Method for detecting pesticide residue quantity in radix ophiopogonis
A technology for pesticide residues and Ophiopogon japonicus, which is applied in the field of detection of pesticide residues in Ophiopogon japonicus, can solve problems such as endangering the health of eaters and reducing the efficacy of Ophiopogon japonicus, and achieves cost-saving experiments, short analysis time, and peak-out time fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for detecting pesticide residues in Ophiopogon japonicus is provided in the present embodiment, comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step (1), the preparation of the first need testing solution;
[0047] Precisely weigh an appropriate amount of Ophiopogon japonicus to be tested, and process the Ophiopogon japonicus with QuEChERS pretreatment technology to make the first test solution;
[0048] Preferably, the QuEChERS pretreatment technology includes an extraction process and a purification process.
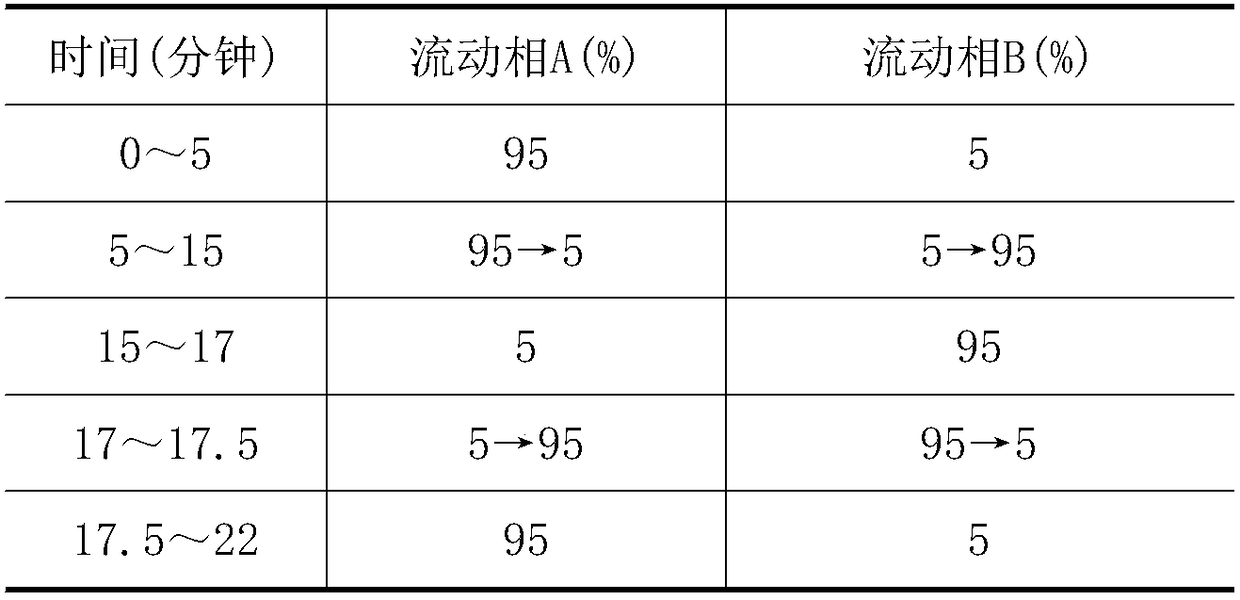
[0049] Further, the extraction process can be as follows: take the Ophiopogon japonicus powder to be tested, pass through a No. 3 sieve, accurately weigh an appropriate amount, put it in a plugged centrifuge tube, add an appropriate amount of glacial acetic acid solution, and vortex to completely infiltrate the Ophiopogon japonicus powder , and let it stand for a period of time; then add an appropriate amount of acetonitrile and place it on a shaker to vibrat...
Embodiment 2
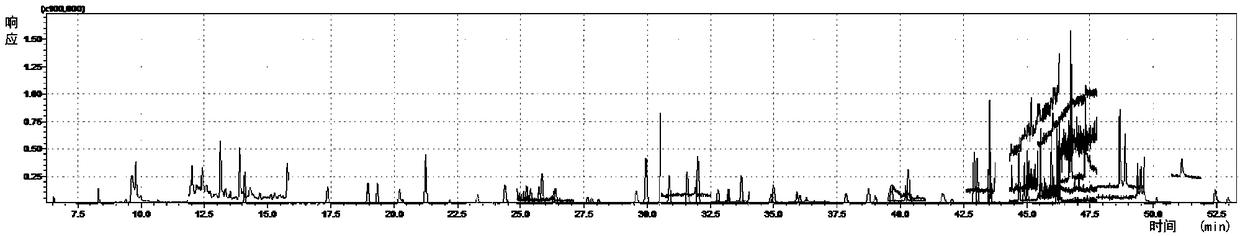
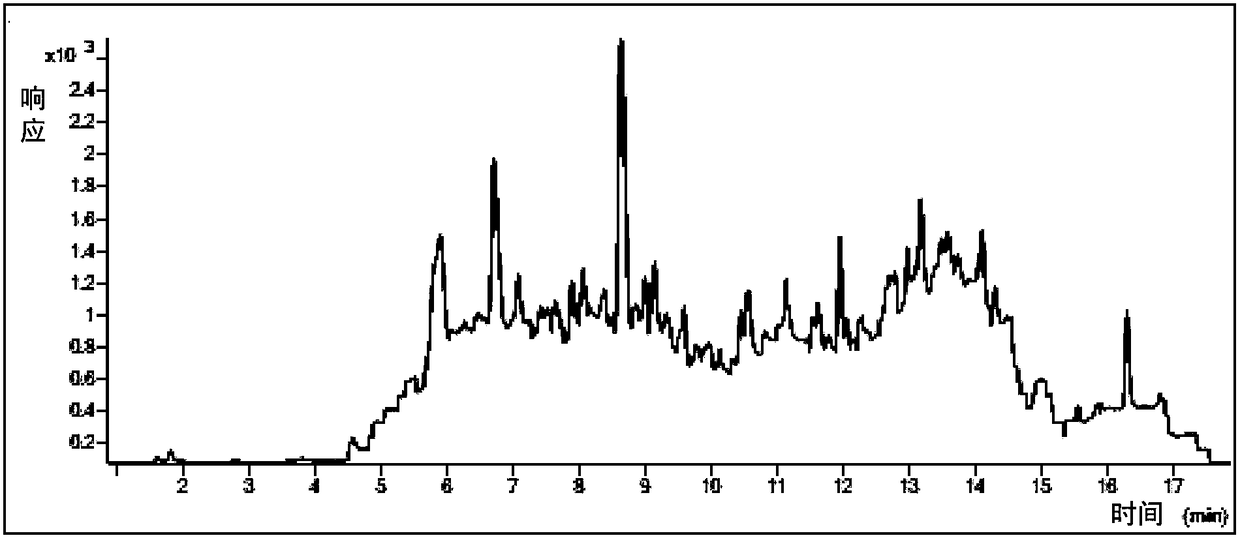
[0081] This embodiment mainly investigates, after preparing the first need testing solution according to the method described in the step (1) described in implementing 1, whether there is still interference component to be tested (being Radix Ophiopogon japonicus) in the first need testing solution residual pesticide ingredients).
[0082] After a lot of research and experiments in the early stage, the pesticides contained in Ophiopogon japonicus were screened. The types of pesticides screened included prohibited and restricted pesticides, highly toxic and high Usually, it may contain some of the 107 pesticide components (some pesticide components also include one or more isomers); when detecting the pesticide residues in Ophiopogon japonicus, these 107 pesticide components can be mainly detected.
[0083] Therefore, in this example, accurately measure 107 kinds (including multiple isomers) of pesticide reference substance in an appropriate amount, and prepare a reference subs...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Methodological investigation of the present invention: linearity and range
[0098] Linearity is the basis of quantitative determination, such as impurity quantitative detection, content and dissolution methods, etc., need to verify linearity and linear range, so that within the designed measurement range, the sample concentration and response value have a linear relationship.
[0099] In this example, prepare 107 pesticide reference substance solutions (including isomers, including the first reference substance solution and the second reference substance solution) according to the method described in Example 1, and dilute to various concentration levels , sample injection respectively, adopt the detection method described in the embodiment 1 to measure, thereby measured the linear equation, linear correlation coefficient (r) and the linear range of 126 kinds of pesticide compositions respectively, shown in table 3 and table 4, wherein , r is the linear correlation coef...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com