Application of starch nanocrystals as flow regulator for drilling fluid and drilling fluid
A technology of starch nanocrystals and flow regulators, which is applied in the field of drilling fluids, can solve the problems of low kinetic plasticity, poor fluid loss control, and poor shear thinning, and achieve the effects of wide sources, improved rheology, and less dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0019] In the preparation process of the starch nanocrystals, the starch used may be the starch commonly used in this field, for example, it may be natural plant starch. Preferably, the starch is selected from at least one of corn starch, wheat starch, sorghum starch, potato starch (including potato starch, tapioca or sweet potato starch, etc.) or bean starch (including pea starch, mung bean starch, etc.) .
[0020] In the preparation process of the starch nanocrystals, the acid used may be a conventional choice in the art, preferably, the acid is selected from at least one of sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid.
[0021] In the preparation process of the starch nanocrystals, the amount of the acid used only needs to ensure sufficient hydrolysis of the starch. Preferably, the ratio of the mass (g) of starch to the volume (ml) of the aqueous acid solution is 1:5-1:20, and the concentration of the acid solution is 2-4mol / L.
[0022] In the prepara...
Embodiment
[0035] The present invention will be described in detail below by way of examples.
[0036] The experimental methods described in the following examples, unless otherwise specified, are conventional methods; the reagents and materials, unless otherwise specified, can be obtained from commercial sources.
[0037] The yield of starch nanocrystals was calculated as follows:
[0038] W(%)=W 2 / W 1 *100%
[0039] In the formula, W is the yield, %;
[0040] W 1 Be the quality of starch (g);
[0041] W 2 is the mass (g) of freeze-dried starch nanocrystals after acid hydrolysis.
[0042] In the following preparation examples, a NanoBrook omni multi-angle particle size and high-sensitivity Zeta potential analyzer (Brookhaven, USA) was used to test the particle size distribution of the suspension, and a JEM-2100 (UHR) transmission electron microscope (Japan Electronics Co., Ltd.) was used to observe For the microscopic morphology of the starch nanocrystal sample, the test method...
preparation example 1
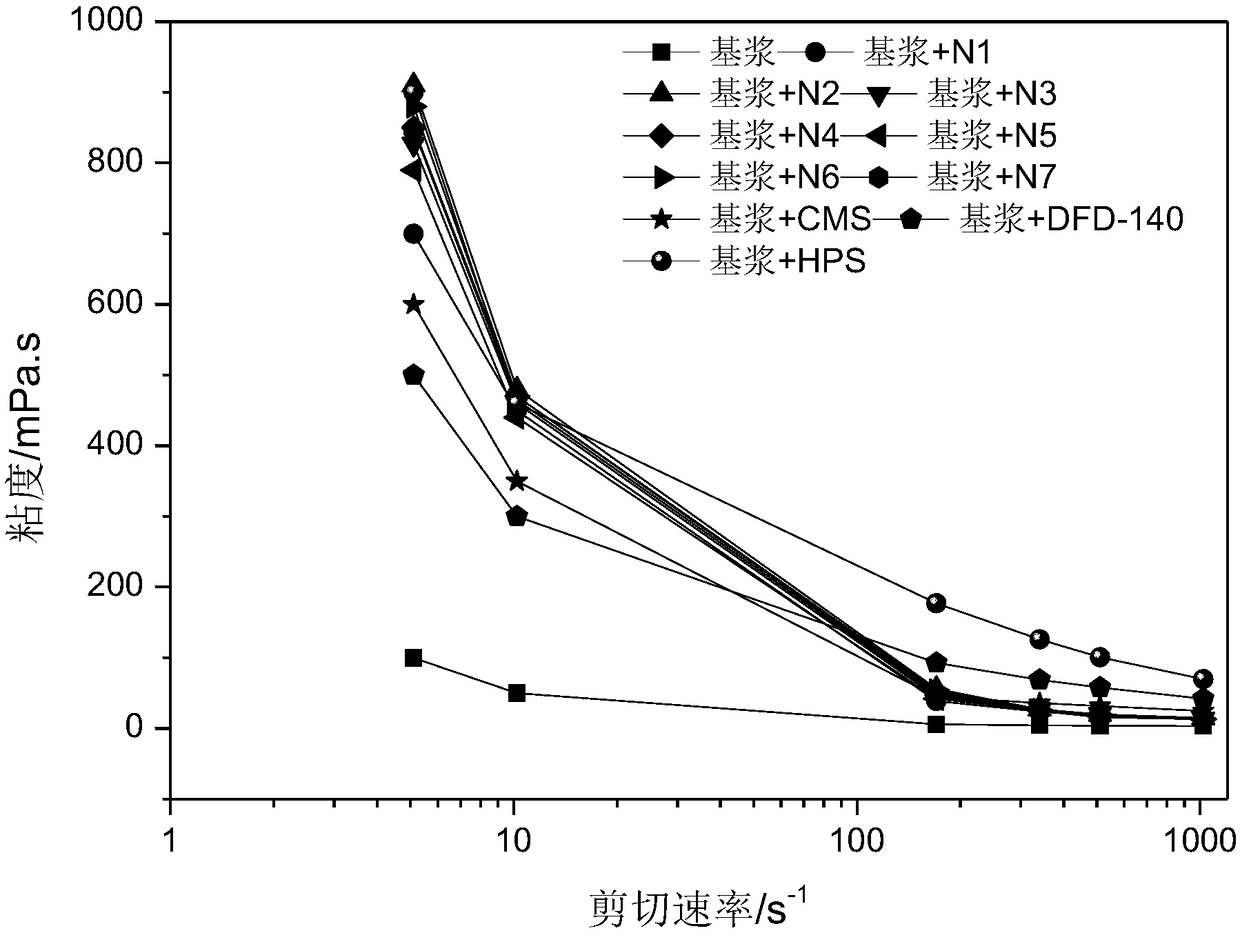
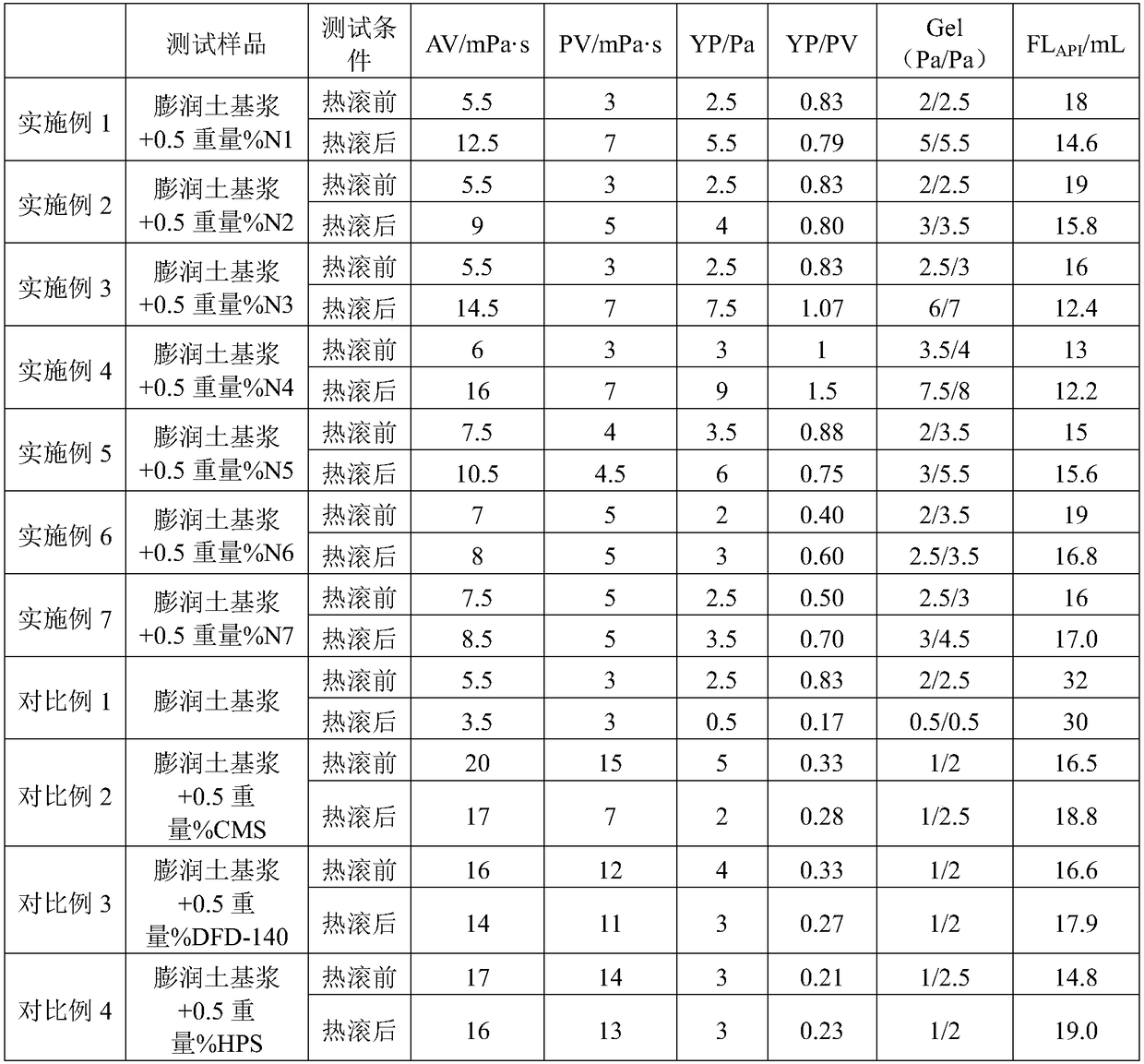
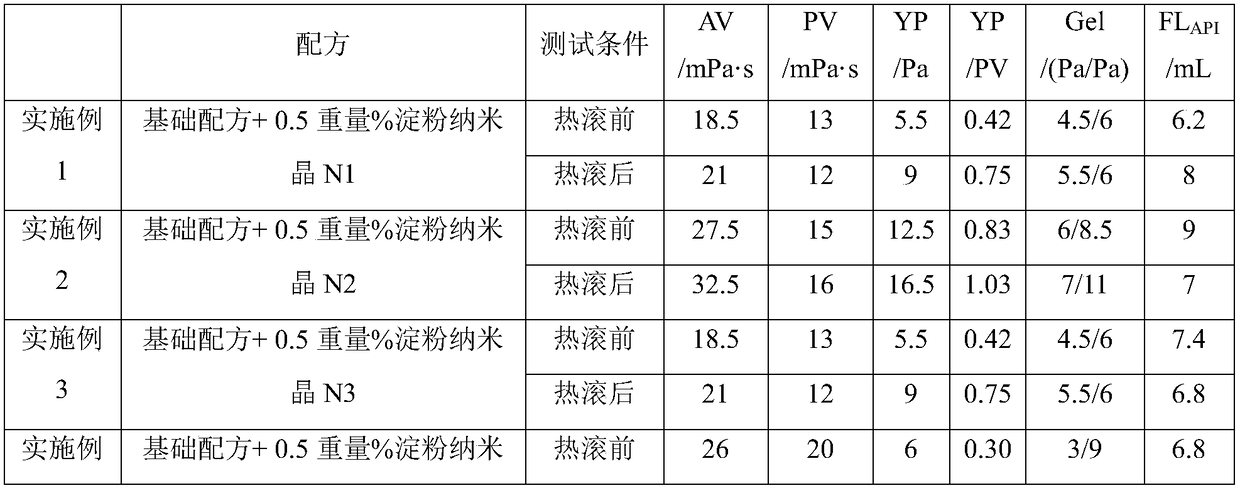
[0045] Weigh 20g of cornstarch and disperse in 100mL of sulfuric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 3.16mol / L, stir at 45°C at a stirring speed of 200rpm, centrifuge and wash the acid hydrolysis product to pH 6 after 5 days, freeze-dry and grind Starch nanocrystal N1 was obtained at 100 meshes, with a yield of 24.1%, an average particle size of 323.7nm, and starch nanocrystal particles in the form of discs.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com