Method for preparing non-woven fabrics using coal direct liquefaction residue-based asphaltenes
A technology of liquefying residue and base asphaltene, which is applied in spinning solution preparation, non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of carbon nano-fiber non-woven fabrics that have not been reported, and achieve the expansion of high value-added application range, The effect of simplifying the preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
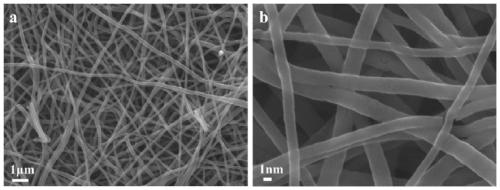
[0025] Grinding the obtained coal direct liquefaction residue into 100-300 mesh powder, and sequentially extracting the coal direct liquefaction residue with n-hexane and tetrahydrofuran to obtain the coal liquefaction residue n-hexane insoluble matter-tetrahydrofuran soluble matter solid (ie asphaltenes); Recorded as AP. Dissolve 1g AP in 5g tetrahydrofuran solution, and record it as solution A; dissolve 1g polyacrylonitrile in 15g N-N, dimethylformamide solution, record it as solution B; mix the above two solutions of A and B, and magnetically stir After 1 h, the spinning dope was obtained. The obtained spinning stock solution is spun by an electrospinning machine, the spinning voltage is 6Kv, the ambient humidity is 30%, the receiving distance is 5cm, and the propulsion speed is 0.5ml / h to obtain a nascent nonwoven fabric. After the initial pre-oxidation of the obtained nascent non-woven fabric in 5wt% nitric acid solution for 0.5h, it was washed to neutral and dried; unde...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Grinding the obtained coal direct liquefaction residue into 100-300 mesh powder, and sequentially extracting the coal direct liquefaction residue with n-hexane and tetrahydrofuran to obtain the coal liquefaction residue n-hexane insoluble matter-tetrahydrofuran soluble matter solid (i.e. asphaltenes), Recorded as AP. Dissolve 0.5g AP in 20g tetrahydrofuran solution, and record it as solution A; dissolve 2g polyacrylonitrile in 10g N-N, dimethylformamide solution, and record it as solution B; mix the above two solutions of A and B, and magnetically After stirring for 24 hours, the spinning dope was obtained. The obtained spinning stock solution is spun by an electrospinning machine, the spinning voltage is 15Kv, the ambient humidity is 40%, the receiving distance is 10cm, and the propulsion speed is 0.2ml / h to obtain a nascent nonwoven fabric. The obtained nascent non-woven fabric was initially pre-oxidized in 10% nitric acid solution for 7 hours, washed to neutrality, ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Grinding the obtained coal direct liquefaction residue into 100-300 mesh powder, and sequentially extracting the coal direct liquefaction residue with n-hexane and tetrahydrofuran to obtain the coal liquefaction residue n-hexane insoluble matter-tetrahydrofuran soluble matter solid (i.e. asphaltenes), Recorded as AP. Dissolve 10g AP in 20g tetrahydrofuran solution, and record it as solution A; dissolve 1g polyacrylonitrile in 5g N-N, dimethylformamide solution, and record it as solution B; mix the above two solutions of A and B, and magnetically stir After 18h, the spinning dope was obtained. The obtained spinning stock solution was spun by an electrospinning machine, the spinning voltage was 18Kv, the ambient humidity was 80%, the receiving distance was 20cm, and the advancing speed was 2.5ml / h. After the initial pre-oxidation of the obtained nascent non-woven fabric in 70% nitric acid solution for 1 hour, it was washed until neutral and dried; in an air atmosphere, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com