Preparation method of ultralight and high-strength GMT (glass mat reinforced thermoplastic) composite board
A composite sheet, high-strength technology, applied in the field of preparation of ultra-light and high-strength GMT composite sheet, can solve the problems of uneven distribution of microspheres, unfavorable continuous production, increased cost, etc. The effect of improving mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] An ultra-light and high-strength GMT composite sheet for preparing automobile bottom guards, which uses polypropylene fiber 1 as a bonding matrix, glass fiber 2 as a reinforcement, and microspheres that have the effect of changing the connection mode of glass fiber spacing points to adjust the expansion ratio of the sheet Blowing agent 3 composition. Its specific preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0031] (1) The polypropylene fiber 1 and the glass fiber 2 are uniformly mixed at a ratio of 60wt%:40wt%, and a uniform single fiber web is obtained through a non-woven process through opening, mixing and carding.
[0032] (2) Uniformly disperse the microsphere foaming agent on the surface of the carded single fiber web by dusting process, wherein the content of the microsphere foaming agent is 5wt% of the mass of the single fiber web.
[0033] (3) The single fiber web containing the microsphere foaming agent is cross-laid and needle-punched to obtain a blended...
Embodiment 1
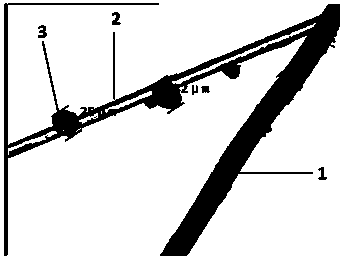
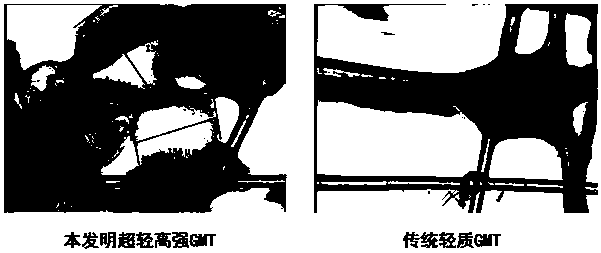
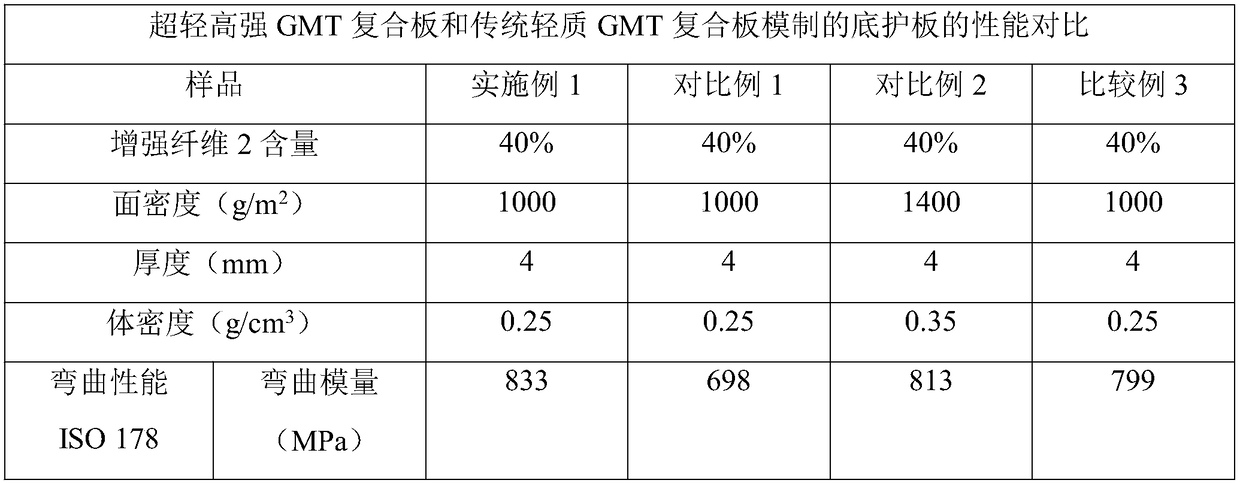
[0064] Example 1 introduces a microsphere foaming agent 3 into the felt net of the existing lightweight GMT composite board, and the introduction of the microsphere foaming agent 3 makes the connection modes between the glass fibers 2 more diverse. In addition to the traditional point connection, the microsphere blowing agent 3 binds the glass fibers 2 around it as a bridge, and the microsphere blowing agent 3 is connected to each other, as figure 1 As shown, these diverse connection methods have fundamentally changed the internal felt network structure of composite panels. figure 2 Comparing the results inside the felt net in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1, it was found that the glass fibers 2 inside the felt net in Example 1 were connected to each other, while the glass fibers 2 in Comparative Example 2 were simply point-connected. Compared with the bottom guard plate at the same density, the mechanical properties of Example 1 are significantly improved compared with C...
Embodiment 2
[0066] An ultra-light and high-strength GMT composite sheet for the preparation of automobile roofs, consisting of ES fiber as a bonding matrix, hemp fiber as a reinforcement, and a microsphere foaming agent 3 that has the effect of changing the connection mode of the reinforcing fiber spacing points to adjust the expansion ratio of the sheet . Its specific preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0067] (1) The ES fiber and the hemp fiber are mixed uniformly at a ratio of 55wt%:45wt%, and a uniform single fiber web is obtained through a non-woven process through opening, mixing and carding.
[0068] (2) Uniformly disperse the microsphere foaming agent on the surface of the carded single fiber web by dusting process, wherein the content of the microsphere foaming agent is 10wt% of the mass of the single fiber web.
[0069] (3) The single fiber web containing the microsphere foaming agent is cross-laid and needle-punched to obtain a blended composite fiber mat unifo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com