Yeast transformant for screening protein with interaction with G protein beta-gamma dimer and screening method of yeast transformant
A dimer, G protein technology, applied in the field of genetic biology, can solve the problem that the function of βγ dimer cannot be fully reflected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1. Yeast transformants for screening proteins interacting with G protein βγ1 dimers
[0026] A method for constructing a yeast transformant for screening proteins interacting with G protein βγ1 dimers, comprising the steps of:
[0027] 1) Insert the coding gene (Genbank accession number: KX099865) of the Mulberry β subunit between the EcoR I and Sal I restriction sites of MCS I of the pBridge vector, and the coding gene (Genbank accession number: KX099866) of the γ1 subunit ) was inserted between the Not I and Bgl II restriction sites of the MCS II of the pBridge vector to recombine the plasmid pBridge-βγ1.
[0028] 2) Transforming the recombinant plasmid pBridge-βγ1 obtained in step 1) into AH109 yeast to obtain an AH109 yeast transformant containing the pBridge-Gβγ1 bait plasmid.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2, Yeast three-hybrid screening method for interacting proteins with Morus alba βγ1
[0030] A method for yeast three-hybrid screening of proteins interacting with Morus alba βγ1, comprising the steps of:
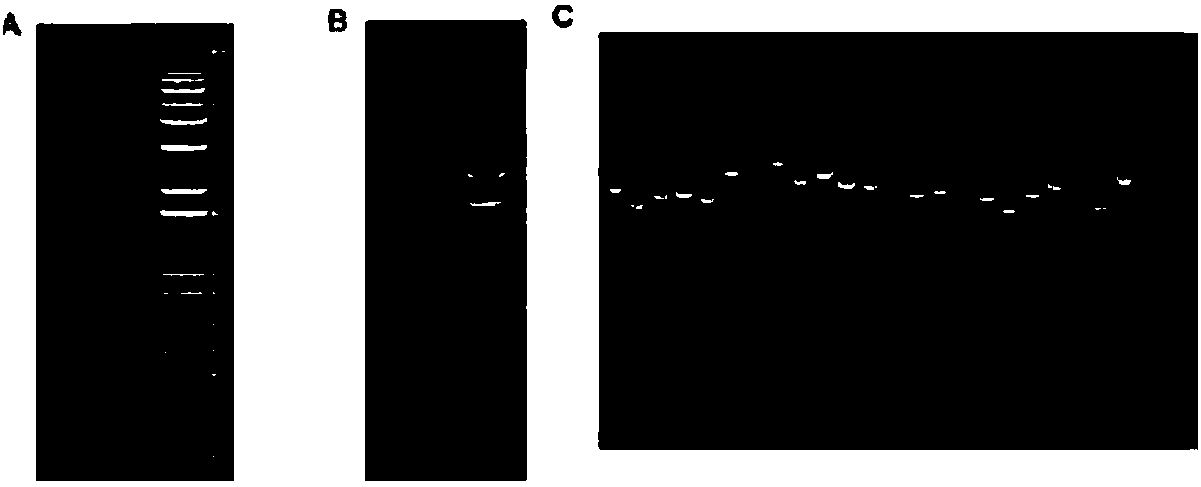
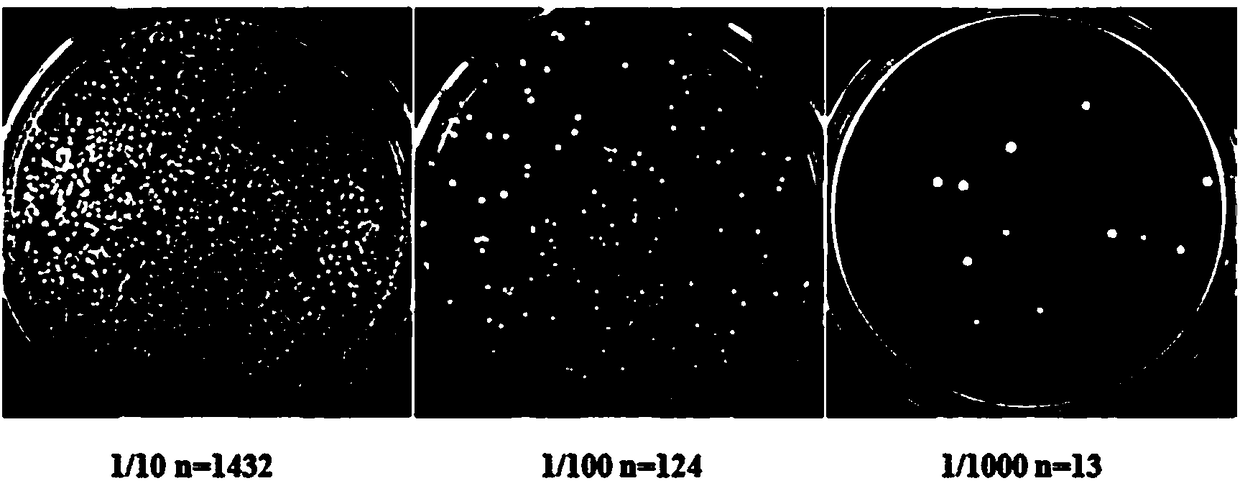
[0031] 1) Treat 15d mulberry seedlings with a mass fraction of 0.6% NaCl, and use the Trizol method to extract and isolate RNA ( figure 1 , A and B), the first and second strands of cDNA were synthesized, and then transferred to the linearized pGADT7 vector to obtain the library plasmid, and finally the identification of the library capacity and the size of the insert were carried out ( figure 1 , C), the library capacity is greater than 3×10 6 CFUml -1 , the average insert fragment is greater than 1200bp, the positive rate is 100%, and the library index is qualified;
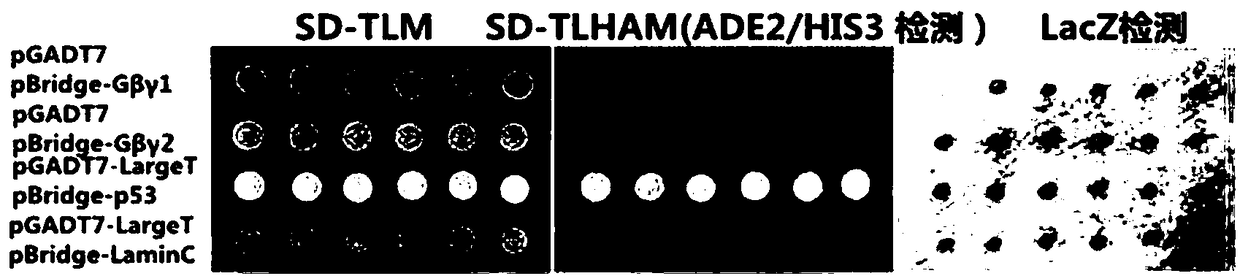
[0032] 2) The recombinant plasmids pBridge-βγ1 and pGADT7 were co-transformed into AH109 yeast, 6 colonies were randomly selected for self-activation detection, and the detection of the HIS...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3, Screening Yeast Transformants for Proteins Interacting with G Protein βγ2 Dimers
[0039] A method for constructing a yeast transformant for screening proteins interacting with G protein βγ2 dimers, comprising the steps of:
[0040] 1) Insert the coding gene (Genbank accession number: KX099865) of the Mulberry β subunit between the EcoR I and Sal I restriction sites of MCS I of the pBridge vector, and the coding gene (Genbank accession number: KX099867 ) were respectively inserted between the Not I and Bgl II restriction sites of MCS II of the pBridge vector to recombine the plasmid pBridge-βγ2.
[0041] 2) Transform the recombinant plasmid pBridge-βγ2 obtained in step 1) into AH109 yeast to obtain an AH109 yeast transformant containing the pBridge-Gβγ2 bait plasmid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com