Method for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose by waste paper serving as raw material
A technology of carboxymethyl cellulose and cellulose, applied in the field of preparing carboxymethyl cellulose, can solve the problems of low level of waste paper recycling and environmental pollution, achieve high recycling rate, reduce costs, and overcome complex post-processing Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
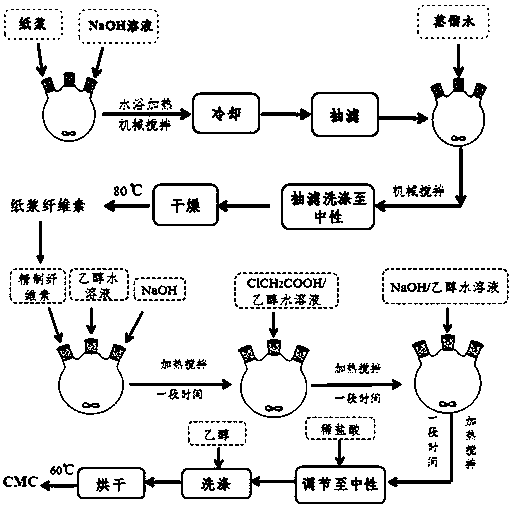
[0033] Weigh 6g of dried pulp and place it in a 250ml three-necked flask, add 200mL of 12% concentration NaOH solution into the three-necked flask, and react with mechanical stirring at 100°C for 1h. After the reaction was finished and cooled, the reaction mixture was transferred to a G2 sand core funnel for suction filtration. Subsequently, the sample after suction filtration was transferred to a three-necked flask again, added with distilled water for mechanical stirring, filtered and washed to neutrality, and dried at 80° C. to obtain refined pulp cellulose. The microscopic morphology of the waste paper fiber surface before and after alkali treatment is as follows: Figure 2a and Figure 2b As shown, the X-ray diffraction curve of refined pulp cellulose is as follows Figure 5 As shown in the middle curve a, the thermogravimetric curve is as Figure 6 Shown in curve a.
[0034] In a 250mL three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirring device, add 5g of refined was...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Weigh 6g of dried pulp and place it in a 250ml three-necked flask, add 200mL of 12% concentration NaOH solution into the three-necked flask, and react with mechanical stirring at 100°C for 1h. After the reaction was finished and cooled, the reaction mixture was transferred to a G2 sand core funnel for suction filtration. Subsequently, the sample after suction filtration was transferred to a three-necked flask again, added with distilled water for mechanical stirring, filtered and washed to neutrality, and dried at 80° C. to obtain refined pulp cellulose. The microscopic morphology of the waste paper fiber surface before and after alkali treatment is as follows: Figure 2a and Figure 2b As shown, the X-ray diffraction curve of refined pulp cellulose is as follows Figure 5 As shown in the middle curve a, the thermogravimetric curve is as Figure 6 Shown in curve a.
[0037]In a 250mL three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirring device, add 5g of refined wast...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Weigh 6g of dried pulp and place it in a 250ml three-necked flask, add 200mL of 12% concentration NaOH solution into the three-necked flask, and react with mechanical stirring at 100°C for 1h. After the reaction was finished and cooled, the reaction mixture was transferred to a G2 sand core funnel for suction filtration. Subsequently, the sample after suction filtration was transferred to a three-necked flask again, added with distilled water for mechanical stirring, filtered and washed to neutrality, and dried at 80° C. to obtain refined pulp cellulose. The microscopic morphology of waste paper fiber surface before and after alkali treatment is shown in Fig. 2, and the X-ray diffraction curve of refined pulp cellulose is shown in Fig. Figure 5 As shown in the middle curve a, the thermogravimetric curve is as Figure 6 Shown in curve a.
[0040] In a 250mL three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirring device, add 5g of refined waste paper cellulose and 100mL o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| free rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com