Electrolyte for aqueous zinc ion secondary battery and preparation method and application of electrolyte
A secondary battery and electrolyte technology, applied in secondary battery, electrolyte storage battery manufacturing, non-aqueous electrolyte storage battery, etc., can solve the problems of poor cycle stability of electrolyte decomposition battery, high charging potential, etc., to overcome battery cycle stability Poor, slow decomposition, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] An electrolyte for an aqueous zinc ion secondary battery in this embodiment, the electrolyte is composed of soluble zinc salt, nickel salt, pH buffer and deionized water, and the zinc salt is zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ), the nickel salt is nickel sulfate (NiSO 4 ), pH buffering agent is citric acid, wherein, the concentration of described zinc sulfate is 2mol / L, the concentration of nickel sulfate is 0.3mmol / L, the concentration of citric acid is 0.1mol / L, above-mentioned electrolyte solution uses nitrogen before 10 mol / L minute.
[0031] An electrolyte for an aqueous zinc ion secondary battery of the present embodiment is prepared by the following method, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0032] (1) 20ml of 2mol / L zinc sulfate is dissolved in deionized water, and stirred to dissolve completely to obtain an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate;
[0033] (2) adding 0.4g of citric acid as a weakly acidic pH buffer to the zinc sulfate aqueous solution, and stirri...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A kind of electrolytic solution that is used for water system zinc ion secondary battery of the present embodiment, described electrolytic solution is made up of soluble zinc salt, nickel salt, pH buffering agent and deionized water, and described zinc salt is zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ), the nickel salt is nickel sulfate (NiSO 4 ), the pH buffering agent is citric acid, wherein, the concentration of zinc sulfate is 2mol / L, the concentration of nickel sulfate is 0.6mmol / L, the concentration of citric acid is 20g / L, and the above-mentioned electrolytic solution is led to nitrogen for 10 minutes before use .
[0044] An electrolyte solution for an aqueous zinc-ion secondary battery in this embodiment is prepared by the following method, specifically including the following steps:
[0045] (1) 20ml 2mol / L zinc sulfate is dissolved in deionized water, stirred until fully dissolved, and an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate is obtained;
[0046] (2) Add 0.4g citric acid as weakly...
Embodiment 3
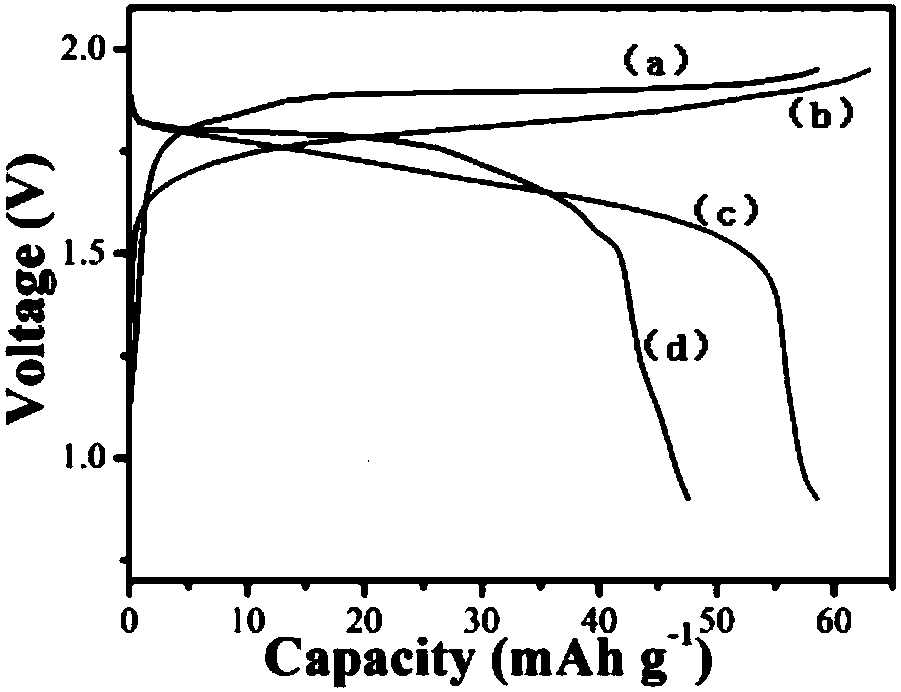
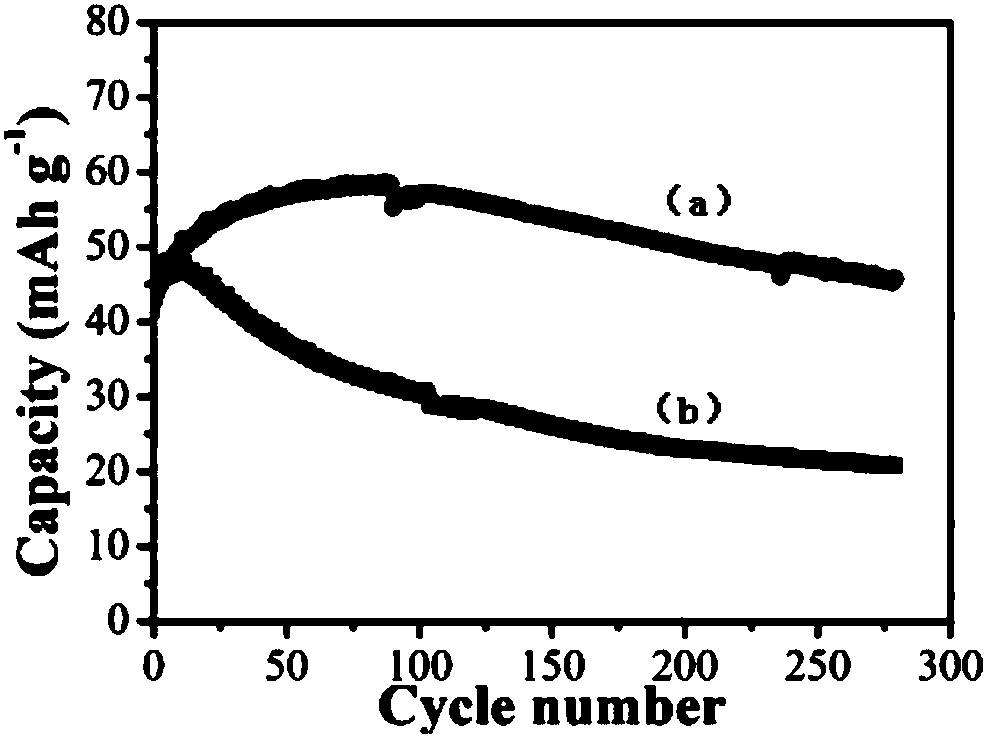
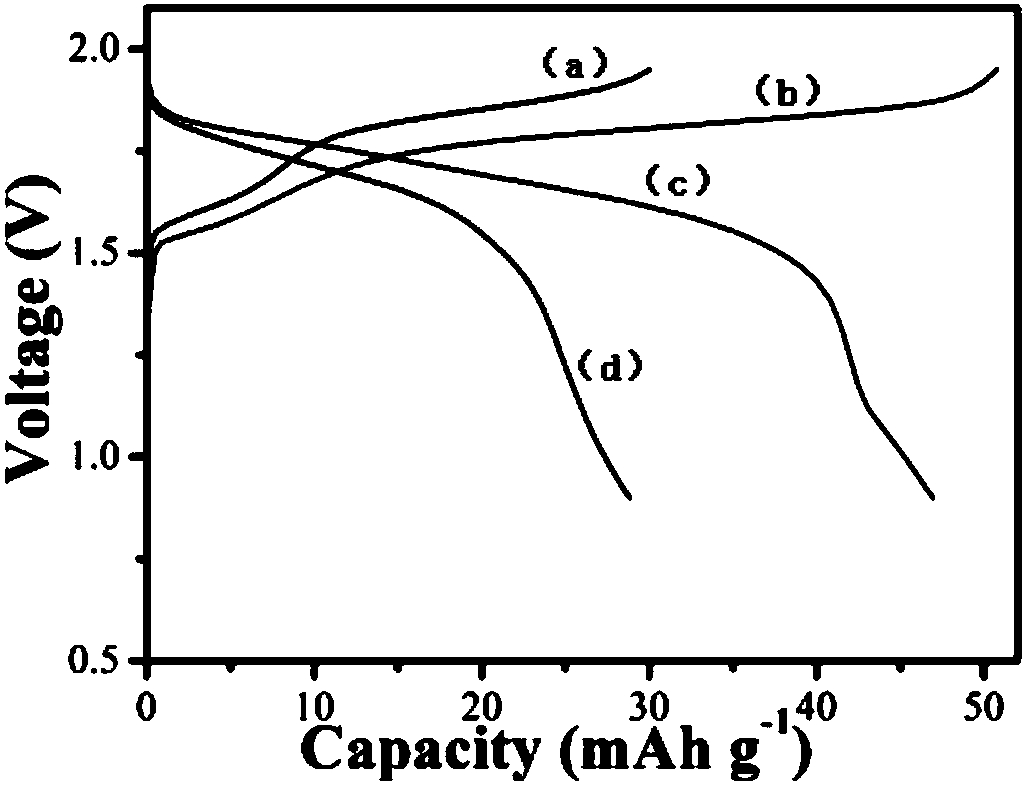
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the concentration of zinc salt in the electrolyte is 1 mol / L, and the concentration of other components is the same as that of embodiment 1. The positive and negative electrode materials of the battery in this example, the diaphragm, the battery assembly method, the test method and test conditions of the electrochemical performance are all the same as in Example 1. The battery of this embodiment does not need to be activated, and the specific capacity can reach 60mAh g -1 , due to the addition of nickel salt and pH buffering agent, the charge and discharge efficiency has been improved, up to 95%, and the electrochemical performance is better than that of the control example 1 without adding nickel salt and pH buffering agent, but there is still a small amount of electrolyte decomposition , so the cycle stability is slightly worse than that of Example 1, and the subsequent use of zinc sulfate as the zinc sal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com