A method for synchronously removing iron and vanadium from trivalent chromium acid solution
A technology of acidic solution and trivalent chromium, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as complex process and low removal efficiency, and achieve the effect of shortening the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
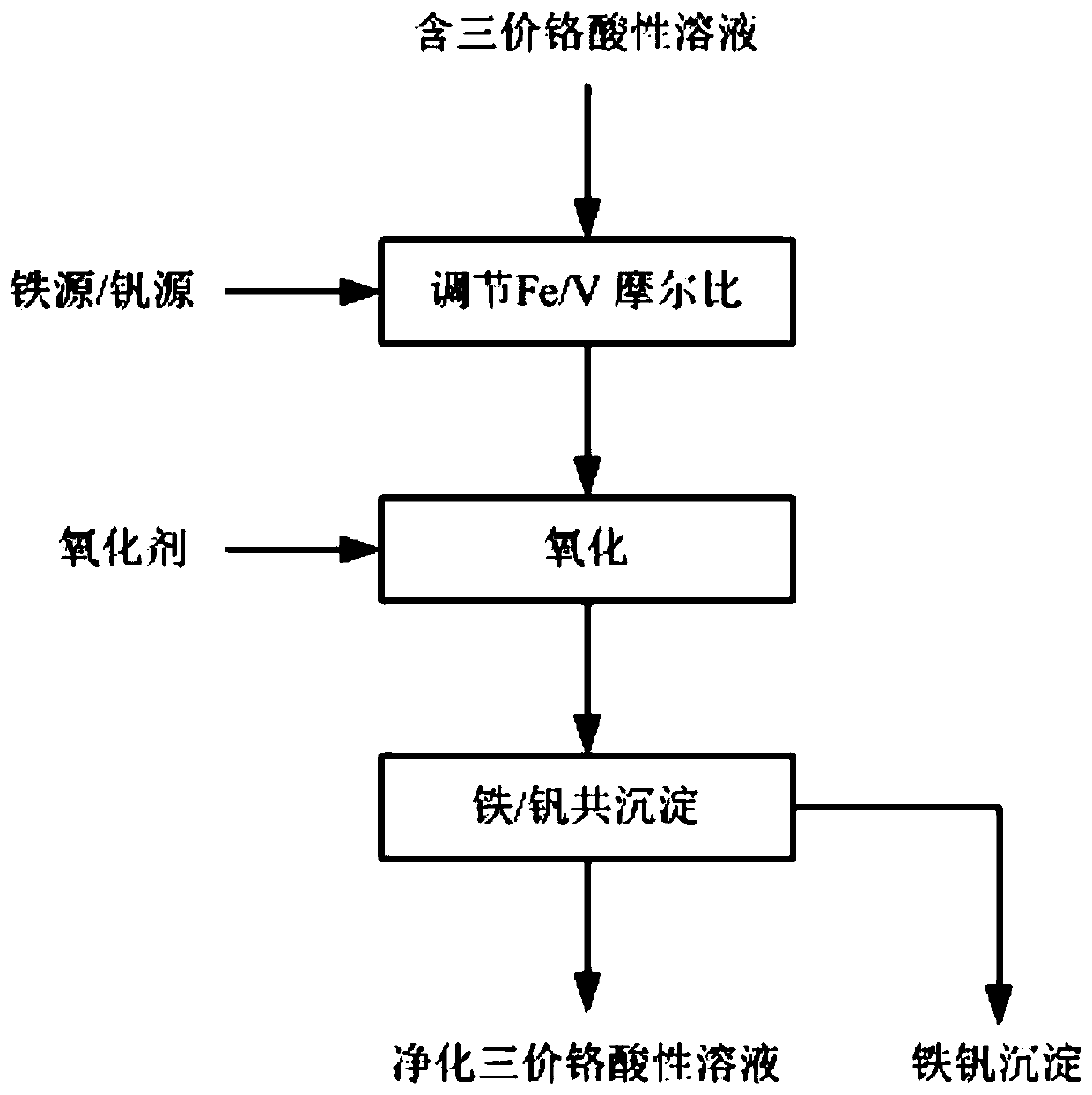
[0026] This embodiment provides a method for synchronously removing iron and vanadium from trivalent chromium acidic solution, said method comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) Add ferrous sulfate to the trivalent chromium acid solution with low iron and high vanadium (molar concentration) to adjust the molar ratio of iron to vanadium to 1:1, and adjust the pH of the solution to 1.2;
[0028] (2) Add hydrogen peroxide to the trivalent chromium acidic solution, iron and vanadium are oxidized to trivalent and pentavalent states respectively, and chromium keeps trivalent unchanged;
[0029] (3) Add ferric vanadate to react at 60 ℃ as crystallization inducer in the solution after oxidation, realize the co-precipitation of iron and vanadium; Iron, vanadium precipitation rate is greater than 90%, and iron concentration in the solution after precipitation is less than 0.2g / L, the concentration of vanadium is less than 0.15g / L.
Embodiment 2
[0031] This embodiment provides a method for synchronously removing iron and vanadium from trivalent chromium acidic solution, said method comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Add ferric sulfate to the trivalent chromium acid solution with low iron and high vanadium (molar concentration) to adjust the molar ratio of iron to vanadium to 1:1, and adjust the pH of the solution to 1.2;
[0033] (2) sodium hypochlorite is added in trivalent chromium acidic solution, iron and vanadium are oxidized to trivalent and pentavalent states respectively, and chromium keeps trivalent unchanged;
[0034] (3) Add ferric vanadate to react at 80 ℃ as crystallization inducer in the solution after oxidation, realize the co-precipitation of iron and vanadium; Iron, vanadium precipitation rate is greater than 90%, and iron concentration in the solution after precipitation is less than 0.2g / L, the concentration of vanadium is less than 0.15g / L.
Embodiment 3
[0036] This embodiment provides a method for synchronously removing iron and vanadium from trivalent chromium acidic solution, said method comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) Add ferric chloride to the trivalent chromium acid solution with low iron and high vanadium (molar concentration) to adjust the molar ratio of iron to vanadium to 1:1, and adjust the pH of the solution to 2.5;
[0038] (2) sodium chlorate is added in trivalent chromium acid solution, iron and vanadium are oxidized to trivalent and pentavalent states respectively, and chromium keeps trivalent unchanged;
[0039] (3) Add ferric hydroxide to the oxidized solution as a crystallization inducer to react at 60°C to realize co-precipitation of iron and vanadium; the precipitation rate of iron and vanadium is greater than 90%, and the concentration of iron in the solution after precipitation is less than 0.2g / L, the concentration of vanadium is less than 0.15g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com