Method for determining branching degree of glucose polymer by using nuclear magnetic resonance
A glucose polymer and nuclear magnetic resonance technology, applied in the direction of nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, etc., can solve the problems of difficult operation, inability to measure the degree of branching, poor reproducibility, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the measurement accuracy and simplifying the measurement steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
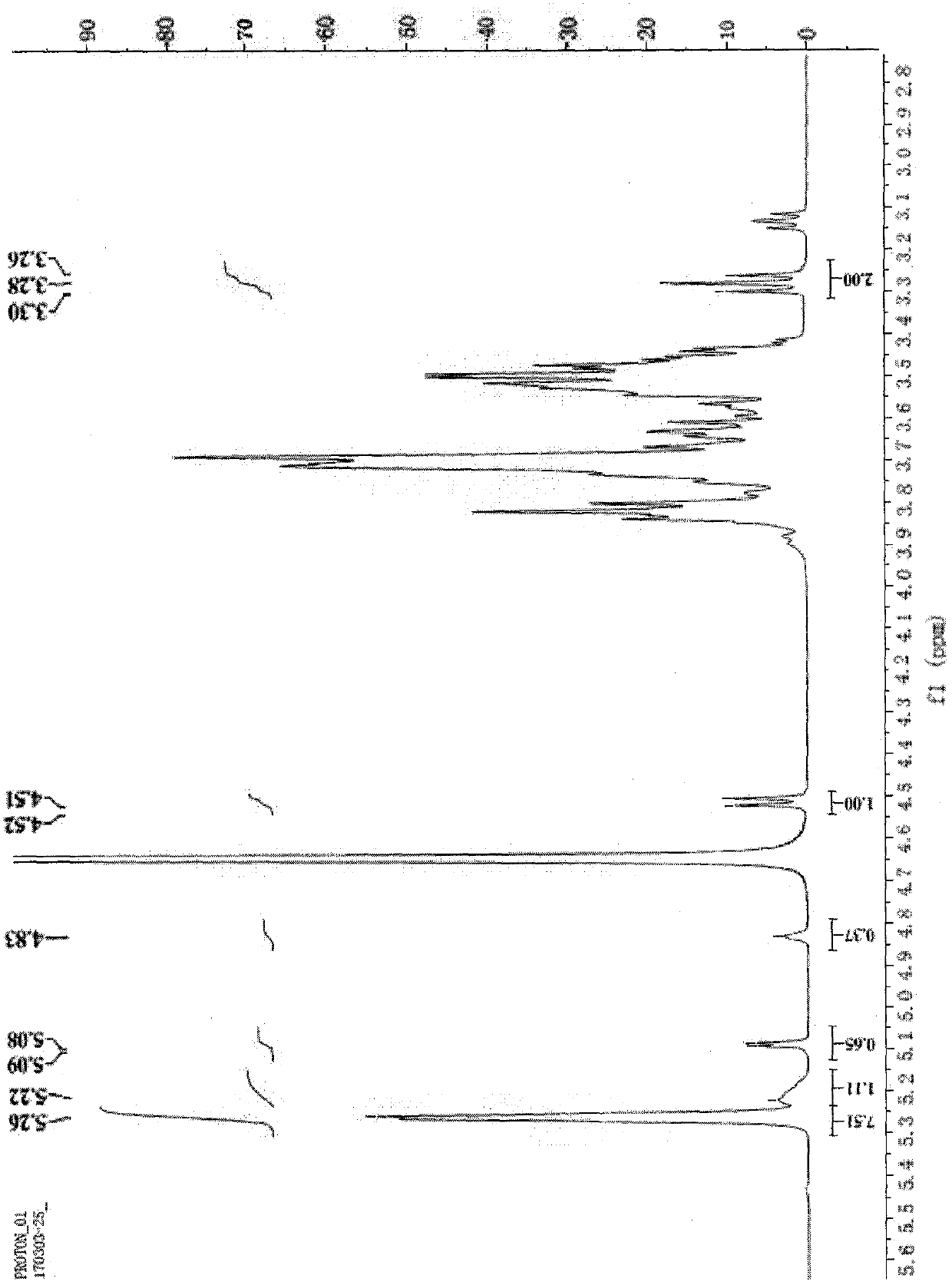
[0033] Weigh 20 mg of icodextrin and place it in a 5 mm sample test tube, add about 0.6 ml of heavy water to dissolve, make the prepared solution reach a depth of 3-4 cm in the sample test tube, cover the NMR cap, and follow the one-dimensional hydrogen Spectrum or carbon spectrum operation requires operation, NMR analysis results such as figure 1 As shown, the following table is made according to the conclusions that can be drawn from the figure:
[0034] Assignment of each peak: 5.2ppm
[0035]
[0036] Through the above results, the degree of branching is calculated:
[0037] Sample branching degree=0.37 / (7.51+1.11+0.37)*100%=4.12%
Embodiment 2
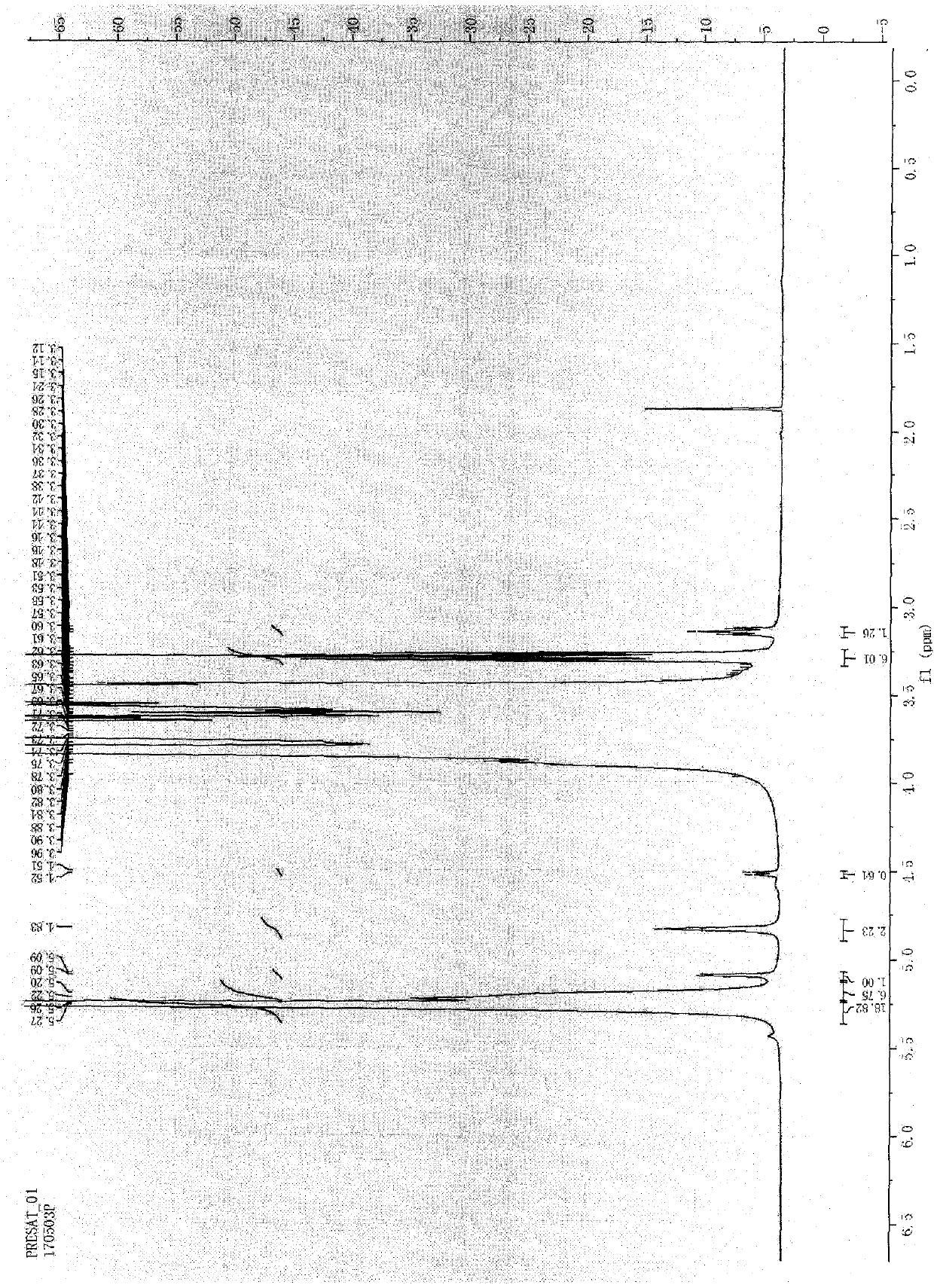
[0039] Take 20 mg of icodextrin and place it in a 5mm sample test tube, add about 0.6ml of heavy water to dissolve it, make the prepared solution reach a depth of 3-4 cm in the sample test tube, cover the NMR cap, and analyze according to the one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum The operation requires operation, suppresses the water peak, and the nuclear magnetic resonance analysis results are as follows figure 2 shown, and according to figure 2 The conclusions drawn in are tabulated below:
[0040] Assignment of each peak: 5.3ppm
[0041]
[0042] Through the above results, the degree of branching is calculated:
[0043] Sample branching degree=2.23 / (18.82+6.75+2.23)=8.02%
Embodiment 3
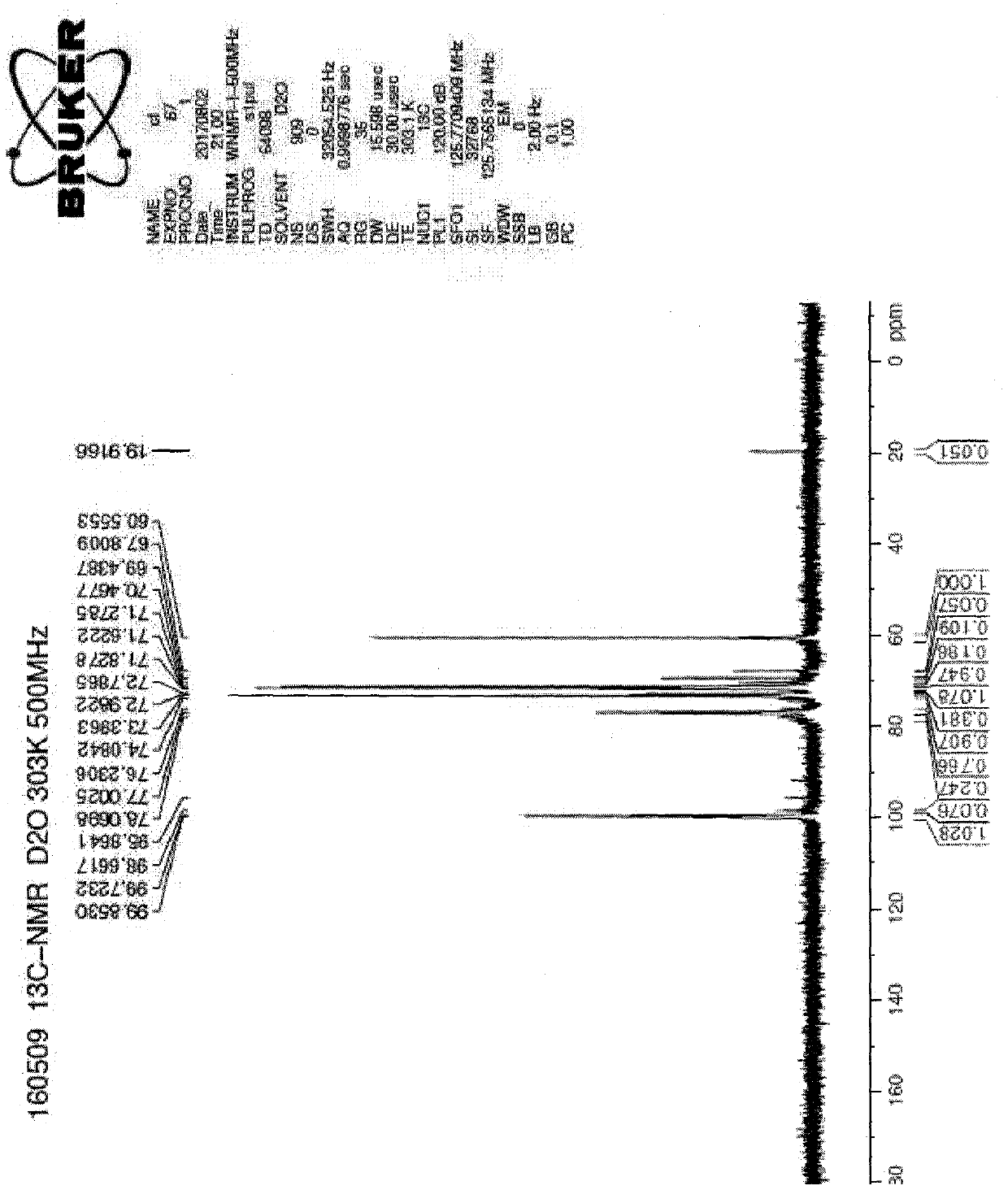
[0045] Weigh 20 mg of icodextrin and place it in a 5 mm sample test tube, add about 0.6 ml of heavy water to dissolve, make the prepared solution reach a depth of 3-4 cm in the sample test tube, cover the NMR cap, and follow the one-dimensional carbon The operation of the spectrum requires operation, and the results of the NMR analysis are as follows: image 3 and Figure 4 shown, and make the following table according to the conclusions drawn in the figure:
[0046] The peaks belong to:
[0047] chemical shift ppm
99.85
76.23-78.06
72.79-73.40
71.28-71.83
70.47
69.44
60.56
C positioning
C1
C4
C2
C3, C5
C4
C6
C6
Integral area
1.028
1.013
1.288
2.025
0.186
0.109
1.00
[0048] Through the above results, the degree of branching is calculated:
[0049] Sample branching degree=0.109 / (0.109+1.0)*100%=9.83%
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com