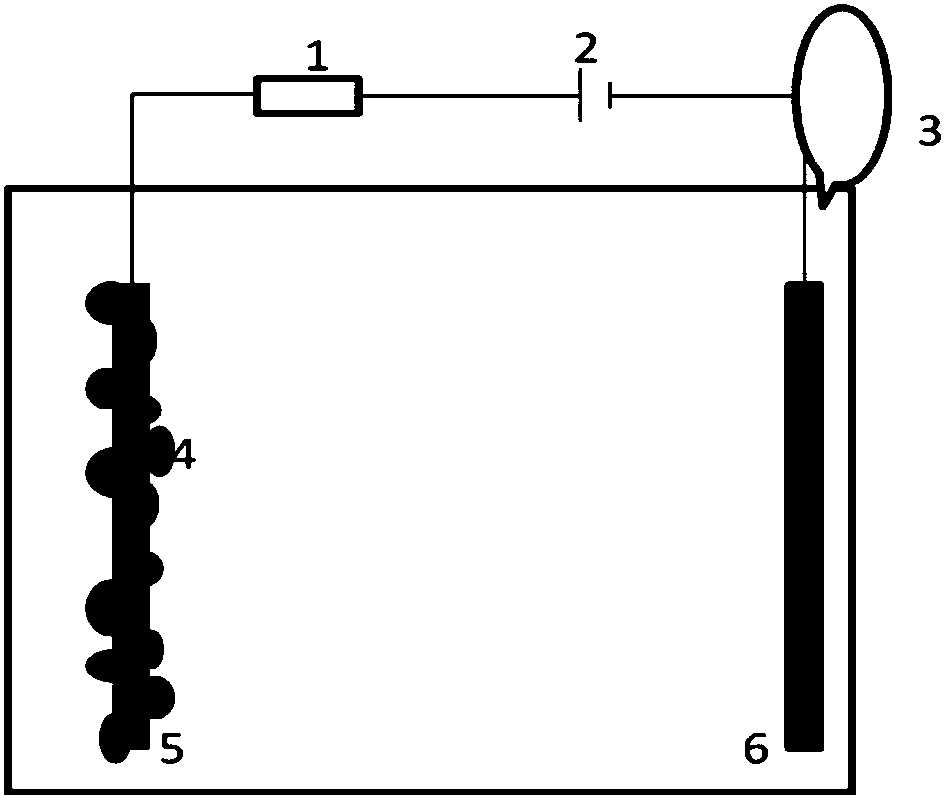
Method for treating sulfonamide wastewater and producing hydrogen synchronously by electrochemical device
A sulfonamide, electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of electrochemical biocombination treatment, chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Step 1: Assemble three single-chamber MFCs, the size of which is a plexiglass column with a length of 4cm and a cross-sectional diameter of 3cm. The effective volume is 28ml. The anode is a circular carbon cloth with a diameter of 3cm, and the cathode is Pt / C of the same size Air cathode (painting method), the two poles are connected together with a copper wire in the external circuit and an external 1500Ω resistor is connected. Start 3 reactors in electricity production mode, mix the anaerobic wastewater from the aeration tank of the sewage treatment plant with the culture solution at a ratio of 1:1 and put it into the MFC, where the culture solution consists of: sodium salt 37.78g / L, monohydrogen phosphate Salt 15.47g / L, dihydrogen phosphate 5.84g / L, potassium salt 0.13g / L, ammonium salt 0.31g / L, chloride salt concentration 0.44g / L, acetate 1g / L, constant temperature at 30°C Run in the box, monitor the voltage changes at both ends in real time, replace the culture med...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that glucose is used instead of sodium acetate to provide nutrients for the start-up stage of microorganisms, and other steps and parameters are the same as in Example 1.
[0025] The result of the present invention is that after 48 hours, the degradation rate of sulfamethoxazole reaches about 80%, and the hydrogen production also reaches 301.1±4 μmol.
Embodiment 3
[0027] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the Pt / C air cathode is produced by rolling method, and other steps and parameters are the same as those of Example 1.
[0028] The result of the present invention is that after 48 hours, the degradation rate of sulfamethoxazole reaches more than 85%, and the hydrogen production also reaches 320.5±4 μmol.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com