A dehydrating agent after electroplating
A dehydrating agent and hydrophobic technology, applied in the field of dehydrating agent after electroplating, can solve the problems of poor dehydration effect, large consumption, and large amount of dehydrating agent used.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
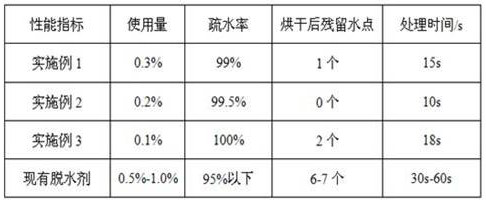
[0027] A dehydrating agent after electroplating, which is composed of the following components by weight: monoethanolamine: 2.2%-4.0%, diethanolamine: 2.5%-3.5%, triethanolamine: 5.0%-7.0%, soybean oleic acid: 10.5%-15.0% , Coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide: 14.7%-16.8%, isomeric alcohol polyoxyethylene ether: 11.9%-13.1%, sodium gluconate: 0.3%-0.5%, 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol : 2.0%-3.2% and deionized water: 36.9%-50.9%.
[0028] In one of the embodiments, the preparation method of the dehydrating agent after electroplating is as follows: Step 1. First, put monoethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethanolamine in the above-mentioned weight ratio into the reaction tank for uniform stirring, and the stirring speed is controlled 50 rpm, until the monoethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethanolamine are stirred until they become a clear and uniform liquid.
[0029] In one embodiment, in step 2, the soybean oleic acid in the above weight ratio is added into the reaction tank fo...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A dehydrating agent after electroplating is composed of the following components by weight: 12% of organic acid, 12% of organic amine, 27% of surfactant, 2.5% of polyol, 0.4% of complexing agent and 46.1% of deionized water.
[0038] In one embodiment, the organic acid is soybean oleic acid.
[0039]In one embodiment, the organic amine is formed by mixing 3% by weight of monoethanolamine, 3% by weight of diethanolamine and 6% by weight of triethanolamine.
[0040] In one embodiment, the surfactant is formed by mixing isomeric alcohol polyoxyethylene ether with a weight ratio of 12% and coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide with a weight ratio of 15%.
[0041] In one embodiment, the polyol is 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol.
[0042] In one embodiment, the complexing agent is sodium gluconate.
[0043] In one of the embodiments, the preparation method of the dehydrating agent after electroplating is as follows: Step 1. First, put monoethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethano...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A dehydrating agent after electroplating is composed of the following components by weight: 13.5% of organic acid, 11.2% of organic amine, 29.5% of surfactant, 3% of polyol, complexing agent: 0.35% and 42.45% of deionized water.
[0053] In one embodiment, the organic acid is formed by mixing soybean oleic acid with a weight ratio of 13% and oleic acid with a weight ratio of 0.5%.
[0054] In one embodiment, the organic amine is formed by mixing 2.5% by weight of monoethanolamine, 3.2% by weight of diethanolamine and 5.5% by weight of triethanolamine.
[0055] In one of the embodiments, the surfactant is composed of 13% isomeric alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, 16% coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide and 0.5% fatty acid by weight. Methyl ester ethoxylate blend.
[0056] In one embodiment, the polyol is formed by mixing 2.5% by weight of 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol and 0.5% by weight of glycerin.
[0057] In one embodiment, the complexing agent is sodium gluconate.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com