Use of molybdenum disulfide for stem cell proliferation and/or differentiation, substrate for stem cell proliferation and/or differentiation and preparation method and use thereof
A technology of stem cell proliferation and molybdenum disulfide, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve the problems of unadjustable electrical conductivity, lack of regulation of stem cell proliferation and differentiation, and poor convenience of graphene biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The preparation method of the molybdenum disulfide thin film, the characteristics of the molybdenum disulfide thin film and the selection of stem cells have been specifically introduced above, and the present invention will not repeat them here.
[0039] According to the present invention, the substrate used for the above molybdenum disulfide thin film can be various substrates known in the art for cell culture, for example, a glass substrate or a polymer film substrate. The polymer membrane can be selected in a wide range, as long as the selected membrane does not decompose at a temperature not higher than 180°C, has good biocompatibility with cells and is non-toxic to cells. Just poison. Examples of the polymer film include, but are not limited to, polyvinylidene fluoride films.
[0040]The inventors of the present invention have found that when the substrate is a flexible polymer film substrate for the cultivation of stem cells, after the cells are inoculated and th...
Embodiment 1
[0053] This embodiment is used to illustrate the substrate for stem cell proliferation and / or differentiation provided by the present invention
[0054] (1) First weigh 30 mg of sodium molybdate powder and 60 mg of thiourea powder, and dissolve them in 20 ml of deionized water. After the two powders are fully dissolved, pour the mixture into a 25ml Teflon reaction kettle. Cut the glass into 20mm x 30mm size, soak it in the reaction kettle, and react at 180°C for 24 hours.
[0055] (2) The glass synthesized in step (1) with attached molybdenum disulfide was ultrasonically treated at a frequency of 55 Hz and a temperature of 25° C. for 10 min. After treatment, the molybdenum disulfide film layer can be firmly attached to the glass surface as a substrate for cell culture.
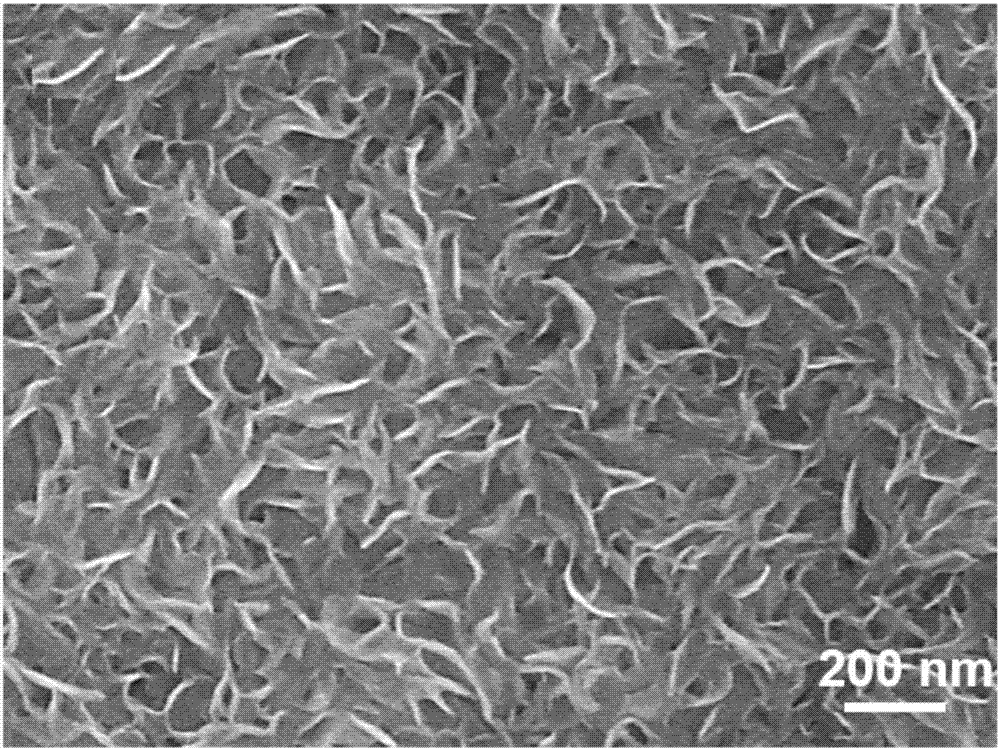
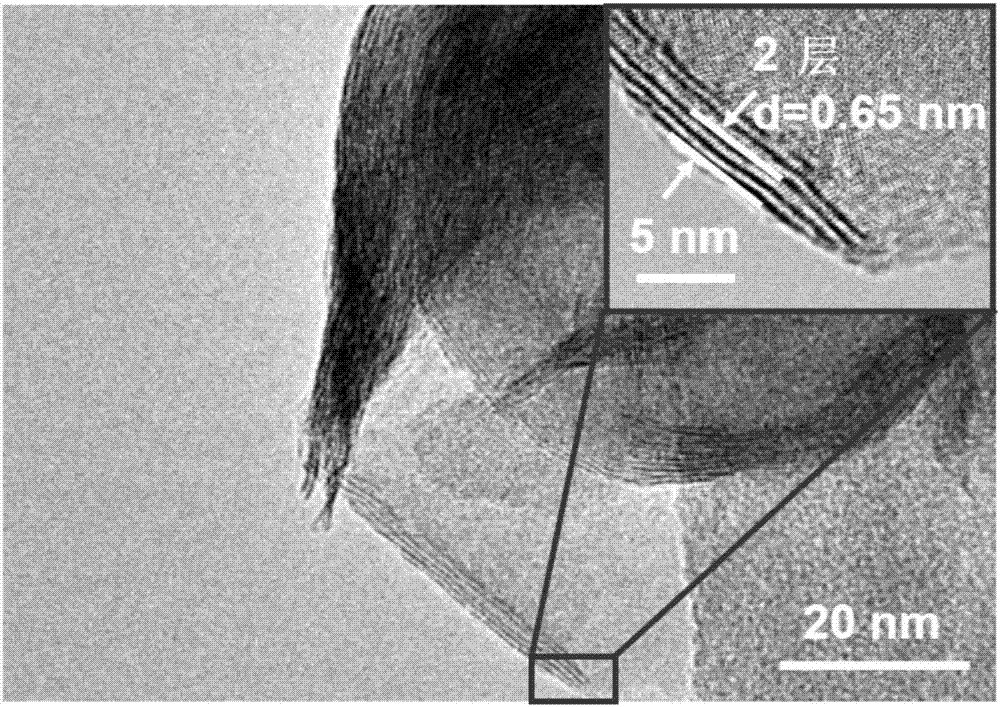
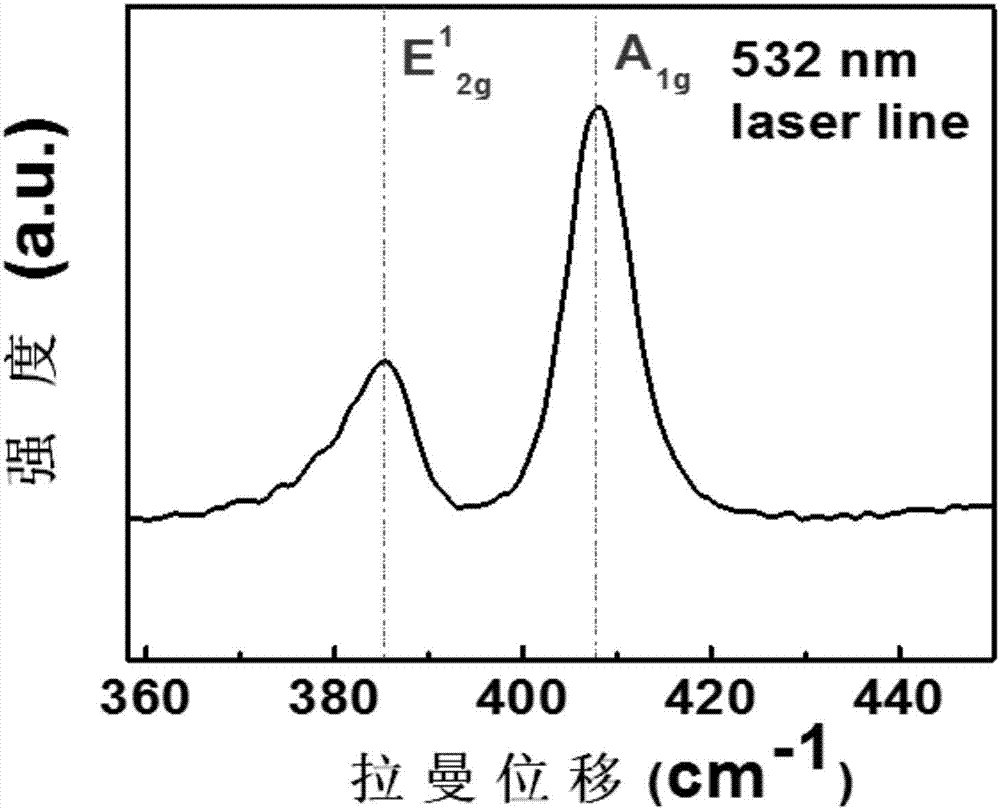
[0056] The thickness of the molybdenum disulfide thin film is 300nm. After the substrate was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, it can be seen that the hydrothermally synthesized molybdenum disu...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment is used to illustrate the substrate for stem cell proliferation and / or differentiation provided by the present invention
[0059] (1) First weigh 25mg of sodium molybdate powder and 50mg of thiourea powder, and dissolve them in 20ml of deionized water. After the two powders are fully dissolved, pour the mixture into a 25ml Teflon reaction kettle. Cut the polyvinylidene fluoride film into a size of 20mm x 30mm, soak it in a reaction kettle, and react at 200°C for 24 hours.
[0060] (2) The polyvinylidene fluoride film attached with molybdenum disulfide synthesized in step (1) was ultrasonically treated at a frequency of 50 Hz and a temperature of 28° C. for 10 min. After treatment, the thin layer of molybdenum disulfide can be firmly attached to the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane as a substrate for cell culture. The substrate structure is as follows: Figure 12 shown.
[0061] The thickness of the molybdenum disulfide thin film is 500nm. A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com