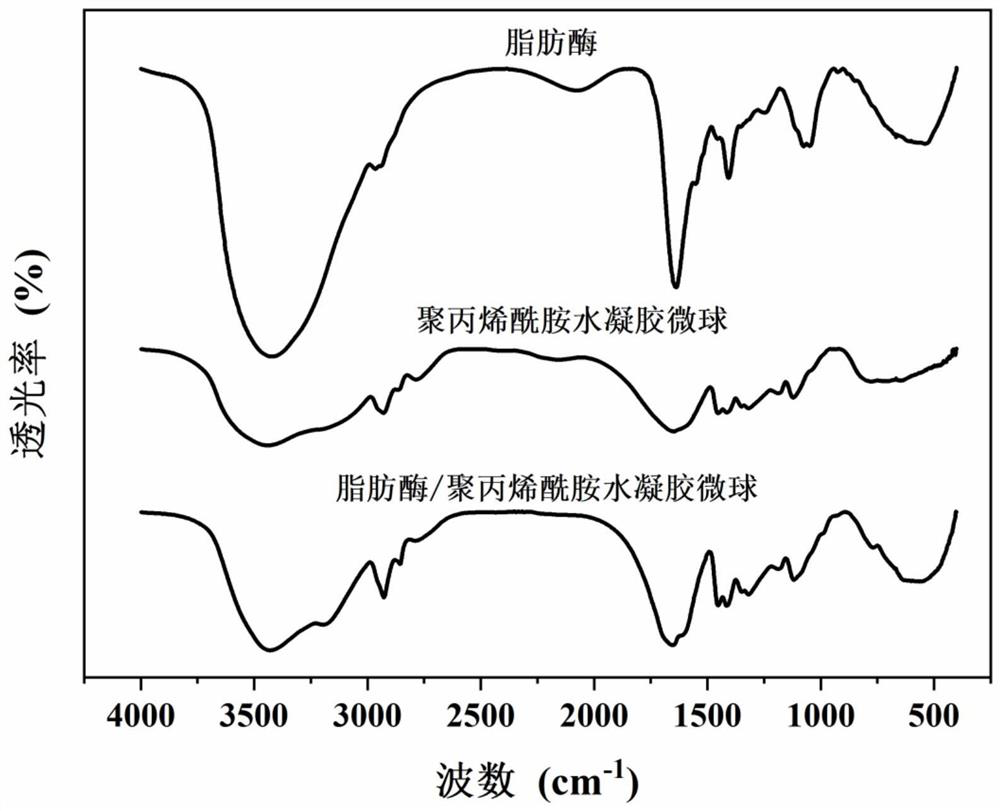
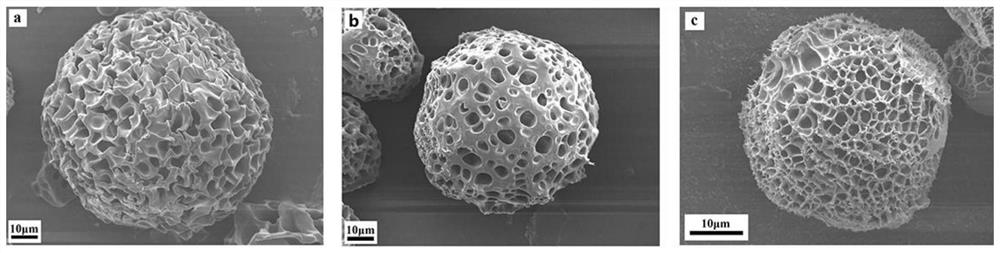
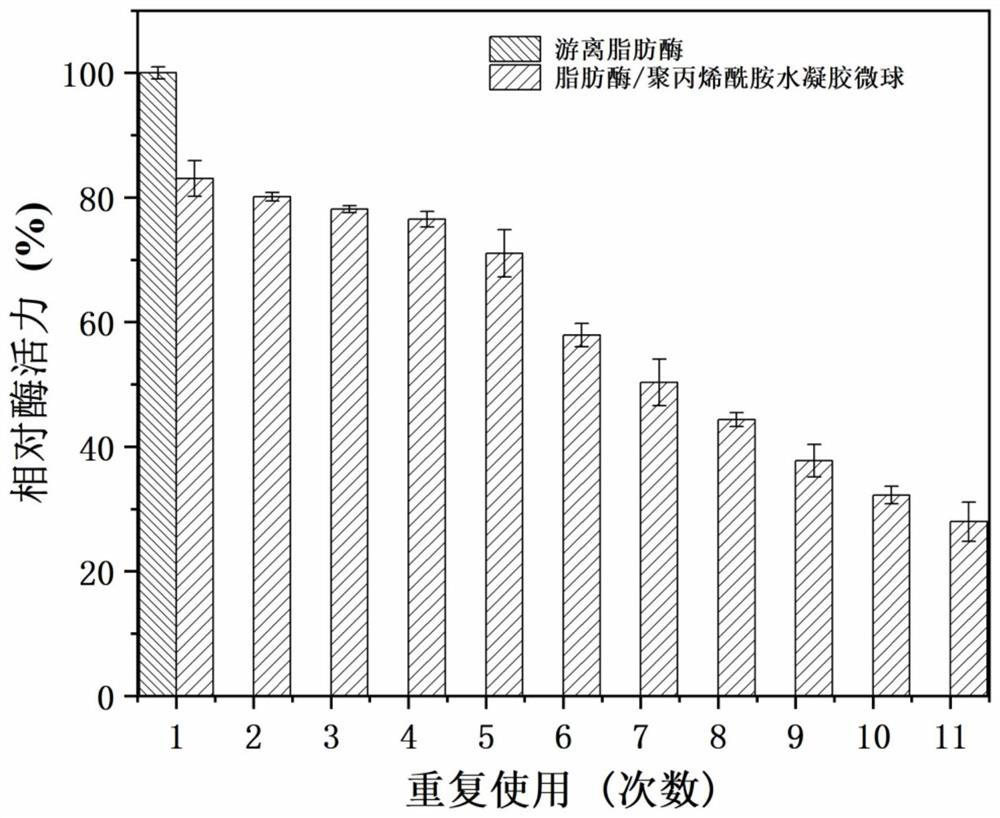
Lipase/polyacrylamide aquagel microsphere catalytic material, preparation method therefor and application of lipase/polyacrylamide aquagel microsphere catalytic material
A technology of polyacrylamide and hydrogel microspheres, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, hydrolytic enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the mass transfer resistance between enzymes and substrates, and achieve low cost, short time consumption, Does not reduce the effect of enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] (1) Add acrylamide (12g, 168.82mmol), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (0.12g, 0.78mmol), 0.18g polyvinylpyrrolidone into 40mL of purified water, stir mechanically at 65°C until dissolved , as the aqueous phase;
[0051] (2) Add 8 g of compound emulsifier (Span 80: Tween 80 = 1: 0.3) into 120 mL of cyclohexane, stir mechanically at 65°C until fully mixed, and use it as the organic phase;
[0052] (3) The organic phase and the water phase are mixed, and the reactor is stirred at 500 rpm for 30 min at 65° C. and feeds nitrogen gas to remove oxygen in the solution to prepare a water-in-oil emulsion, add ammonium persulfate (0.12 g, 0.08%), and Inverse emulsion polymerization was carried out at 70°C for 2 hours, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 350rpm during the polymerization;
[0053] (4) After the reaction, thoroughly wash the prepared polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres with ethanol and water successively to remove unreacted monomers;
[0054] (5) Weig...
Embodiment 2
[0056] (1) Add acrylamide (12g, 168.82mmol), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (0.12g, 0.78mmol), 0.18g polyvinylpyrrolidone into 40mL of purified water, stir mechanically at 65°C until dissolved , as the aqueous phase;
[0057] (2) Add 9 g of compound emulsifier (Span 80: Tween 80 = 1: 0.3) into 120 mL of cyclohexane, stir mechanically at 65°C until fully mixed, and use it as the organic phase;
[0058] (3) The organic phase and the water phase are mixed, and the reactor is stirred at 500 rpm for 30 min at 65° C. and feeds nitrogen gas to remove oxygen in the solution to prepare a water-in-oil emulsion, add ammonium persulfate (0.12 g, 0.08%), and Inverse emulsion polymerization was carried out at 70°C for 2 hours, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 350rpm during the polymerization;
[0059] (4) After the reaction, thoroughly wash the prepared polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres with ethanol and water successively to remove unreacted monomers;
[0060] (5) Weig...
Embodiment 3
[0062] (1) Add acrylamide (12g, 168.82mmol), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (0.12g, 0.78mmol), 0.18g polyvinylpyrrolidone into 40mL of purified water, stir mechanically at 65°C until dissolved , as the aqueous phase;
[0063] (2) Add 10 g of compound emulsifier (Span 80: Tween 80 = 1: 0.3) into 120 mL of cyclohexane, mechanically stir at 65°C until fully mixed, and use it as the organic phase;
[0064] (3) The organic phase and the water phase are mixed, and the reactor is stirred at 500 rpm for 30 min at 65° C. and feeds nitrogen gas to remove oxygen in the solution to prepare a water-in-oil emulsion, add ammonium persulfate (0.12 g, 0.08%), and Inverse emulsion polymerization was carried out at 70°C for 2 hours, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 350rpm during the polymerization;
[0065] (4) After the reaction, thoroughly wash the prepared polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres with ethanol and water successively to remove unreacted monomers;
[0066] (5) Wei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com