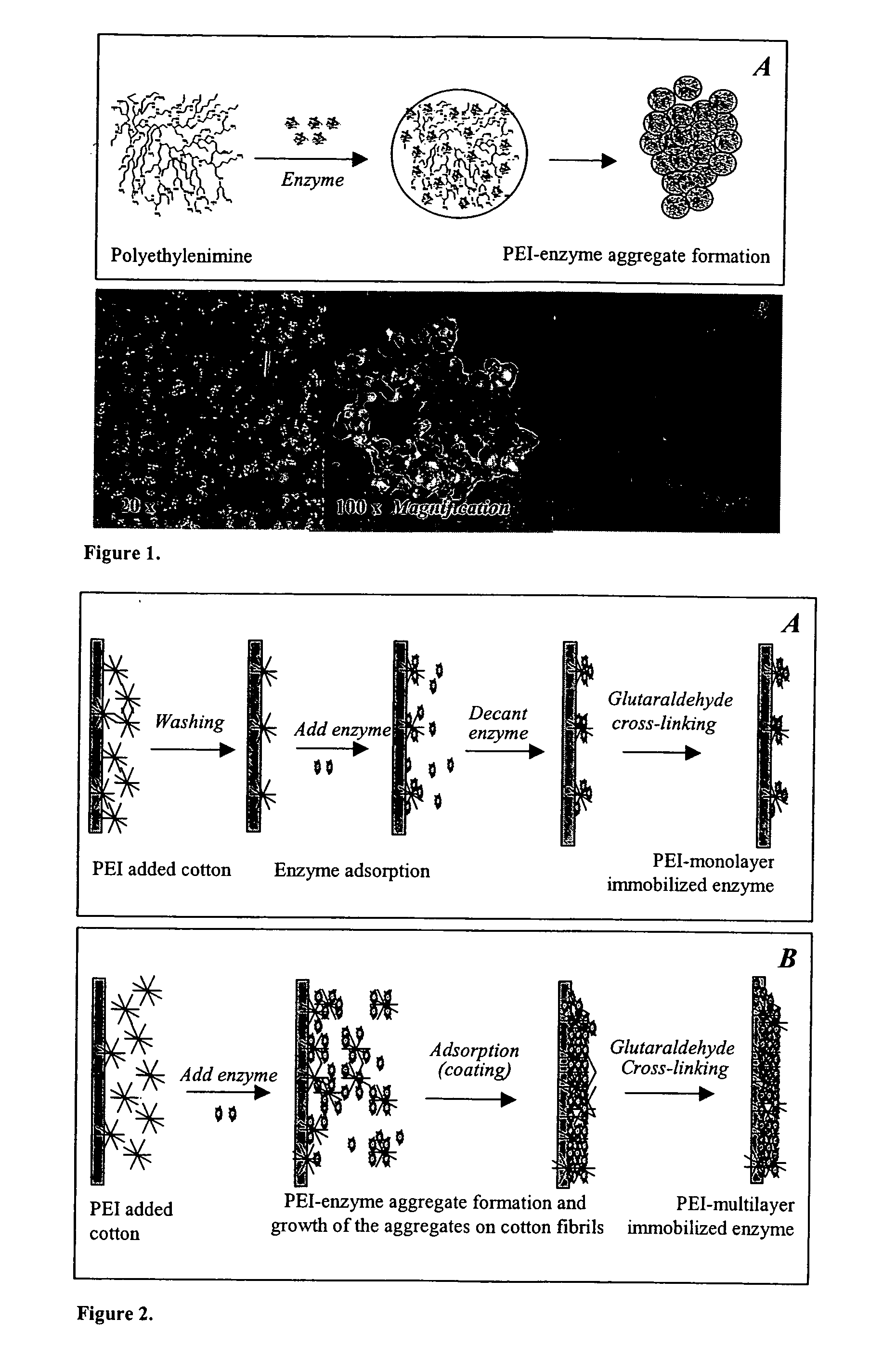
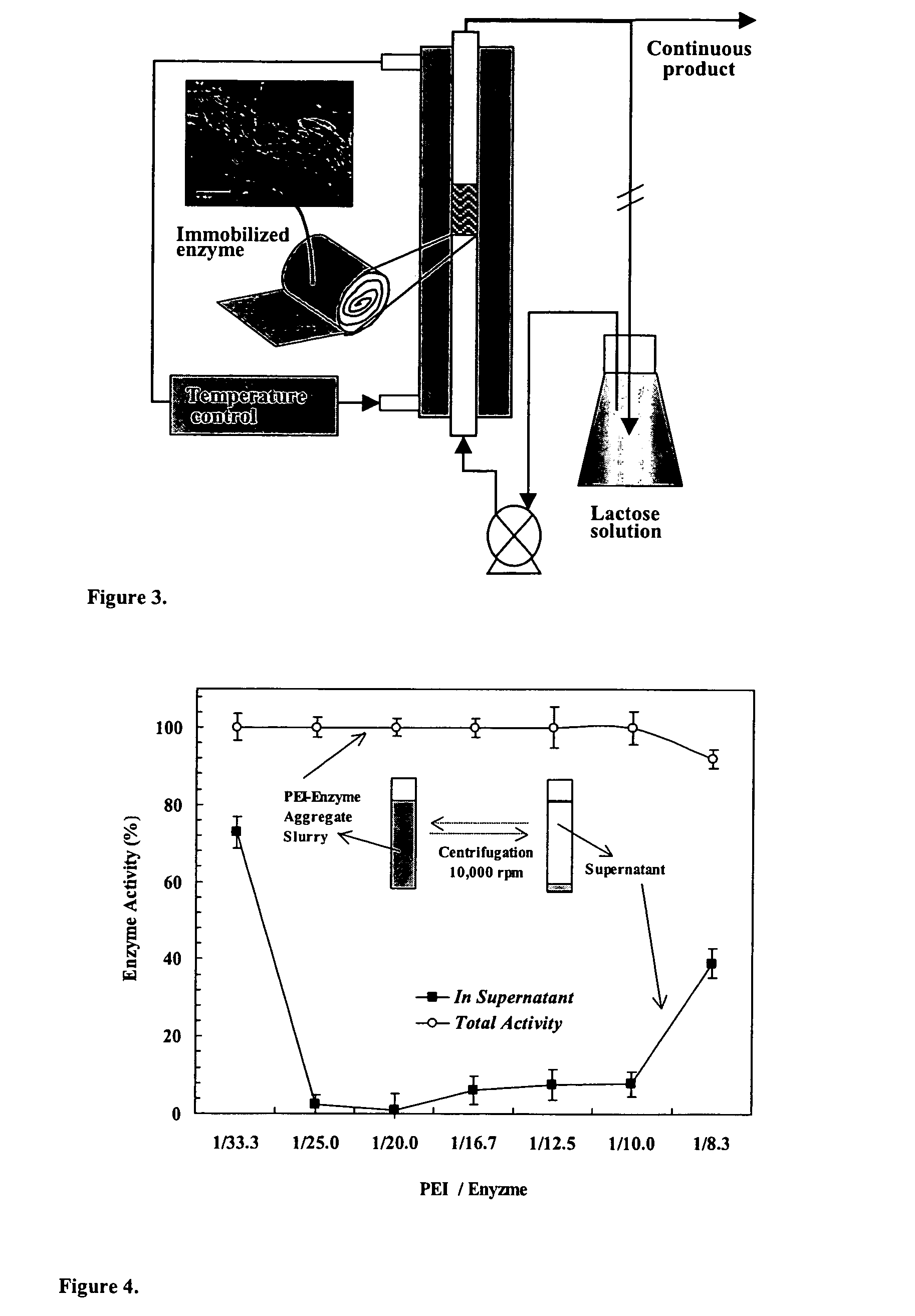
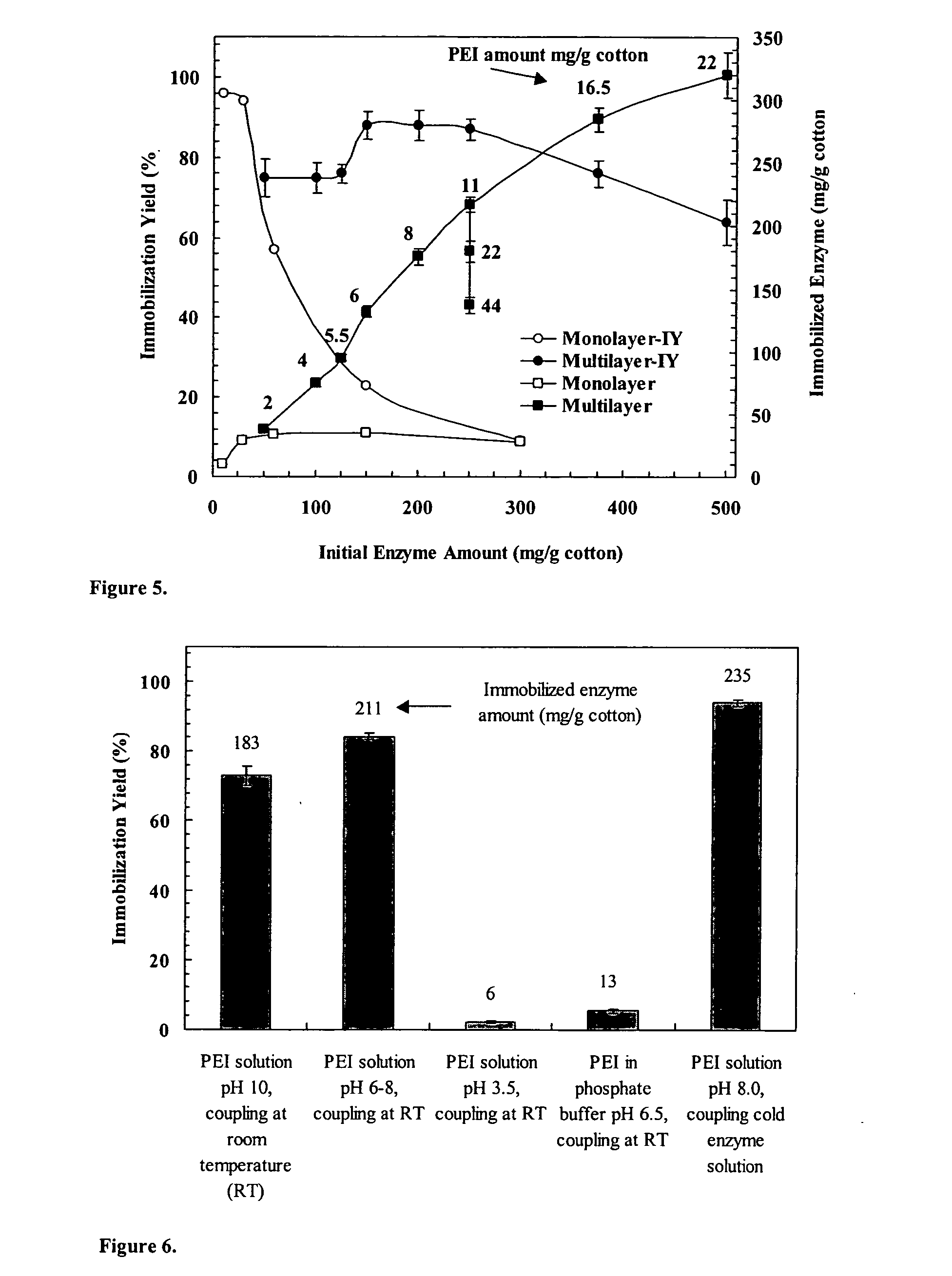
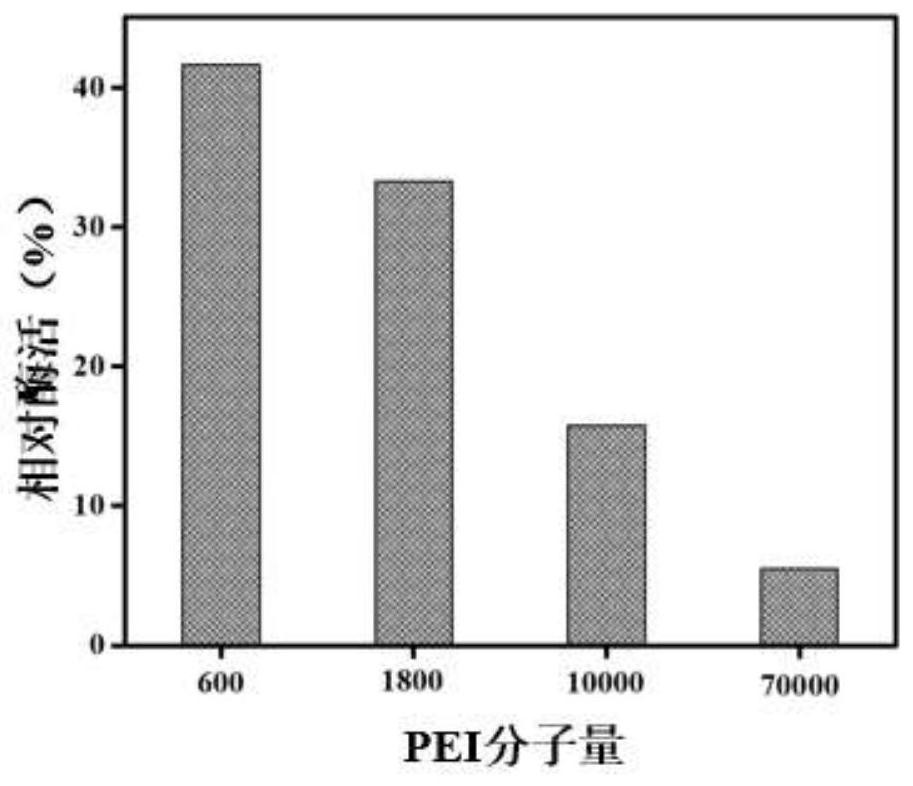
Immobilization of enzyme on a fibrous matrix
ActiveUS20070111289A1High enzyme loadingEasy loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCross-linkFiber
A multilayer enzyme immobilization process is provided comprising adsorbing a polyethyleneimine (PEI) solution in a fibrous matrix, and adding an enzyme to the fibrous matrix, which comprises a plurality of fibrils. The process further comprises forming at least two layers of PEI-enzyme aggregates on the fibrils, and cross-linking the multilayer PEI-enzyme aggregates. The process can further comprise washing the fibrils containing the cross-linked PEI-enzyme aggregates with distilled water and acetic acid buffer subsequent to cross-linking. However, the PEI-containing matrix is not washed prior to the addition of enzyme. The enzyme can be β-galactosidase and the fibrous matrix can be cotton cloth. The multilayer immobilized enzyme can be employed in a biocatalyst reactor for production of galacto-oligosaccharides from lactose and the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Reagent set and method for detecting cholesterol in a high-density lipoprotein or low density lipoprotein
InactiveUS7208287B2Raise the pHMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingVery low-density lipoproteinHigh-density lipoprotein
A method for quantitating a specific component in lipoproteins contained in a biological sample, for example, HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein) or VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein) by using a commonly employed automatic analyzer without centrifuging or making the reaction liquor cloudy due to complexes or aggregates. Namely, a controlling means, whereby an enzyme reaction can be carried out exclusively for the target component, is introduced into a method for enzymatically assaying a component in a specific lipoprotein fraction in the serum, thereby specifically assaying the component.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
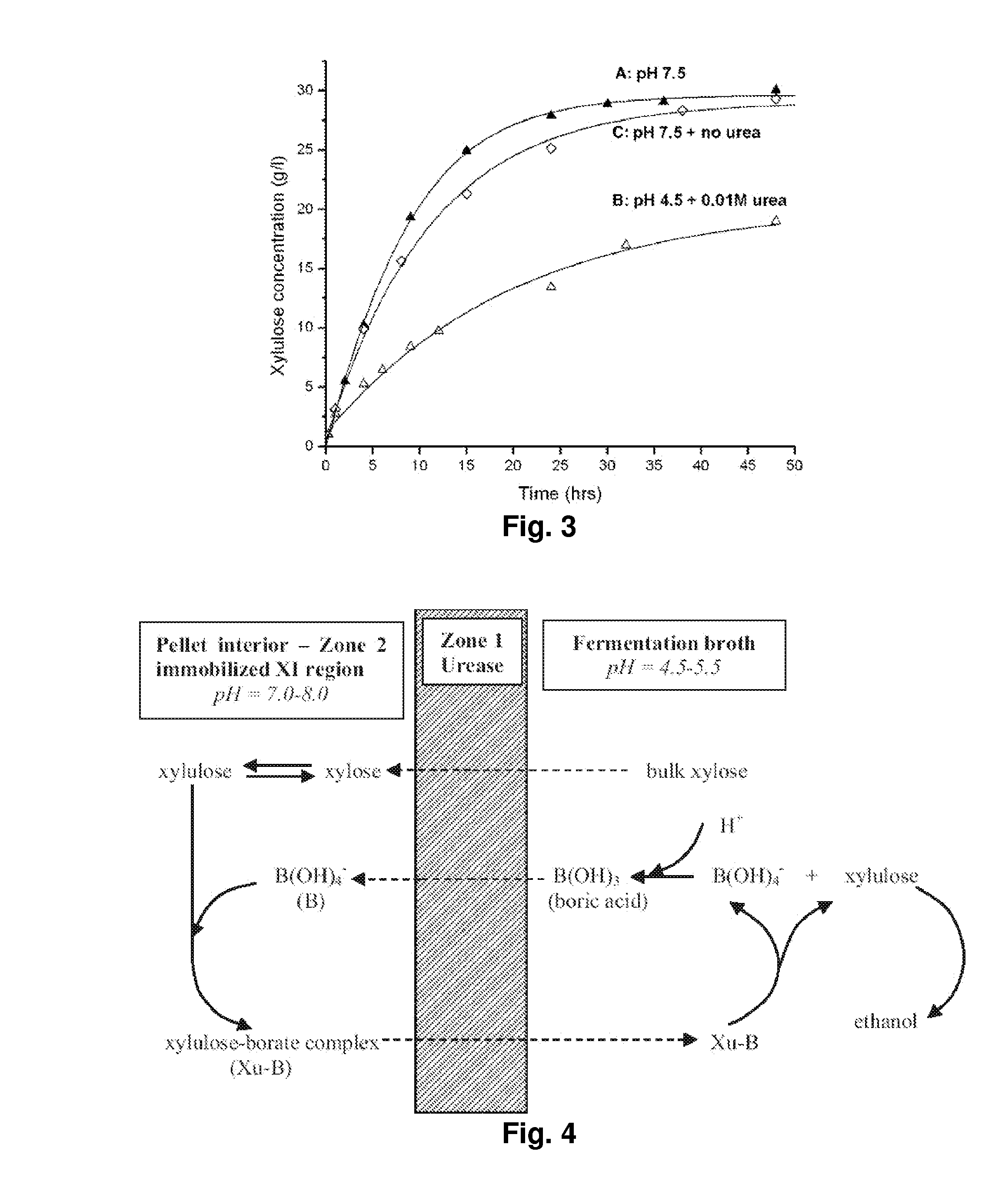
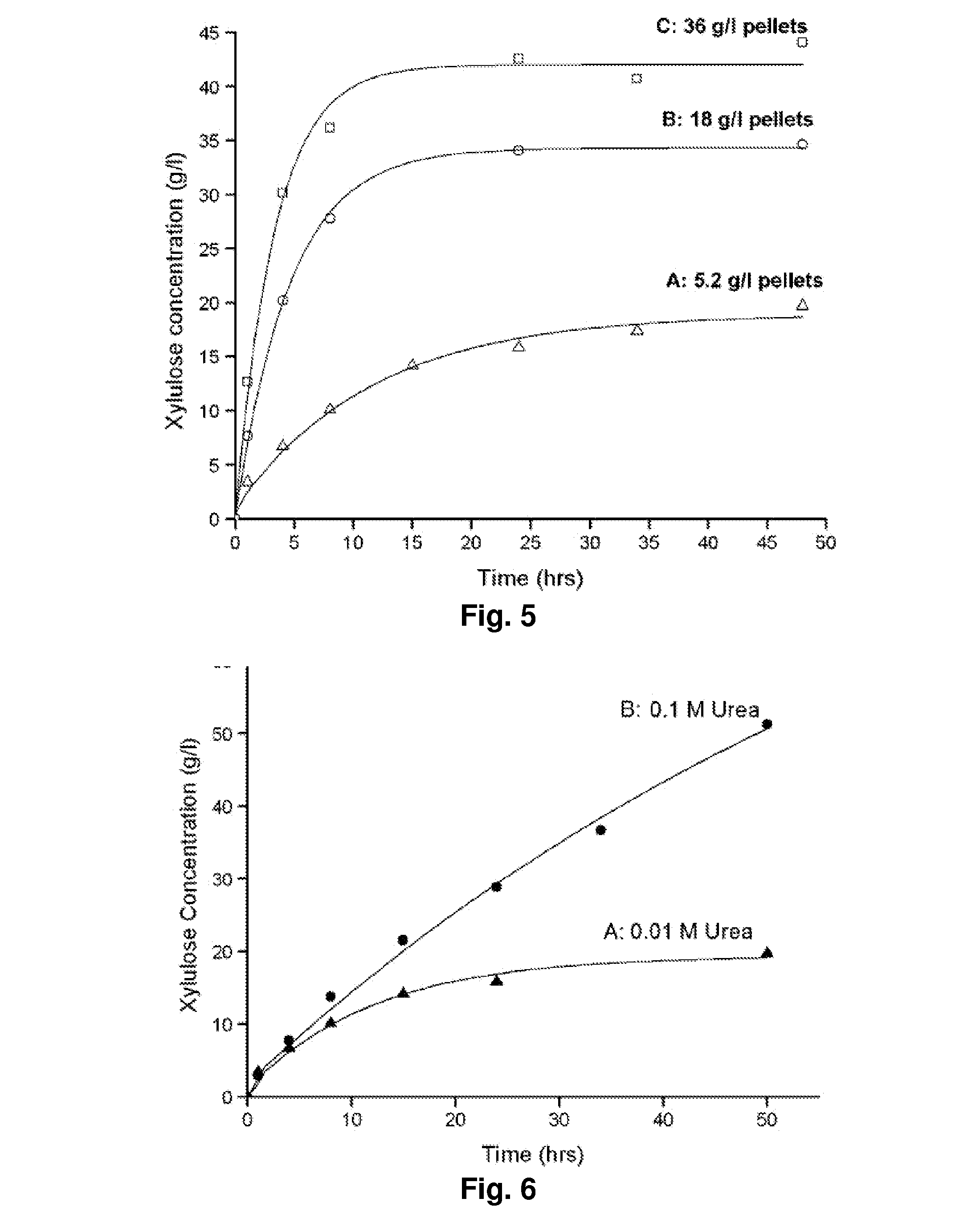
Methods for Fermentation of Xylose and Hexose Sugars
Methods and systems for the isomerization and / or fermentation of xylose and hexose sugars are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Method of detecting an antibody in a liquid sample
InactiveUS6939681B1Risk of interferenceEliminate the problemMagnetic measurementsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemistryImmunological status
The invention relates to a method of evaluating the immunological status of a subject comprising the steps of 1) determining the content of an antibody in a liquid sample from the subject using an immunoassay, wherein the reaction between the antibody of the sample and a ligand in the form of an antigen, an antibody or a hapten, the ligand being directed to the Fab region of the sample antibody, is carried out in the presence of other constituents of the sample to obtain a measurement 1, 2) determining the content of an antibody in the liquid sample using an immunoassay, wherein the reaction between the antibody of the sample and a ligand in the form of an antigen, an antibody or a hapten, the ligand being directed to the Fab region of the sample antibody, is carried out in the absence of other constituents of the sample to obtain a measurement 2, and 3) interrelating measurements 1 and 2 to express the interference and using the interference as a parameter for evaluating the immunological status of the subject.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Method of staggered release or exposure of microorganisms for biological remediation of hydrocarbons and other organic matter
InactiveUS8298425B2Solid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismSoil organic matter
A methodology, and related systems and structures for accomplishing the methodology, of biological remediation of hazardous or undesirable organic matter, wherein a plurality of carrier members are disposed in a localized retaining member, the carrier members releasing or exposing microorganisms to the undesirable organic matter on a staggered basis over an extended period of time, the microorganisms being capable of biologically remediating the undesirable organic matter by utilizing the organic matter as a food source, thereby converting it into environmentally safe bi-products. Carrier members containing nutrients necessary for the survival of the microorganisms and having release times corresponding to the release times of the microorganisms are also provided to insure that the microorganisms remain viable upon release.
Owner:SHAW MARK D
Process for preparing a polymer/biological entities alloy
InactiveUS20140303278A1Promote degradationImpairing mechanical propertyHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierRoom temperatureAlloy
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a polymer / biological entities alloy, comprising a step of mixing a polymer and biological entities that degrade it, during a heat treatment, said heat treatment being performed at a temperature T above room temperature and said biological entities being resistant to said temperature T, characterized in that said biological entities are chosen from enzymes that degrade said polymer and microorganisms that degrade said polymer.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
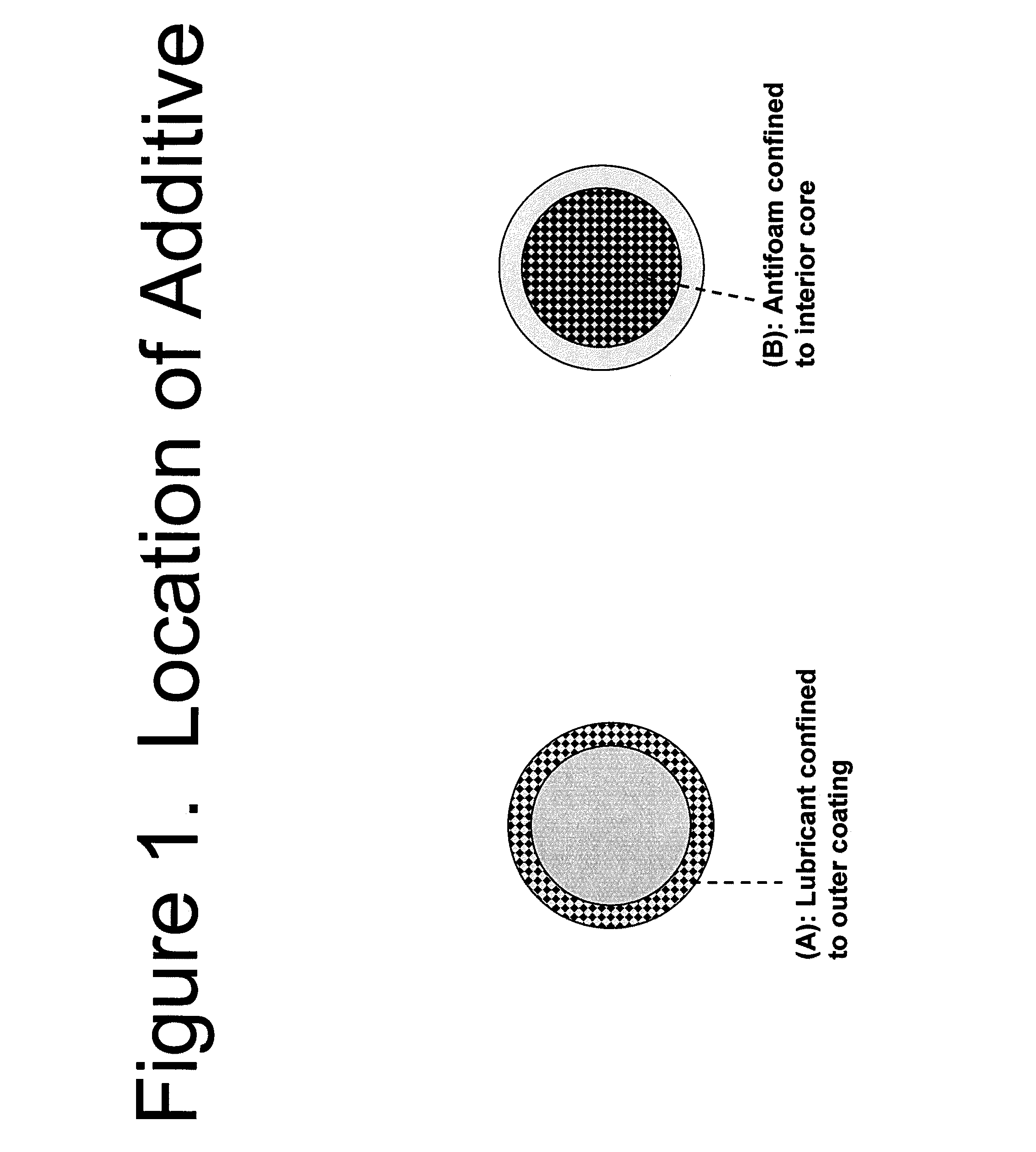
Method for producing granules with reduced dust potential comprising an antifoam agent
InactiveUS8076113B2Reduced dusting potentialProduce some attenuationBiochemical fibre treatmentNon-surface-active detergent compositionsAntifoam agentMaterials science
Owner:DANISCO US INC
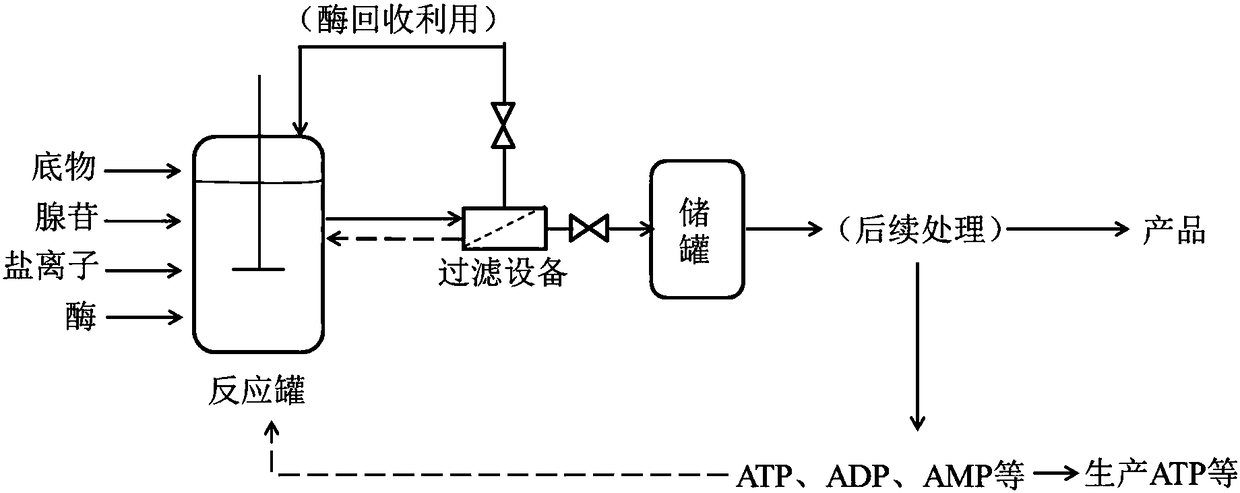
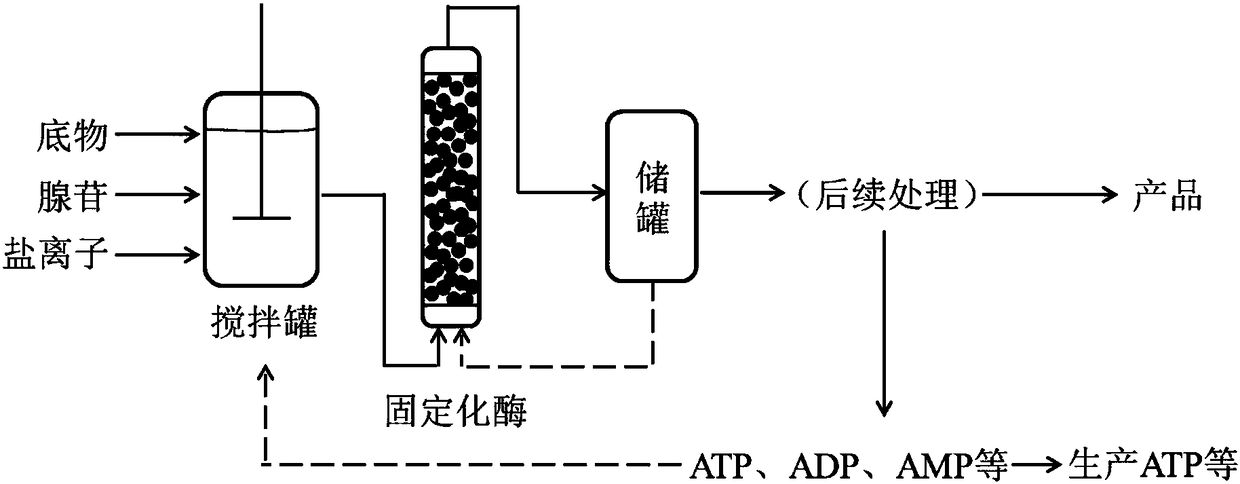
Production method for enzymatic reaction by utilizing adenosine to replace ATP
The invention discloses a production method for enzymatic reaction by utilizing adenosine to replace ATP and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps that (1) in an enzymatic reaction system, ATP regeneration enzyme, AK enzyme and the adenosine are added in proportion for enzymatic reaction; (2) immobilized ATP regeneration enzyme and AK enzyme are directly separated in a reaction tank, and free ATP regeneration enzyme and AK enzyme are subjected to ultrafiltration membrane separation in a filter; (3) percolate in step (2) is separated and purified to obtain a product. Theproduction method for enzymatic reaction by utilizing the adenosine to replace the ATP and the application thereof have the advantages that a large amount of cost is saved for industrial production by utilizing the adenosine to replace the ATP or AMP; a stable enzyme recovery system is established, and the energy conservation and environment protection are achieved; a small quantity of generatedby-products ATP, ADP and AMP are directly used for cyclic reaction, or used for producing the ATP, or purified intensively through filtration, ion exchange and other methods, and the operation is simple.
Owner:BEIJING TIANKAI YIDA BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Penicillium funiculosum mutant strain
The present invention relates to novel micro-organism, Penicillium funiculosum, to new enzymes mixture obtained from it and nucleic acid sequences thereto.
Owner:J P MORGAN EURO
Immobilized enzymes
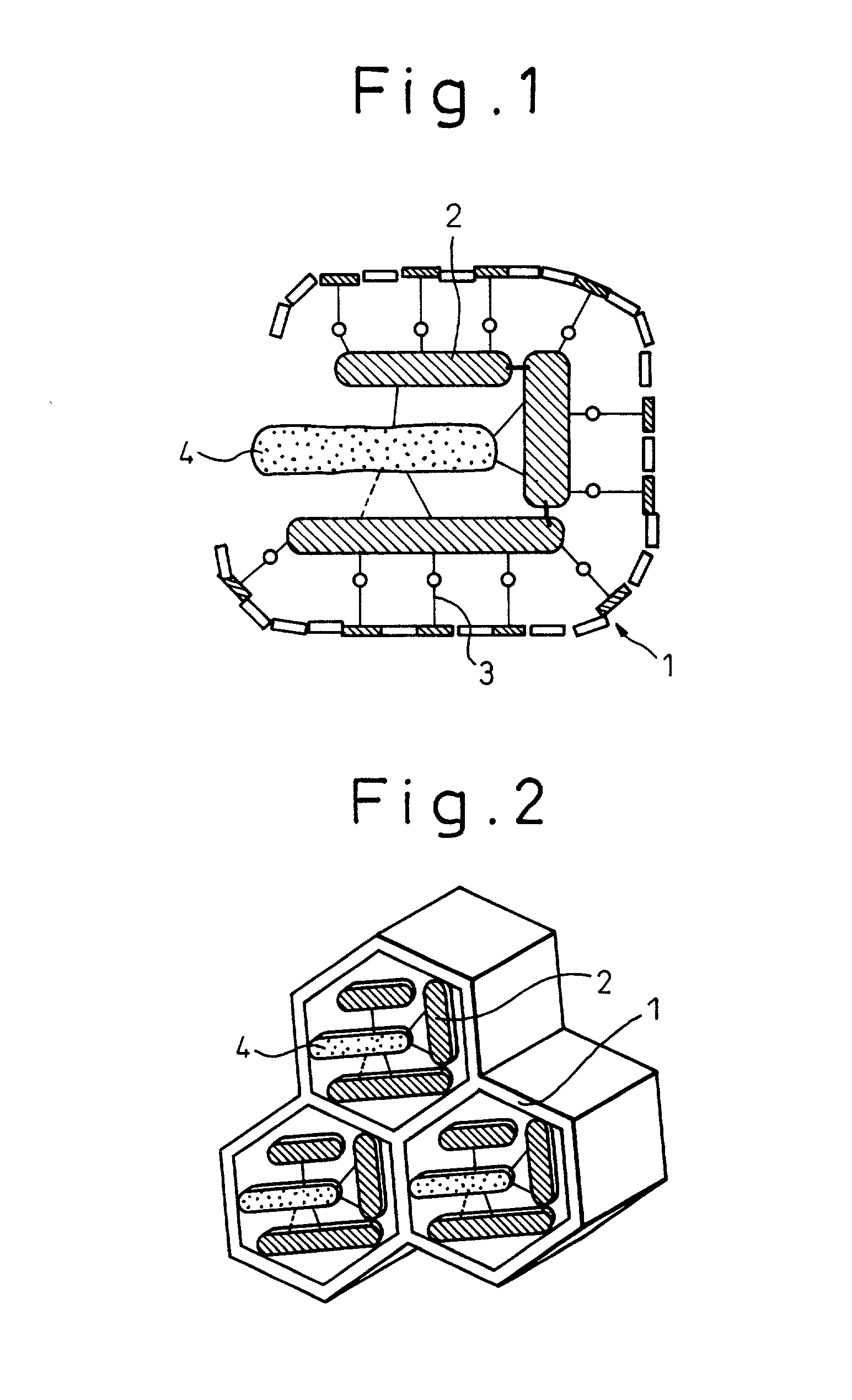
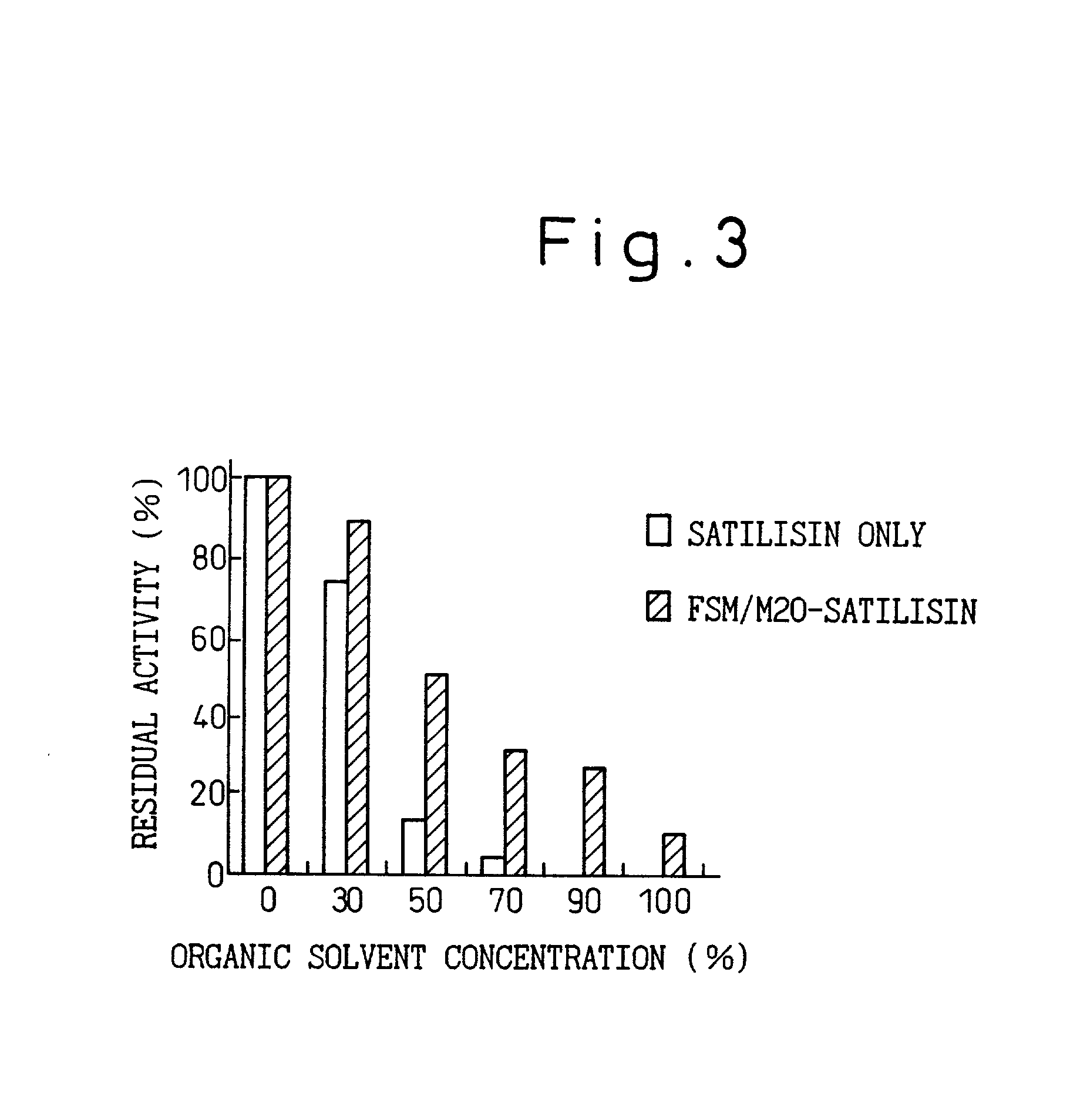
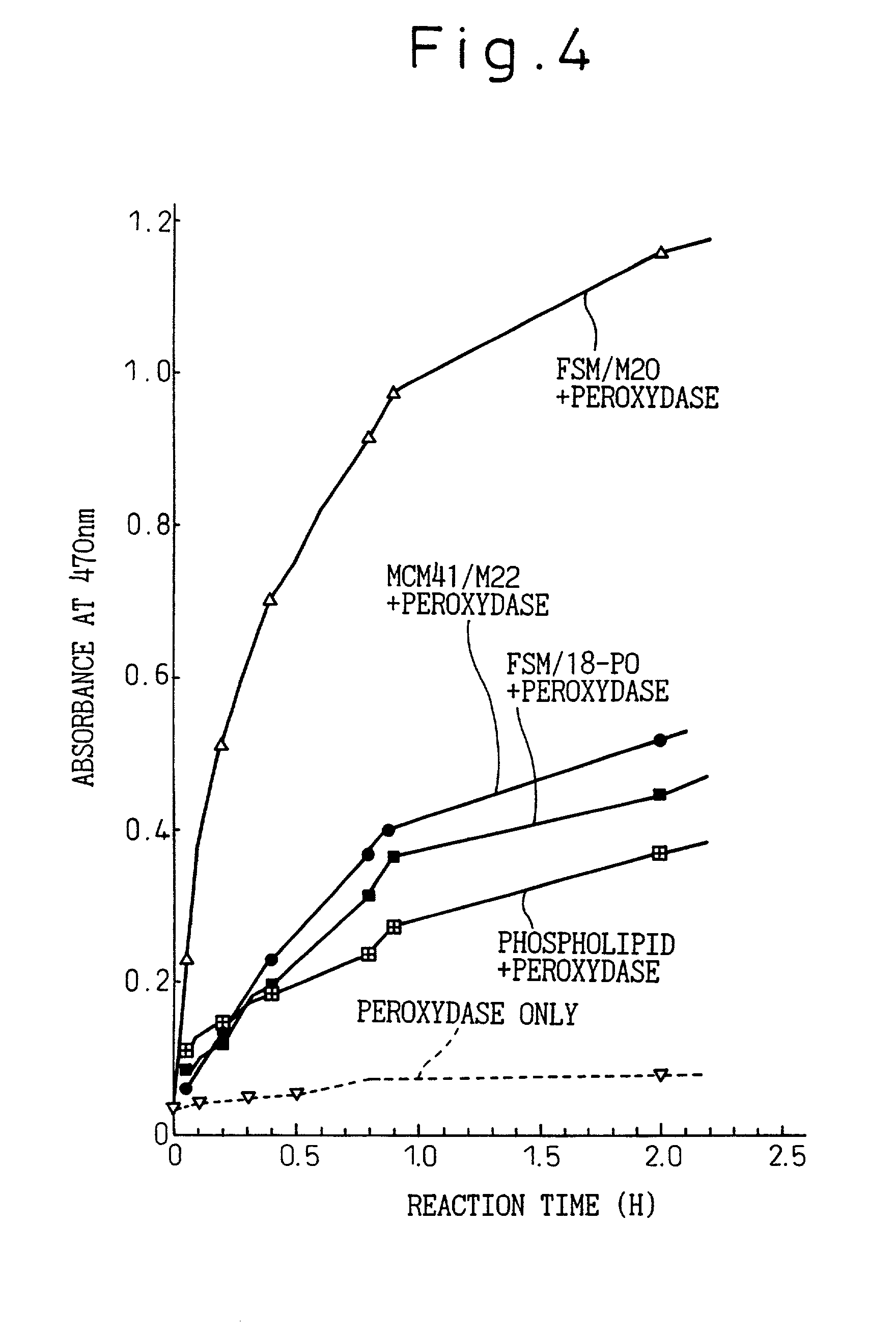
InactiveUS20020015985A1Degree of avoidanceEffectively prevent the stereostructure of the active unitOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierMesoporous silicaSilicon dioxide
The invention features an immobilized enzyme wherein an enzyme or an active unit of the enzyme is immobilized in a structural unit having structural stability; namely, the present invention provides an immobilized enzyme comprising: a structural unit having structural stability; and an enzyme having an active unit, the enzyme, or the active unit being immobilized in the structural unit; in the preferred aspects, the structural unit is a porous substance having homogeneous pores, a pore size (diameter) of the porous substance of the structural unit is almost the same as that of the enzyme to be immobilized or the active unit of the enzyme, and the structural unit comprises a mesoporous silica porous material to be formed via a layered silicate.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Method of detecting an antibody in a liquid sample
InactiveUS6379909B1Risk of interferenceEliminate the problemUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsHaptenImmunological status
The invention relates to a method of evaluating the immunological status of a subject comprising the steps of 1) determining the content of an antibody in a liquid sample from the subject using an immunoassay, wherein the reaction between the antibody of the sample and a ligand in the form of an antigen, an antibody or a hapten, the ligand being directed to the Fab region of the sample antibody, is carried out in the presence of other constituents of the sample to obtain a measurement 1, 2) determining the content of an antibody in the liquid sample using an immunoassay, wherein the reaction between the antibody of the sample and a ligand in the form of an antigen, an antibody or a hapten, the ligand being directed to the Fab region of the sample antibody, is carried out in the absence of other constituents of the sample to obtain a measurement 2, and 3) interrelating measurements 1 and 2 to express the interference and using the interference as a parameter for evaluating the immunological status of the subject.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Enzyme catalyst immobilized on porous fluoropolymer support
Enzyme catalyst immobilized on porous fluoropolymer supports. Catalytically active enzymes can be bound to a variety of fluoropolymer supports for use as a reaction catalyst. Moreover, consistently high rate of conversion during catalyst re-use over time is achieved. Furthermore, inactive enzyme catalyst can be stripped from the support and fresh enzyme can be bound to the support to achieve the original conversion rate. The immobilization of catalytic enzymes on porous fluoropolymers is a viable and novel technology for the preparation of advantaged catalysts.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
DNA sequencing method
InactiveUS20050214849A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyEnzyme bindingFluorophore
The present invention pertains to a method for determining the sequence of a polynucleotide, the method relying on the detection of a conformational change in an enzyme that interacts with and processes along the polynucleotide. The detection of a conformational change may be carried out by measuring changes in a fluorophore bound to the enzyme.
Owner:DENSHAM DANIEL
Hydrolysis of arabinoxylan
The present invention relates to a process for enzymatic hydrolysis of arabinoxylan, and an enzyme composition suitable for use in such a process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Polyamine-polyphenol modified graphene oxide carrier, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111961660AShorten the time of self-assemblyImprove stabilityCarbon compoundsPhosphorus-oxygen lyasesPolyphenolHigh activity
The invention discloses a crosslinking enzyme polymer based on polyamine-polyphenol codeposition, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of immobilized enzyme application. Graphene oxide is dispersed in a buffer solution, and then, polyphenol solution and multi-amido polymer solution are added into the buffer solution so as to react to obtain the polyamine-polyphenol modified graphene oxide. The polyamine-polyphenol modified graphene oxide carrier obtained by the method is used for the immobilized enzyme so as to obtain the crosslinking enzyme polymer. The polyamine-polyphenol modified graphene oxide carrier has the advantages of universality, high activity, simpleness in operation and the like.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
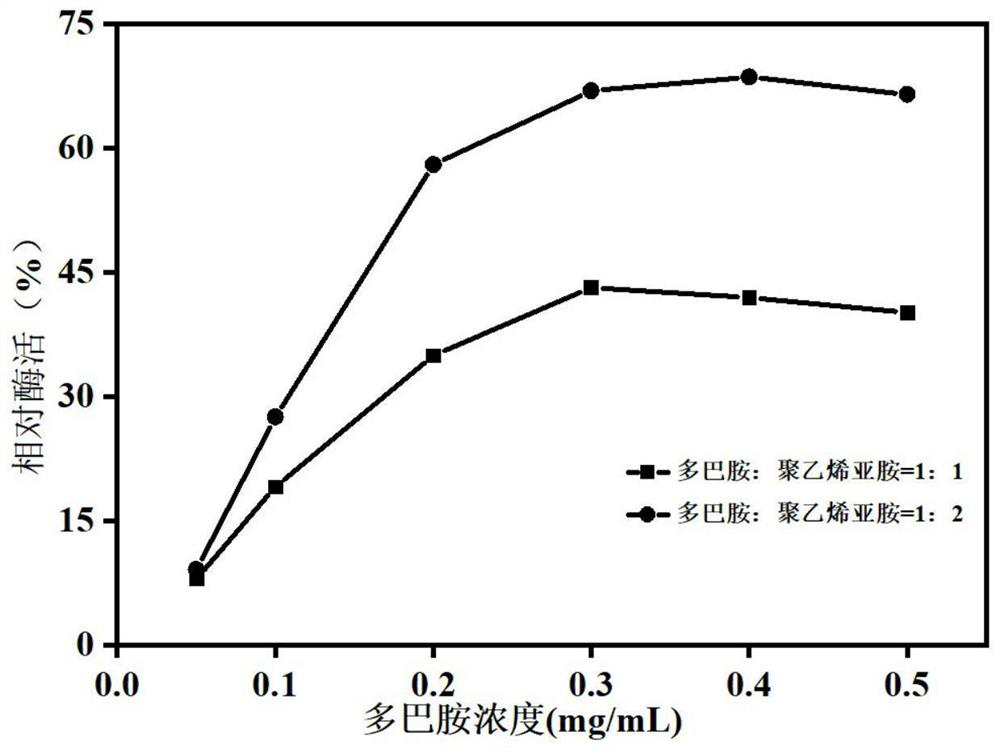
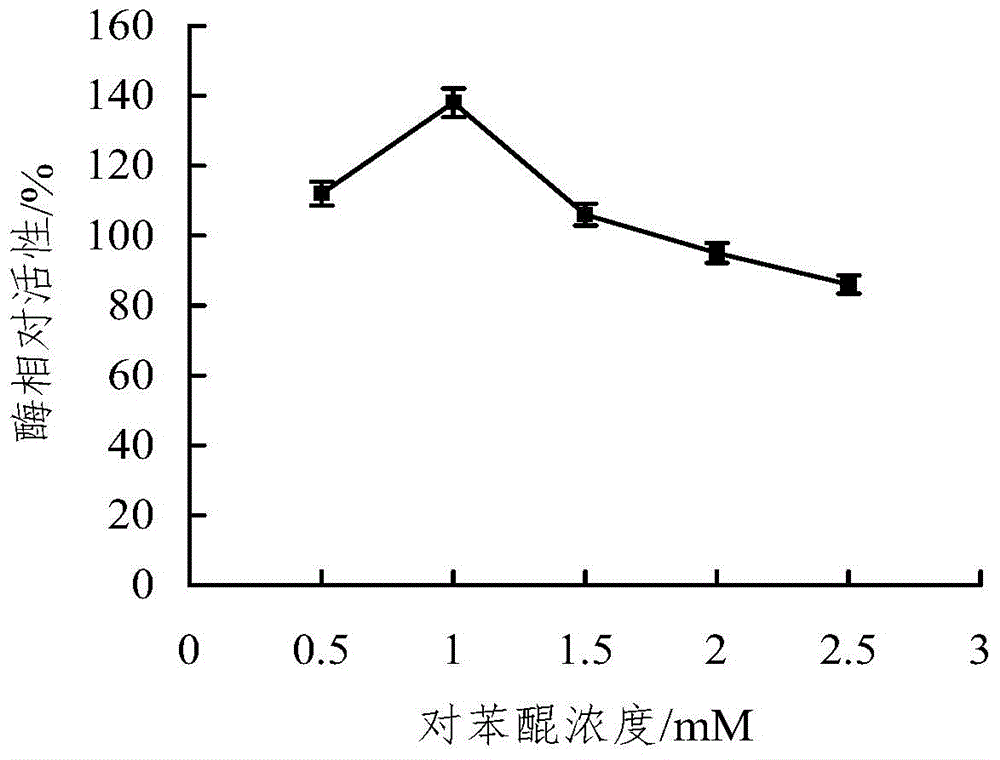
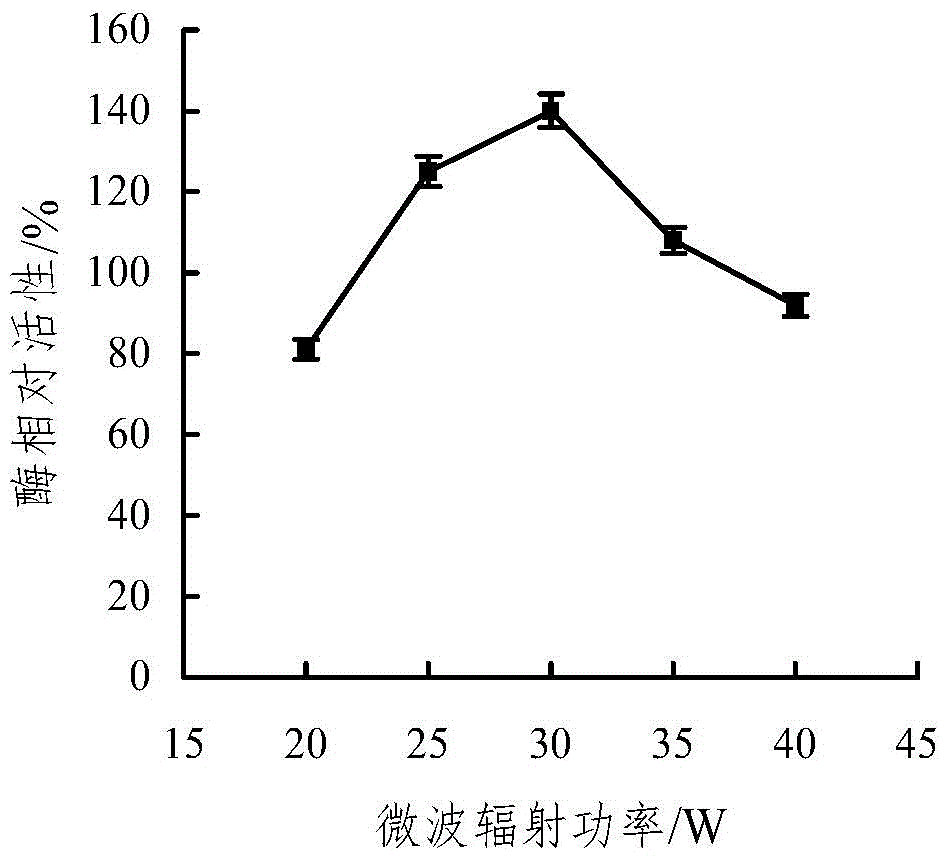
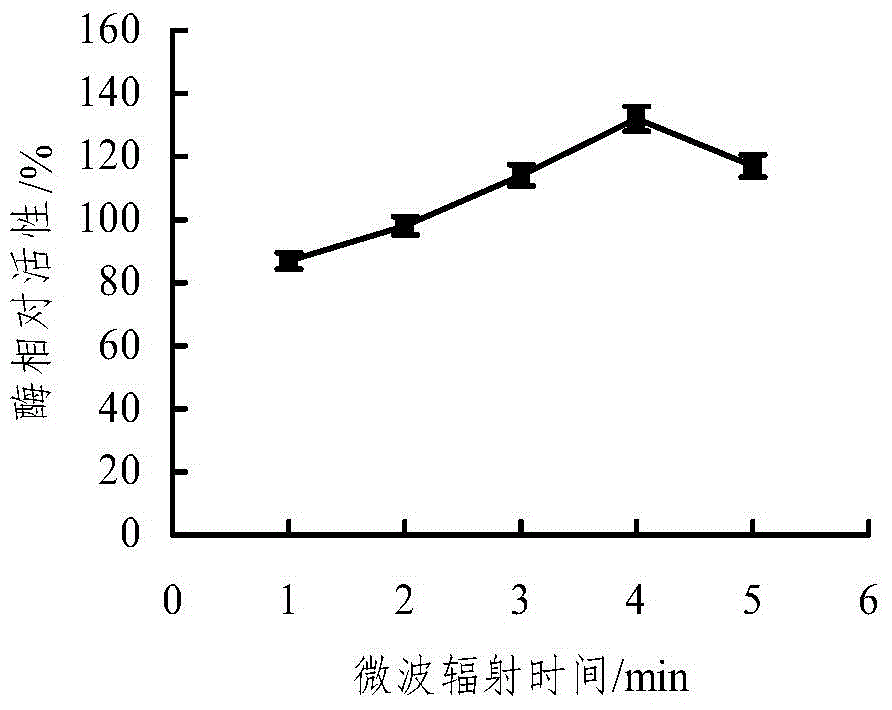
Microwave-assisted co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN104988132AIncrease forceReduce manufacturing costOn/in inorganic carrierMulti-enzyme systemsThermal stabilityGlucose dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a microwave-assisted co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase. The method includes the steps that a carrier and a crosslinking agent are mixed and activated, centrifuging is conduced, sediments are taken and washed through a PBS solution, centrifuging is conducted, and the sediments are re-dispersed in the PBS solution; the aldehyde ketone reductase and the glucose dehydrogenase are added to a dispersed solution, the mixed liquid is irradiated at the temperature of 0 DEG C to 10 DEG C under the 20-45 W microwave condition for 1 min to 5 min, centrifuging is conducted, sediments are taken and washed through the PBS solution, and co-immobilized enzyme is obtained; compared with free enzyme, the catalytic activity, heat stability and PH stability of the co-immobilized enzyme prepared through the method are improved; the glucose dehydrogenase serves as a coenzyme regeneration system of the glucose dehydrogenase to provide NAD(P)H required by a reaction, the cost is lowered, and industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Embedding and co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN104988133AHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityOn/in organic carrierMulti-enzyme systemsFiltrationRefrigerated temperature
The invention discloses an embedding and co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase. The method includes the steps that the aldehyde ketone reductase and the glucose dehydrogenase are mixed and then added to a sodium alginate aqueous solution to be stirred and mixed evenly, then the mixture is dropwise added to a Cacl2 aqueous solution, the mixture is made to stand in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C, washing is conducted through distilled water, vacuum filtration is conducted, and immobilized particles are obtained. Compared with free aldehyde ketone reductase, the catalytic activity of the co-immobilized enzyme prepared through the method is increased by 1.32 times, the heat stability, the PH stability and other performance of the co-immobilized enzyme prepared through the method are improved as well, and meanwhile, the cost is lowered due to reuse of the co-immobilized enzyme.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
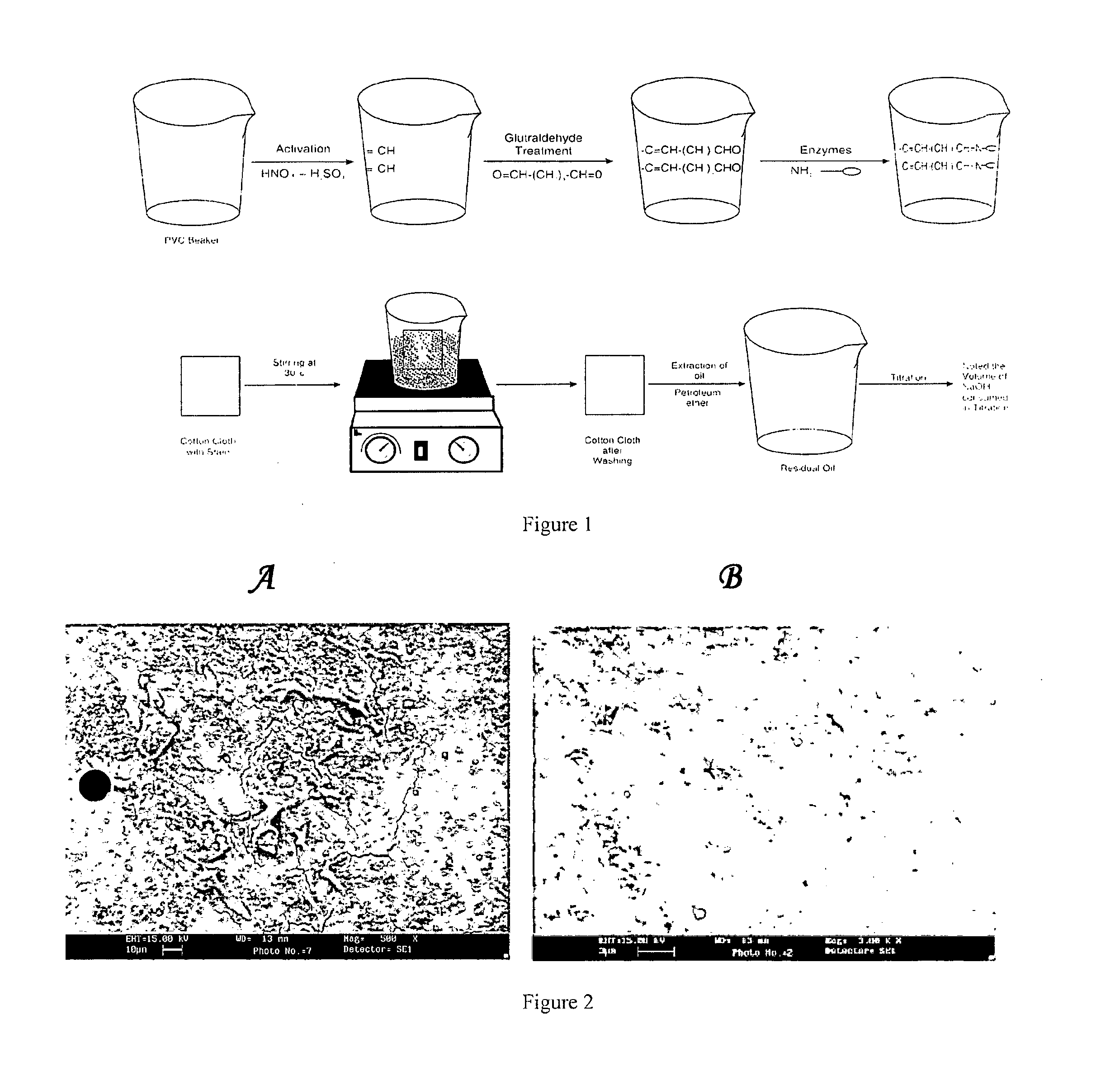
Polyvinyl chloride surface co-immobilized with enzymes and uses thereof
A PVC surface co-immobilized with the multiple enzymes for removal of stains useful in the field of washing or cleaning cloth and other household textile such as towels and sheets. The present invention also provides a process of preparation of the PVC surfaces and using such PVC surface. The PVC surface co-immobilized with the enzymes is useful as cheap and reusable alternative for washing of cloths.
Owner:MAHARSHI DAYANAND UNIV
Method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by double immobilized multi-enzyme systems
InactiveCN102517351AImprove recycling ratesImprove regeneration efficiencyChemical industryFermentationEnzyme systemOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by double immobilized multi-enzyme systems. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps that 1, threonine dehydrogenase and leucine dehydrogenase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized multi-enzyme system is obtained; and 2, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized coenzyme regeneration system is obtained. The method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by the double immobilized multi-enzyme systems utilizes dissolution reversibility of co-immobilized enzymes, realizes effective separation of the co-immobilized enzymes and products, improves accessibility between the co-immobilized enzymes and reactants, improves recovery and utilization rates of threonine dehydrogenase, leucine dehydrogenase, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase, improves coenzyme regeneration efficiency, reduces follow-up separation purification processes, simplifies a process flow and reduces a production cost.
Owner:李鑫
Nanofiber biological membrane immobilized bi-enzyme system and trehalose catalytic synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN105838704AImprove conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencyBacteriaChemical industryAmylaseEnzyme system
The invention provides a nanofiber biological membrane immobilized bi-enzyme system and a trehalose catalytic synthesis method thereof. A starchiness nanofiber biological membrane is arranged on the surface of an escherichia coli cell generating high-temperature-resistant trehalose synthase through fermentation, polypeptide tag SpyTag-SpyCatcher capable of gene coding is used for specificity covalent binding and efficient immobilization recombination of beta-amylase, a trehalose synthase-beta amylase bi-enzyme catalytic system is constructed autonomously, and finally extracellular and intracellular two-step catalysis is conducted continuously. The immobilization efficiency of beta-amylase can reach 50-62%, maltose is generated by 20-25wt% of soluble starch under catalysis of beta-amylase on the extracellular biological membrane, enters the cell and reacts with trehalose synthase to generate trehalose, and the conversion rate of starch can reach 45-55% after the immobilized cell is reused for 10-16 times.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com