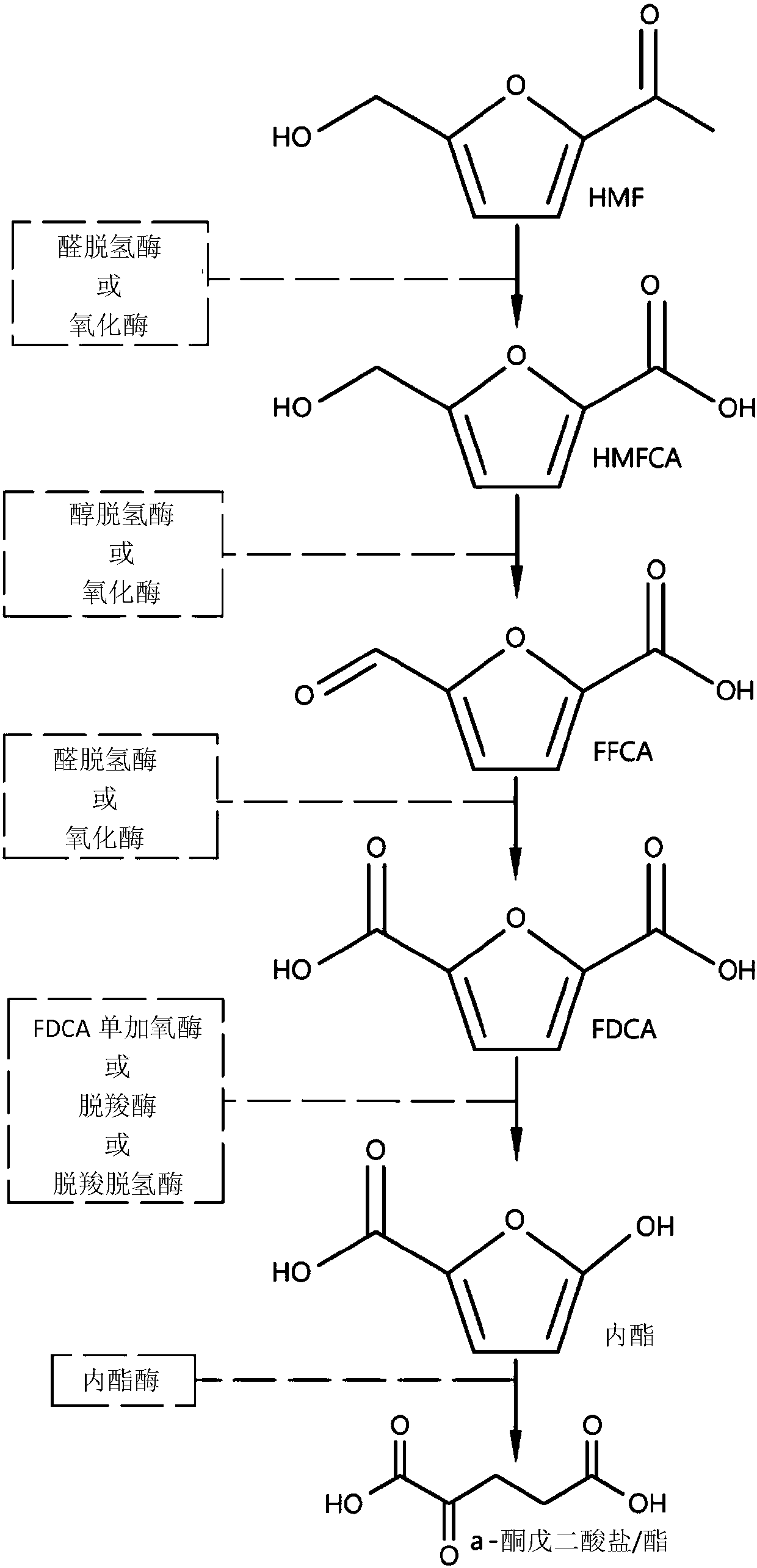
Fungal production of fdca
A fungal cell and wild-type technology, applied in the fields of molecular genetics, biotransformation and fermentation, and metabolic engineering, can solve the problems of FDCA produced by yeast or filamentous fungi that have not been described
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0381] Example 1: Isolation of Penicillium brasiliensis Batista
[0382] Fungal strains with the ability to grow at low pH to consume HMF were enriched and isolated from Dutch soil. 1 g of air-dried soil was provided to contain 20 ml of K-omitted 2 HPO 4 solution in a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask. The pH of the medium was lowered to pH=3 by titration with HCl solution. The initial HMF concentration was 1 g / l. To inhibit bacterial growth, naladixic acid (20 mg / l) was included in the medium. The vials were incubated at 30°C under air. After 2 weeks of incubation, the material (1 ml) from the enriched culture was transferred to fresh medium with the same initial composition. From the second culture, agar plates were streaked, containing mineral medium and 0.5 g / l HMF. Colonies that emerged after 10 days of incubation at 30°C under air were restreaked on plates with the same initial medium until the organisms were purified. Isolates were tested for HMF-depleted growth by growi...
Embodiment 2
[0385] Example 2: Limitation of Penicillium brasiliensis Growth at Low pH
[0386] The Penicillium brasiliensis C1 strain was isolated by incubating the soil in an initial pH=3 medium. However, pH changes in the medium during growth also varied in subsequent batch experiments with pure cultures. To verify the pH limitation of growth, chemostat cultures were performed to allow a predetermined growth rate at a constant predetermined pH. The growth rate was set at 0.08h -1, and the pH was maintained at pH=2.9. In 3 separate experiments, HMF, HMFCA or FDCA were used as carbon source. Under each of the three conditions the organism was able to establish itself at steady state; no washout occurred. The concentration of any of the 3 furans in the culture vessel was below the limit of detection in any of the three runs. The results show the ability of the organism to grow at pH values below 3, which is a desirable property for FDCA production from HMF at low pH values. In ad...
Embodiment 3
[0387] Example 3: Identification of the Penicillium brasiliensis C1 gene encoding an enzyme involved in HMF catabolism
[0388] Sequencing and Annotation of the Penicillium brasiliensis C1 Genome
[0389] DNA from Penicillium brasiliensis C1 was isolated and sent to BaseClear for paired-end sequencing using the Illumina HiSeq2500 system. After quality checking, filtering, and adapter removal, read sequences were assembled into contigs and ligated and placed in scaffolds.
[0390] Genome annotation was performed using the BaseClear annotation pipeline based on Augustus for structural annotation (Stanke and Waack, 2003, Bioinformatics.19 Supp1 2:ii215-25) and the Prokka Prokaryotic Annotation system for functional annotation (http: / / vicbioinformatics .com) combination. A set of Penicillium species was used as a reference for annotations that included information on rRNA, tRNA, signal peptides, Pfam protein family predictions, cellular localization, and conserved domains.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com