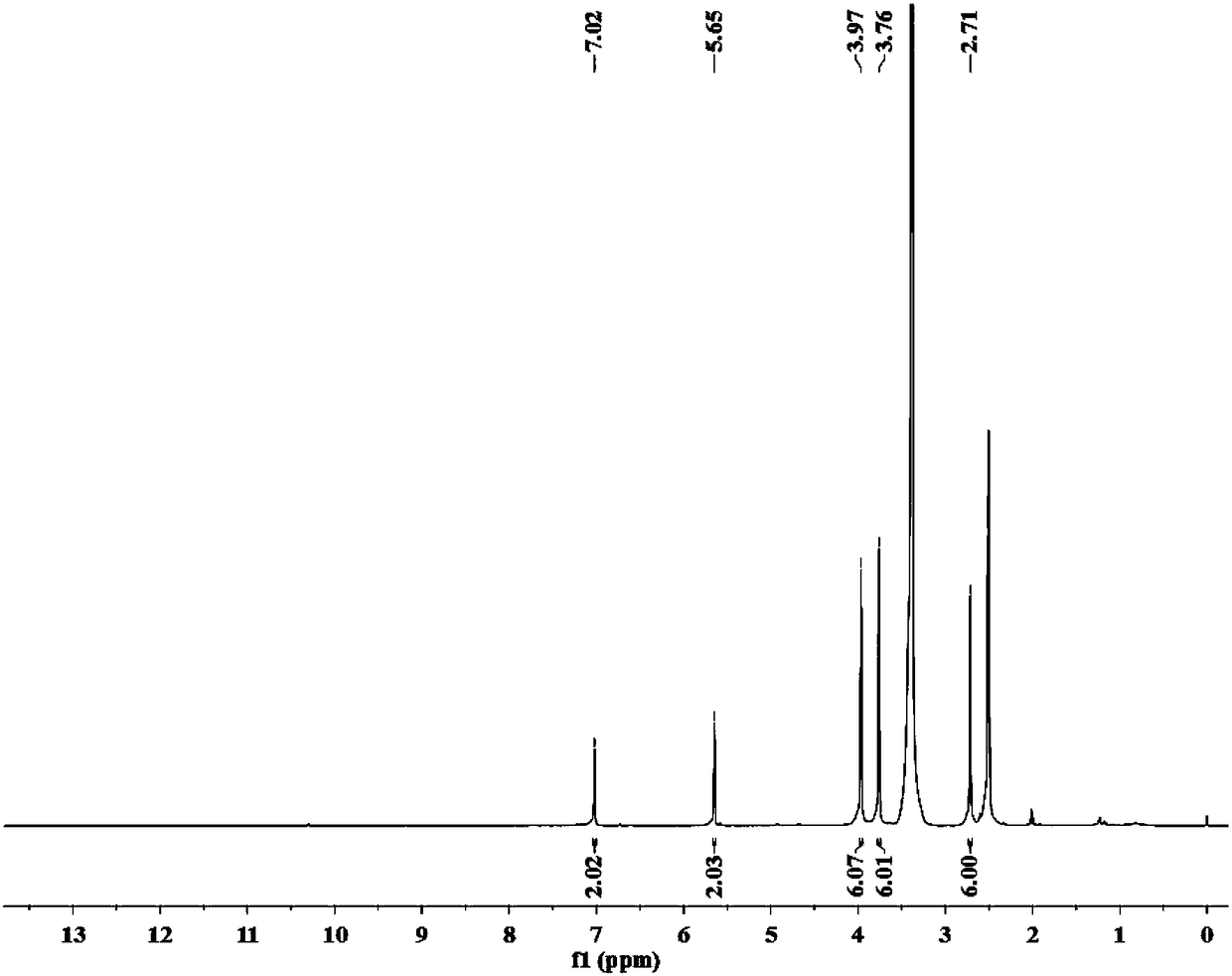
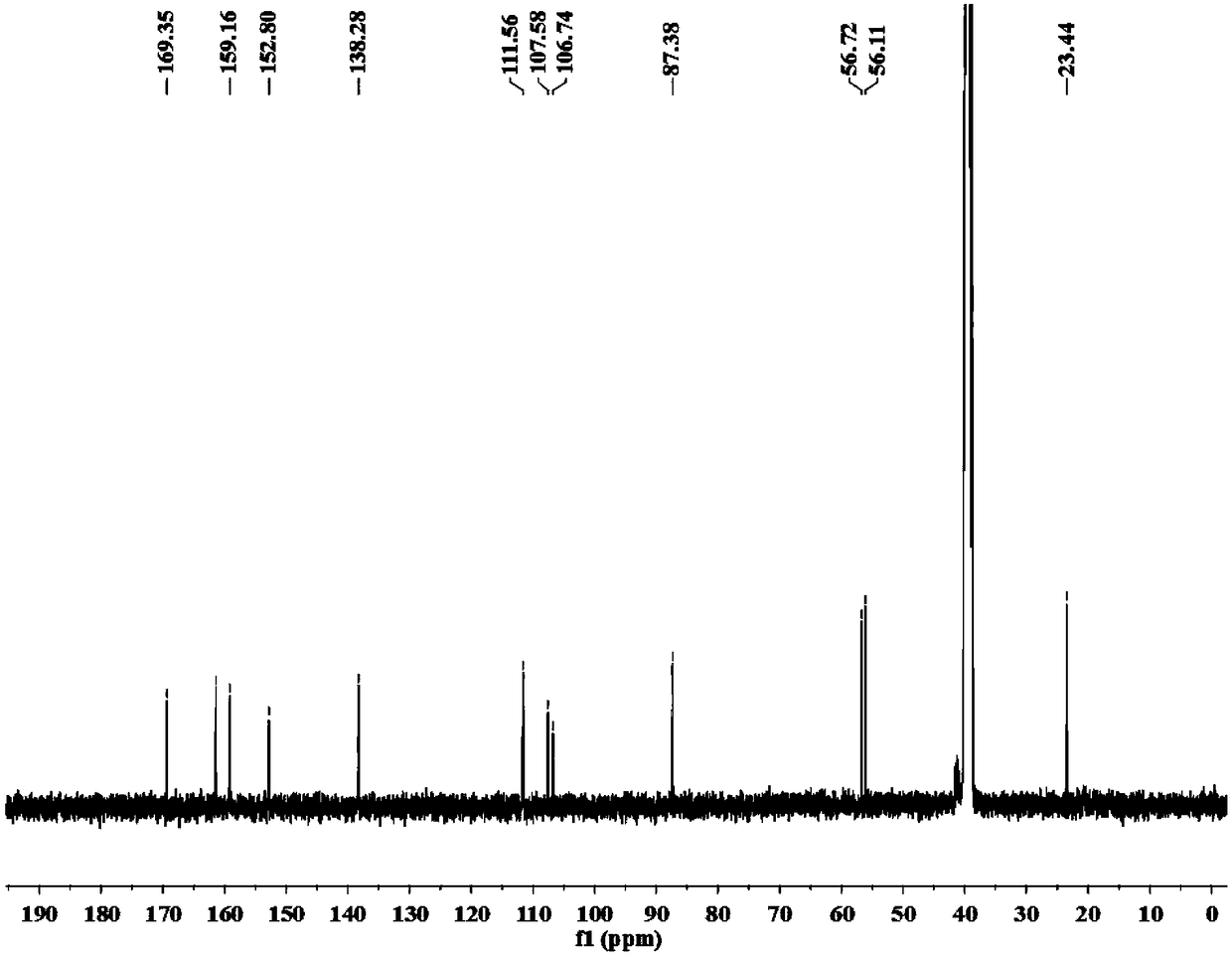
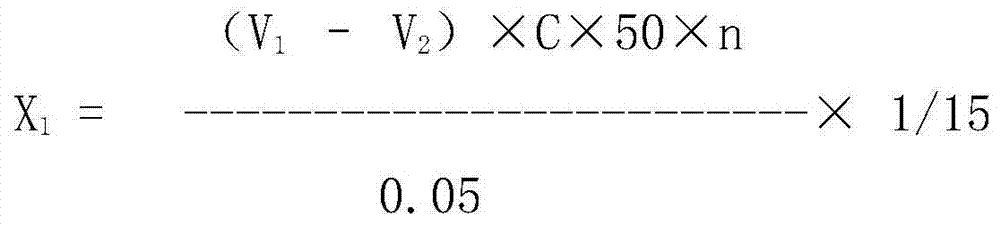Patents
Literature
57 results about "Aspergillus tubingensis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspergillus tubingensis is a darkly pigmented species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus section Nigri. It is often confused with Aspergillus niger due to their similar morphology and habitat. A. tubingensis is often involved in food spoilage of fruits and wheat, and industrial fermentation. This species is a rare agent of opportunistic infection.
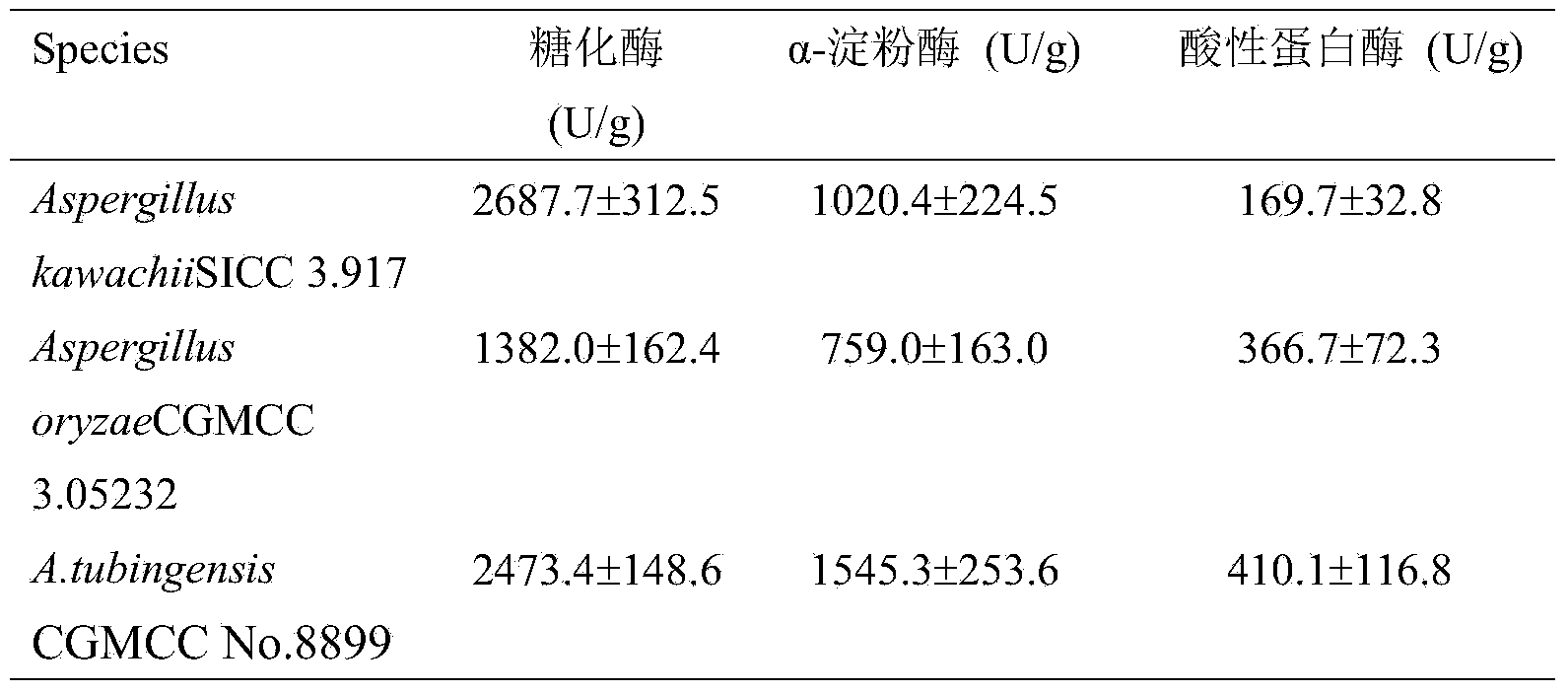
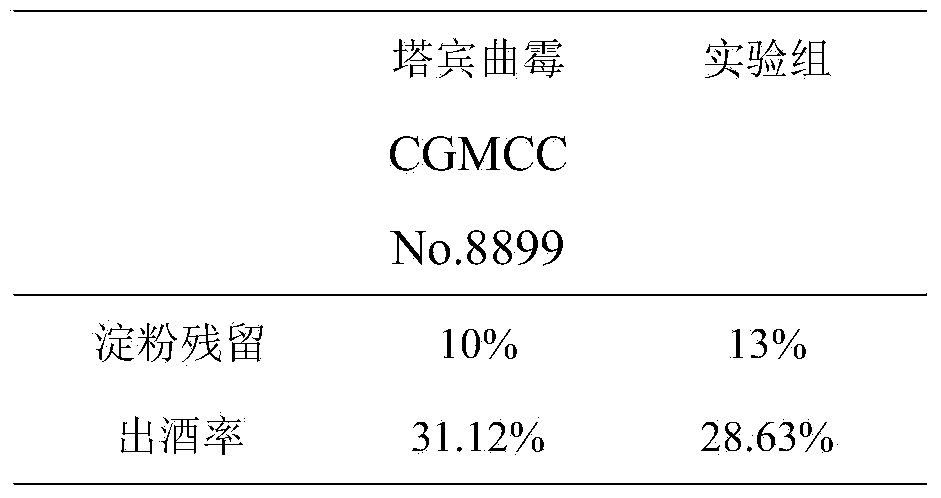
Aspergillus tubingensis for high-yield production of glucoamylase, alpha-amylase and acidic protease and application thereof
The invention discloses Aspergillus tubingensis for high-yield production of glucoamylase, alpha-amylase and acidic protease and application thereof in liquor making, the Aspergillus tubingensis is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the accession number is CGMCC No.8899. The Aspergillus tubingensis strain can be used for simultaneous high-yield production of the glucoamylase, alpha-amylase and acidic protease, and belongs to the microbiology and fermentation engineering field. By solid starter propagation of two strains of the aspergillus, high-yield production of the glucoamylase, alpha-amylase and acidic protease can be achieved, starch and protein use ratio in the liquor making process can be increased, and by use of the Aspergillus tubingensis, the liquor yield rate can be improved, and a good flavor can be kept.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
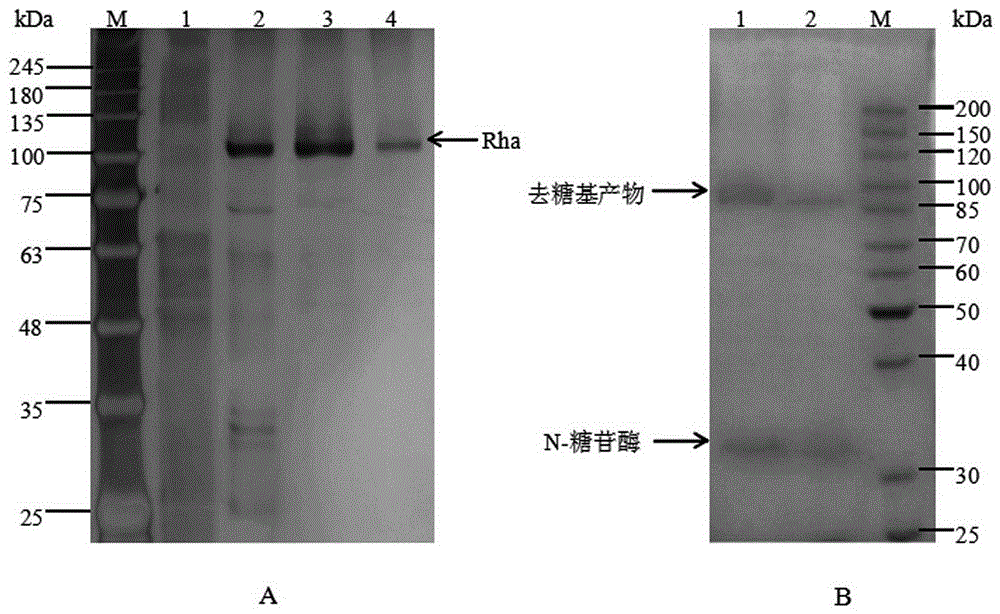
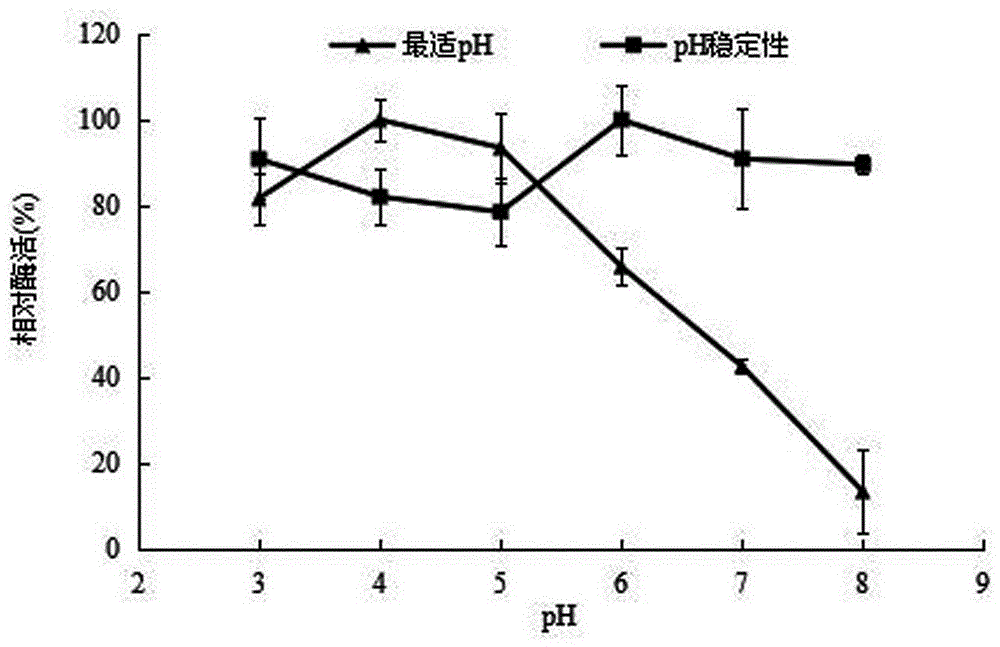
Cloning, expression and application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene
InactiveCN106191084AReduce manufacturing costIncreased substrate specificityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention discloses cloning, expression and application of an alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene. A coding gene is obtained from aspergillus tubingensis and is expressed in pichia pastoris GS115; specifically, total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of the aspergillus tubingensis is used as a template and cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of alpha-L-rhamnosidase is cloned through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technologies; pPIC9k is used as an expression vector and is subjected to secreting expression in the pichia pastoris GS115. The alpha-L-rhamnosidase can be used for efficiently hydrolyzing naringin; when the naringin is used as a substrate, Km and Vmax values respectively are 1.27mu.mol / mL and 3445mu.M min<-1>; the thermal stability at 60 DEG C is good and the alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene has a good application prospect in food and biopharmaceutical industries.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
'Tabin' aspergillus capable of producing pectase in high yield, and application in production of solid-state fermentation
A novel strain of Aspergillus tubingensis able to prepare the pectase with high output and its application in the solid-state fermentation of pectase are disclosed. The resultant pectase has high enzyme activity (more than 250 u / g at pH=2.5-4.2, or more than 120 u / g at pH=5.5).
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Aspergillus tubingensis with disease prevention and growth promoting functions as well as preparation and application of aspergillus tubingensis metabolites
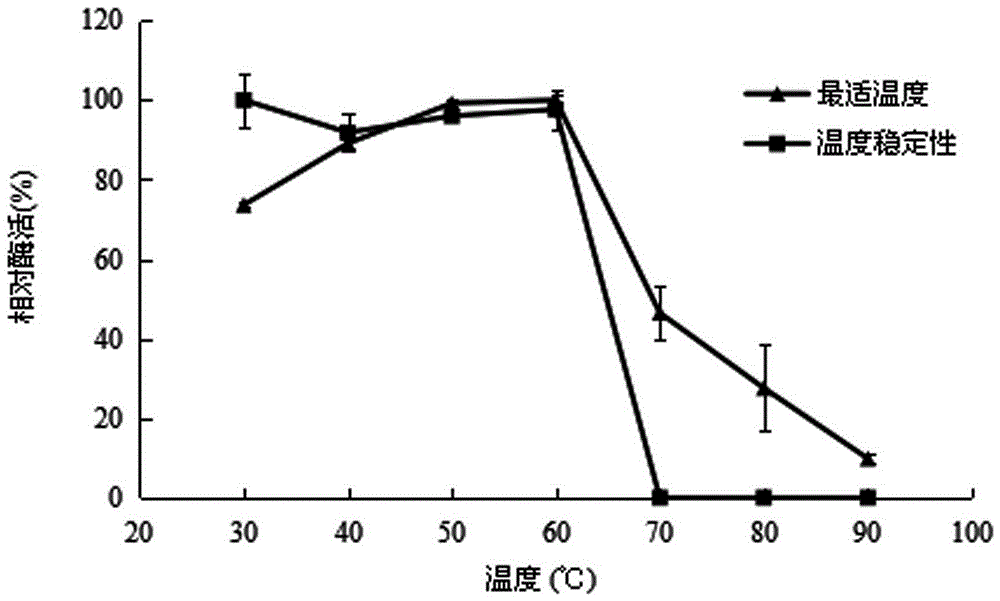
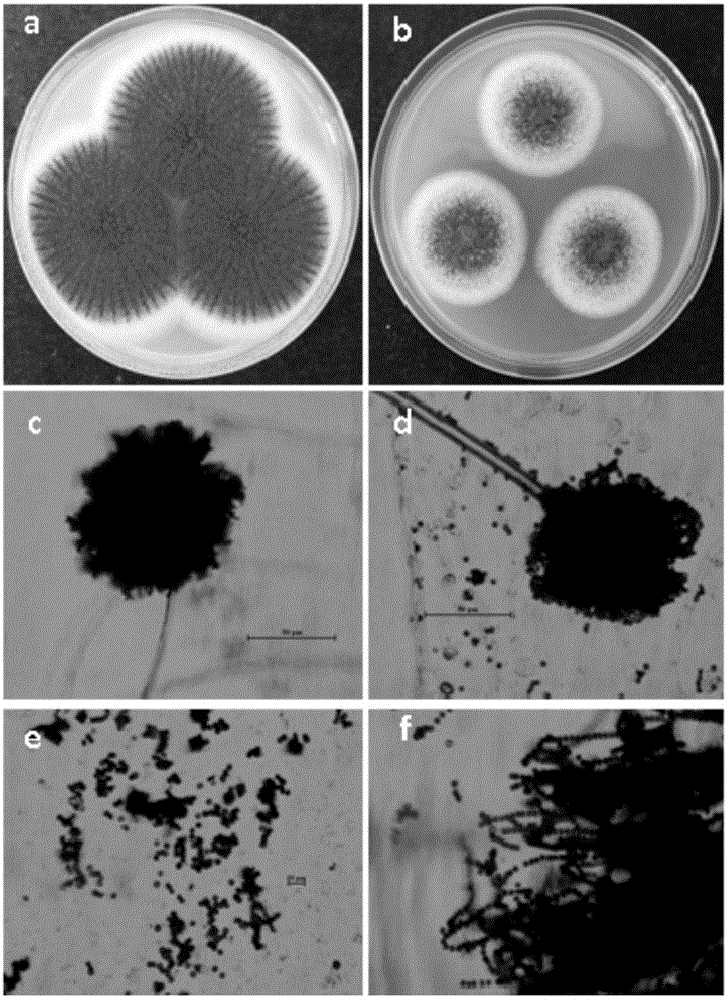
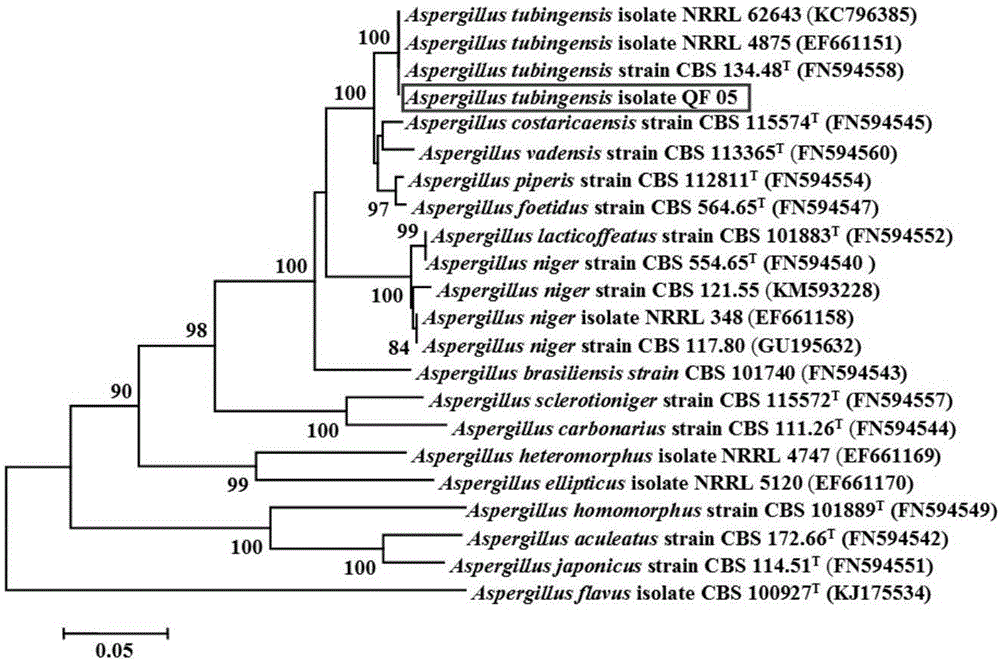
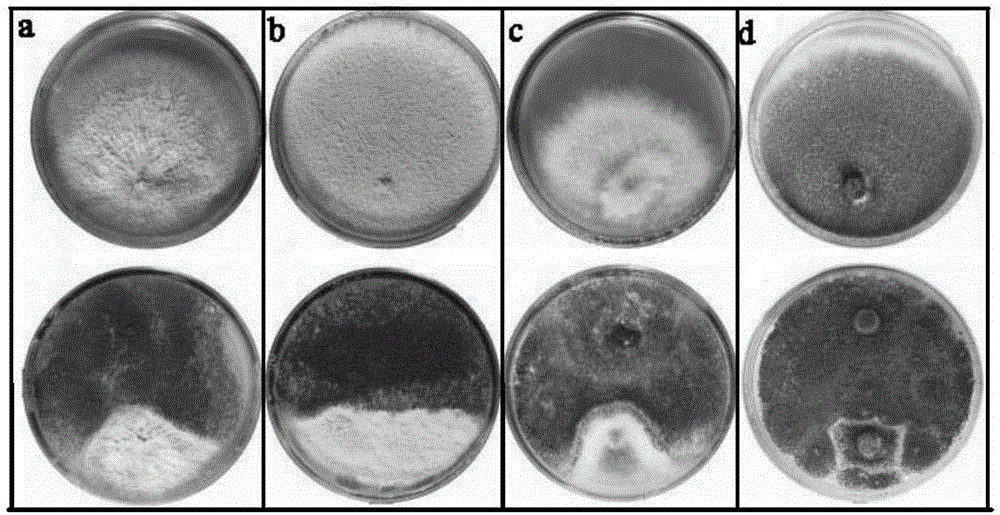
The invention discloses aspergillus tubingensis with disease prevention and growth promoting functions as well as preparation and an application of aspergillus tubingensis metabolites. The bacterial strain No. of aspergillus tubingensis is QF05, and the registration No. of aspergillus tubingensis in CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) is CGMCC No.13563. Aspergillus tubingensis QF05 has an inhibition function on botrytis cinerea, colletotrichum capsici, fusarium wilt of cucumbers, alternaria solani and pseudomonas syringae pv.lachrymans. Sterile fermentation filtrate of aspergillus tubingensis QF05 can remarkably increase the germination rate of pepper seeds and promote elongation of radicle. Aspergillus tubingensis QF05 metabolites containing bacteria effectively promote growth of true leaves of cucumbers and effectively increase the plant height and the yield of the cucumbers.
Owner:北京奥沃伽科技有限公司
Aspergillus tubingensis and a theabrownin producing method by liquid state fermentation thereof
InactiveCN106167765AQuick conversionEasy to controlFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobiological cultureTea leaf
The invention relates to aspergillus tubingensis and a theabrownin producing method by liquid state fermentation thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The production strain is aspergillus tubingensis KUtea 01, and is conserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center the address of which is number 3, courtyard 1, Beichenxi Road, Chaoyang District of Beijing. The conserving time is 30 December, 2014. The accession number is CGMCC No.10022. By inoculating the aspergillus tubingensis KUtea 01 into pasteurized green tea soup and culturing under culture conditions in a shake-flask single-strain manner for 3-4 days, the theabrownin content is 11-12 g / L, and the volumetric productivity is 11 times higher than that of solid fermentation. The aspergillus tubingensis and the method are advantageous in that production conditions and environments can be controlled easily and are not limited to the tea leaf production season, and automation, a high efficiency and a low cost can be achieved. The strain is directly bred in the green tea soup, does not need extra addition of carbon sources or nitrogen sources, and can rapidly and biologically convert polyphenols in the green tea soup into the macro-molecule water soluble theabrownin.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
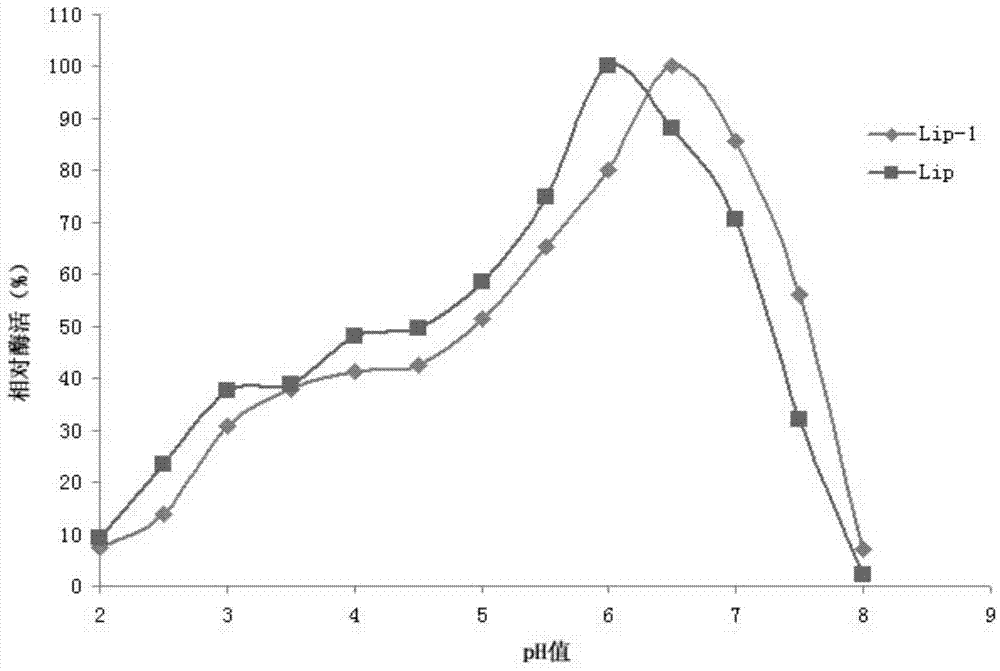
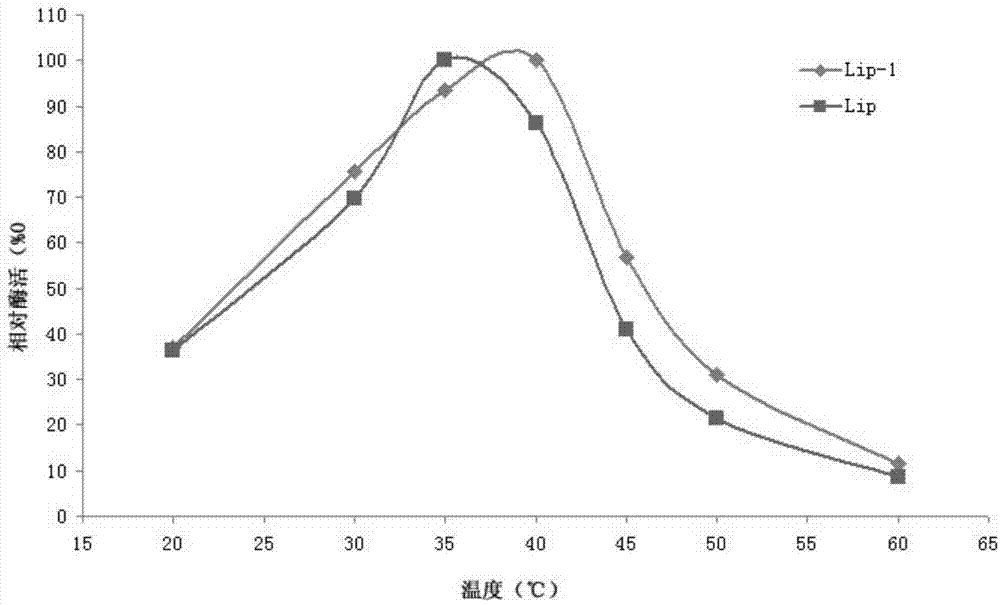
Lipase and mutant thereof
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Efficiently phosphorus-dissolving Aspergillus tubingensis strain and application thereof
InactiveCN106434391AStrong Phosphorus Soluble PropertiesImprove compatibilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses an efficiently phosphorus-dissolving Aspergillus tubingensis strain and application thereof. An efficient phosphorus-dissolving fungus is separated and purified from soil and is capable of activating various refractory phosphorus sources, inorganic phosphorus in decomposition solution is converted into effective phosphorus usable by plants, and the effective phosphorus is applicable directly to the preparation of plant nutrient solutions. Experiments prove that the phosphorus-dissolving fungus herein has high phosphorus-dissolving characteristics, is good in compatibility with a group of functional composite microbial colonies, and is also applicable to the research and development of composite microbial fungus fertilizers.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
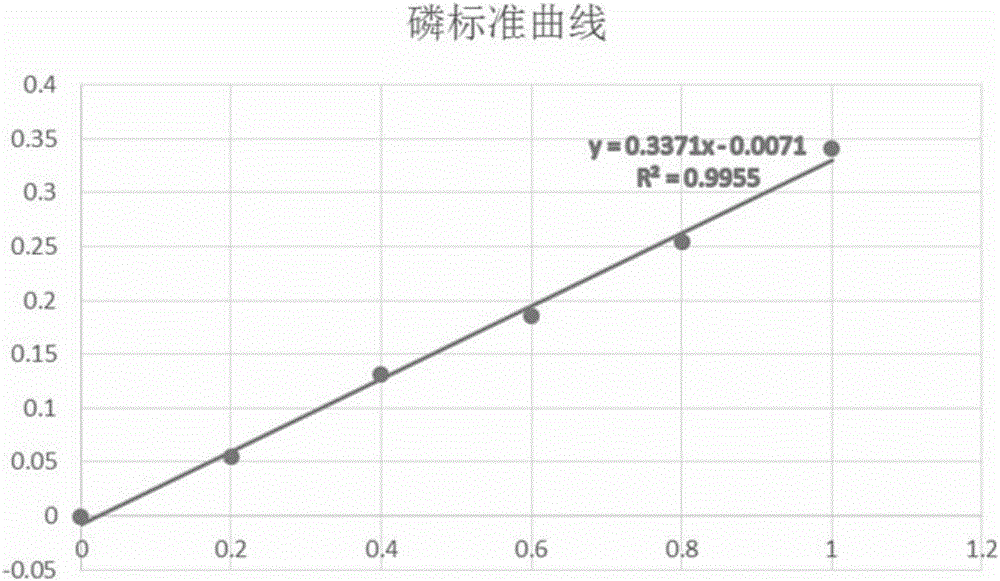
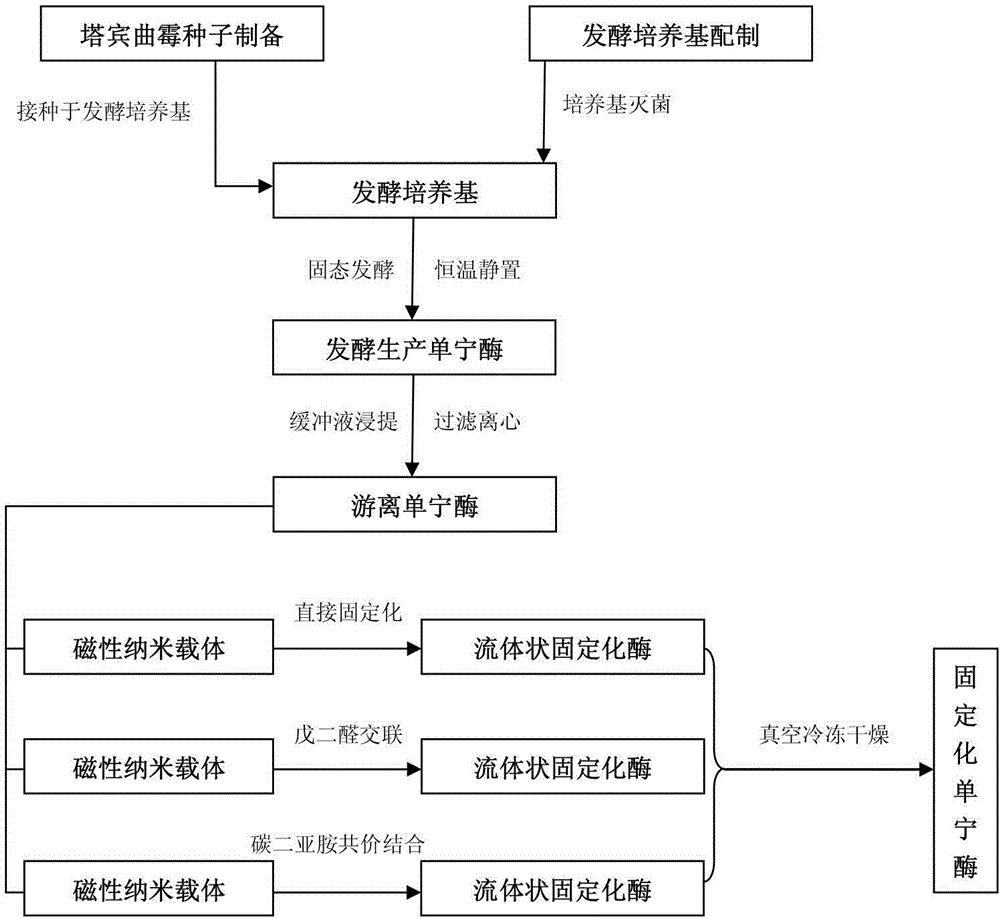
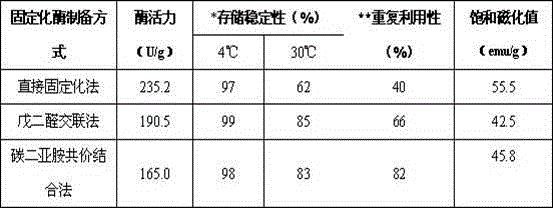
Method for directly immobilizing tannase in fermentation liquor
ActiveCN104962544AAchieve purificationAchieve fixityOn/in inorganic carrierBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for directly immobilizing tannase in fermentation liquor. The method includes (1), fermenting Tie Guanyin tea stems by the aid of aspergillus tubingensis to obtain free crude tannase; (2), utilizing hydrophilic super-paramagnetic nano-particles as carriers for immobilizing free tannase; (3), immobilizing the free tannase on the nano-particles by a direct immobilizing process, a glutaraldehyde cross-linking process and a carbodiimide covalent binding process so as to obtain liquid immobilized tannase; (4), carrying out vacuum freeze-drying on the liquid immobilized tannase to obtain powder immobilized tannase. The aspergillus tubingensis is used as an enzyme producing strain. The method has the advantages that the magnetic nano immobilized tannase is directly immobilized in the fermentation crude enzyme liquor and accordingly can be easily and quickly prepared; the immobilized tannase is excellent in enzyme activity, storage stability, reusability and magnetic control performance.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Aspergillus tubingensis and application of aspergillus tubingensis in preparing yam diosgenin
The invention discloses aspergillus tubingensis and an application of the aspergillus tubingensis in preparing yam diosgenin. The aspergillus tubingensis HG-57 has a preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) M2016389. The method comprises the steps of inoculating an appropriate amount of aspergillus tubingensis hyphae to a PDA solid culture medium for activation, adding water to collect a spore suspension after spore production, inoculating the spore suspension to a seed culture medium for amplification to form a seed solution, inoculating the spore suspension or the amplified seed solution to a yellow ginger water extract, a yellow ginger alcohol extraction aqueous solution or a yellow ginger water suspension for aerobic fermentation for 1-7 days to form fermentation liquid, and separating and extracting the yam diosgenin product from the fermentation liquid. A yam diosgenin content is increased by 1.2-1.4 times, 1.1-1.4 times and 1.4-1.8 times compared with a content of the yam diosgenin obtained by directly adding acid into the system for hydrolysis. The strain can effectively convert yellow ginger saponin into the yam diosgenin; an acid hydrolysis conversion process in the traditional technology is substituted thoroughly; engineering amplification is very easy; and the strain has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
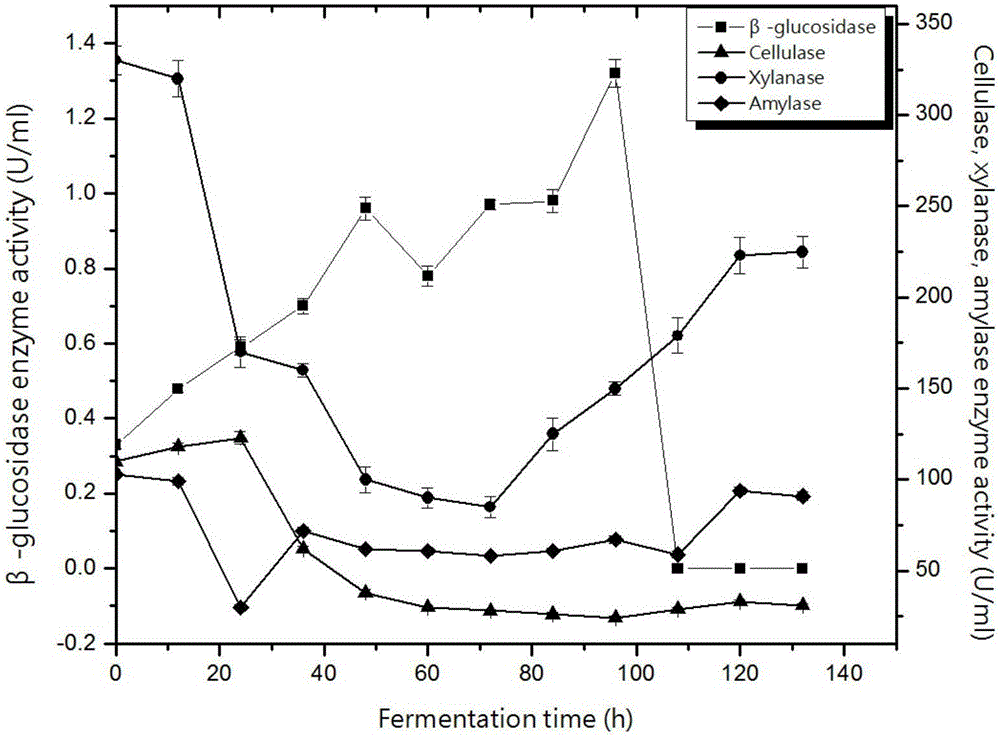
Aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain, fermentation broth, herbicide and active component enrichment method
The invention belongs to the technical field of herbicides, and discloses an aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain of which a fermentation broth has herbicidal activity, the fermentation broth and an herbicide which are prepared from the strain, and an enrichment method and an identification method of herbicidal active components in the aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain fermentation broth. By screening herbicidal activities of fermentation broths of 30 soil fungus strains, phenomena are found that inhibition rates of the aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain fermentation broth on roots and stemsof amaranthus retroflexus, descurainia sophia and portulaca oleracea reach 100%; and regarding pharbitis purpurea, only stems grow weakly, and an inhibition rate still reaches 77.8%. A weak-base anion-exchange resin D301 is screened out to serve as an enrichment resin of the herbicidal active components, and after adsorption, growth inhibition rates of a residual liquid on roots and stems of wheat are only 1% and 7% respectively; and finally, a 100% ethanol solution of 0.1 mol / L HCL is determined to serve as a desorption agent of the active components enriched by the D301 resin. The herbicidal activity of the fermentation broth of the L-27 strain has potential development value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Benzopyrone dipolymer and extracting method and application thereof
ActiveCN108383824AHigh antibacterial activityHigh cytotoxic activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBenzopyroneChemical control
The invention discloses a benzopyrone dipolymer and an extracting method and an application of the benzopyrone dipolymer. The extracting method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing a strain ofmedium endophytic fungi aspergillus tubingensis DS37 of decaisnea insignis in a strain culture; (2) fermenting and culturing the strain obtained in the step (1) in a fermenting and culturing medium,extracting with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and methyl alcohol for a plurality of times, mixing extracting solutions, filtering, recovering a mixed solvent, implementing vacuum concentration on a filtrate to obtain a coarse product of an extractum, and finally conducting column chromatography on silica gel to obtain the benzopyrone dipolymer. The prepared benzopyrone dipolymer has an excellenteffect on inhibiting staphylococcus aureus, and can be used in the technique of chemical control; the benzopyrone dipolymer is relatively strong in anti-A549 cell strain activity and provides a possibility for the development of the antitumor drug; and meanwhile, the benzopyrone dipolymer has a certain antioxidant activity.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aspergillus tubingensis and method for producing theabrownins through liquid fermentation of Aspergillus tubingensis
InactiveCN105925490AQuick conversionEasy to controlFungiMicroorganism based processesLaboratory cultureAspergillus tubingensis
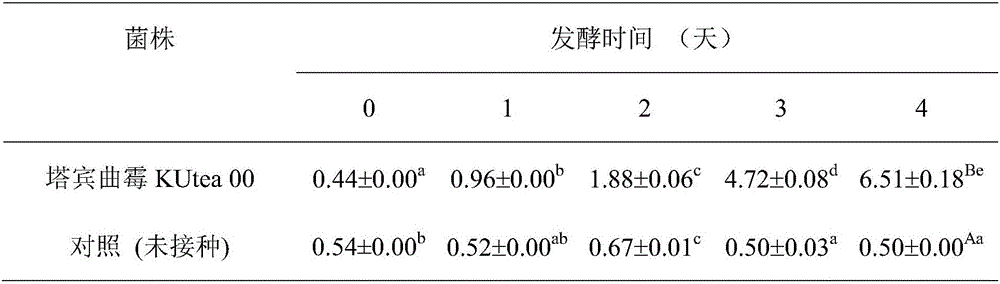
The invention relates to Aspergillus tubingensis and a method for producing theabrownins through liquid fermentation of Aspergillus tubingensis, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The producing strain of the invention is Aspergillus tubingensis KUtea 00, and Aspergillus tubingensis KUtea 00 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 30th, 2014, the preservation unit address is No.3. No.1 Courtyard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.10021. According to the invention, Aspergillus tubingensis KUtea 00 is inoculated in an aqueous extract of Camellia sinensis var. assamica which is pasteurized, after a single bacterial strain is purely cultured for 4 days in a shake flask, the content of theabrownins is 6.5g / L, and the volumetric productivity of theabrownins is 5.5 times higher than that of solid state fermentation. The Aspergillus tubingensis and the method for producing theabrownins by the liquid fermentation of Aspergillus tubingensis disclosed by the invention have the advantages of easy control of production conditions and environment, no limit to tea production seasons, automation, high efficiency and low cost. According to the invention, the strain is directly grown and reproduced in the aqueous extract of Camellia sinensis var, without adding any additional carbon sources and nitrogen sources, and polyphenols in the aqueous extract of Camellia sinensis var can be biologically transformed into macromolecule water-soluble theabrownins quickly.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lemon fermented cigarette perfume and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107041567AComfortable tasteImprove aftertasteTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentFlavorAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a lemon fermented cigarette perfume and a preparation method and application thereof. The cigarette perfume is acquired by the following steps: (1) performing pretreatment on lemons, and preparing a cultivation medium; (2) performing high temperature sterilization on the cultivation medium; (3) performing inoculation, using strain Aspergillus tubingensis GYC501 to inoculate the aseptic cultivation medium; (5) performing fermentation in a cultivation box; and (5) performing separation and purification to acquire the lemon fermented perfume which is clear and transparent, and has natural fragrance and brewing fragrance. The fragrance components of the lemon fermented cigarette perfume are coordinated with tobacco, can enrich the cigarette fragrance, make cigarette smoke soft and smooth, is comfortable in suction, can reduce the mouth spicy sense, and can improve the smoking taste.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGXI IND
Water quality modifier for fishery culture and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106630176AHigh activityImprove quality and quantityWater treatment compoundsBiological water/sewage treatmentBifidobacteriumEutrophication
The invention discloses a water quality modifier for fishery culture. The water quality modifier comprises the following components: peanut cake, corn flour, microelements, nitrobacteria, bifidobacterium, aspergillus tubingensis, green syrup, tea cake and acetylcholin esterase. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) taking the component raw materials in parts by weight; and (2) mixing the peanut cake, corn flour, microelements, tea cake and acetylcholin esterase, adding nitrobacteria, bifidobacterium, aspergillus tubingensis and green syrup, preparing a mixture into tablet or particle, thereby acquiring the water quality modifier. According to the invention, the aspergillus tubingensis, the green syrup and the acetylcholin esterase are used as the raw materials of the water quality modifier, so that the effects of improving water quality and purifying can be promoted; the adopted acetylcholin esterase can improve the activity of enzyme and bacteria in the modifier; the water quality modifier provided by the invention has a better purifying effect for water; the water quality modifier prepared according to the invention can effectively solve the problems of easiness in damaging and eutrophication of water quality in the fishery culture water, so that the quality and quantity of the aquatic products can be promoted.
Owner:南宁海世界生物科技有限公司
Biological decolorizing method of melanoidin pigment
ActiveCN103435167AVariety of decolorization methodsGood biological decolorization efficiencyBiological water/sewage treatmentLiquid mediumMelanoidin
The invention discloses a biological decolorizing method of melanoidin pigment. According to the technical scheme, aspergillus tubingensis is used for decolorizing the melanoidin pigment. The biological decolorizing method comprises the following steps of: culturing a strain with preservation number of CGMCC No. 7174 for 3 to 5 days at the temperature of 29-31 DEG C so as to prepare the aspergillus tubingensis, then inoculating aspergillus tubingensis spore suspension into a melanoidin pigment liquid medium, and carrying out shake cultivation for 4 to 10 days under the condition of controlling the temperature at 30-50 DEG C, the pH at 3.0-8.0 and the rotating speed at 50-350rpm for decolorizing reaction. The biological decolorizing method can be used for directly decolorizing the melanoidin pigment and has the advantages of safety, effectiveness, mild conditions, little secondary pollution, environmental protection, economy and the like; the decolorizing rate of the melanoidin pigment can reach up to 75%; a good strain and biological treatment method is provided for practical industrial wastewater treatment.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Bacterial strain with antiviral activity and application thereof
The invention relates to a bacterial strain with an antiviral activity and an application thereof. The bacterial strain is aspergillus tubingensis FJBJ11, and has already been registered and preserved in the common microorganism center of the china microorganism strain preservation management council on January 26th, 2015, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC No.10435. The bacterial strain is used for preparing a virus disease prevention preparation. According to the bacterial strain, an antiviral activity substance is separated and purified from bacterial strain fermentation liquid and developed into a microorganism source antiviral agent, and therefore the bacterial stain has wide application prospects. The activity substance prepared through the bacterial strain is high in antiviral activity, free from pollution to the environment, capable of being used for preventing and treating plant viruses caused by tobacco mosaic viruses (TMV), and suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
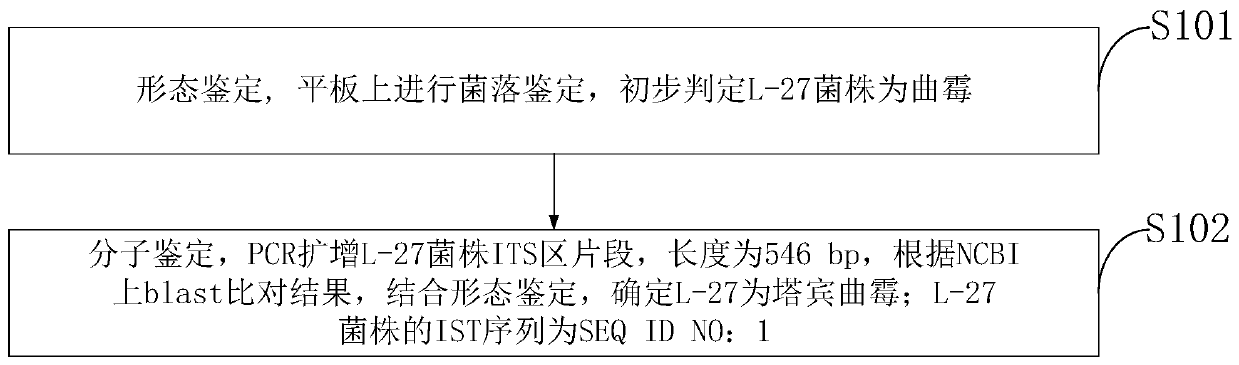
Separation method of aspergillus tubingensis and application of aspergillus tubingensis
PendingCN114262669AThe separation method is simpleEfficient degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a method for separating Aspergillus tubingensis and application of Aspergillus tubingensis, straws are taken as a carrier to extract microorganisms capable of degrading straws, strains can be massively propagated through culture, red brown to brown black conidia are obtained through separation, the conidia are spherical or radial, most of molecular sporophores are generated from a matrix, and most of the molecular sporophores grow from the matrix. Most spore production structures are double layers, and bacterial colonies of top sacs are densely generated; the method comprises the following steps: selecting bacterial colonies, activating the selected bacterial colonies, culturing the bacterial colonies by using an ABTS chromogenic solid culture medium and an aniline blue chromogenic solid culture medium, seeing that decolorized rings are generated after the bacterial strains are dyed, proving that the bacterial strains can secrete laccase and lignin peroxidase, amplifying ITS sequences of the screened bacterial strains, and comparing the sequences in NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information) to obtain similar sequence information. A phylogenetic tree is established by utilizing MEGA-X, the strain is determined to be Aspergillus tubingensis, and the Aspergillus tubingensis can be applied to lignin degradation and dye decoloration.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh1 by biotransformation of panax notoginseng saponins
ActiveCN110982869AOvercome the shortcomings of instability and difficult purificationGreen Fermentation MethodFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOT
The invention discloses a method for preparing 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh1 by biotransformation of panax notoginseng saponins. The 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh1 is prepared by biotransformation of panax notoginsengsaponins by adopting aspergillus tubingensis. The strain adopted by the method is convenient and easy to obtain, the method is simple to operate, the product conversion yield is high, and the methodcan be used for mass preparation of the 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh1. The method is simple, efficient, safe and green and is low in cost, and provides a new method for industrial production, food productionand new medicine preparation.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
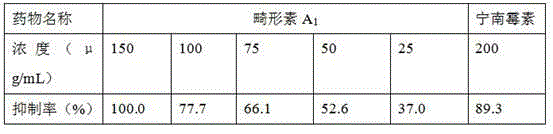
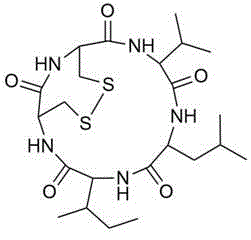
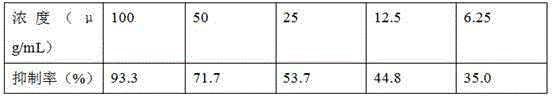
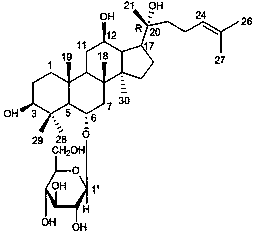
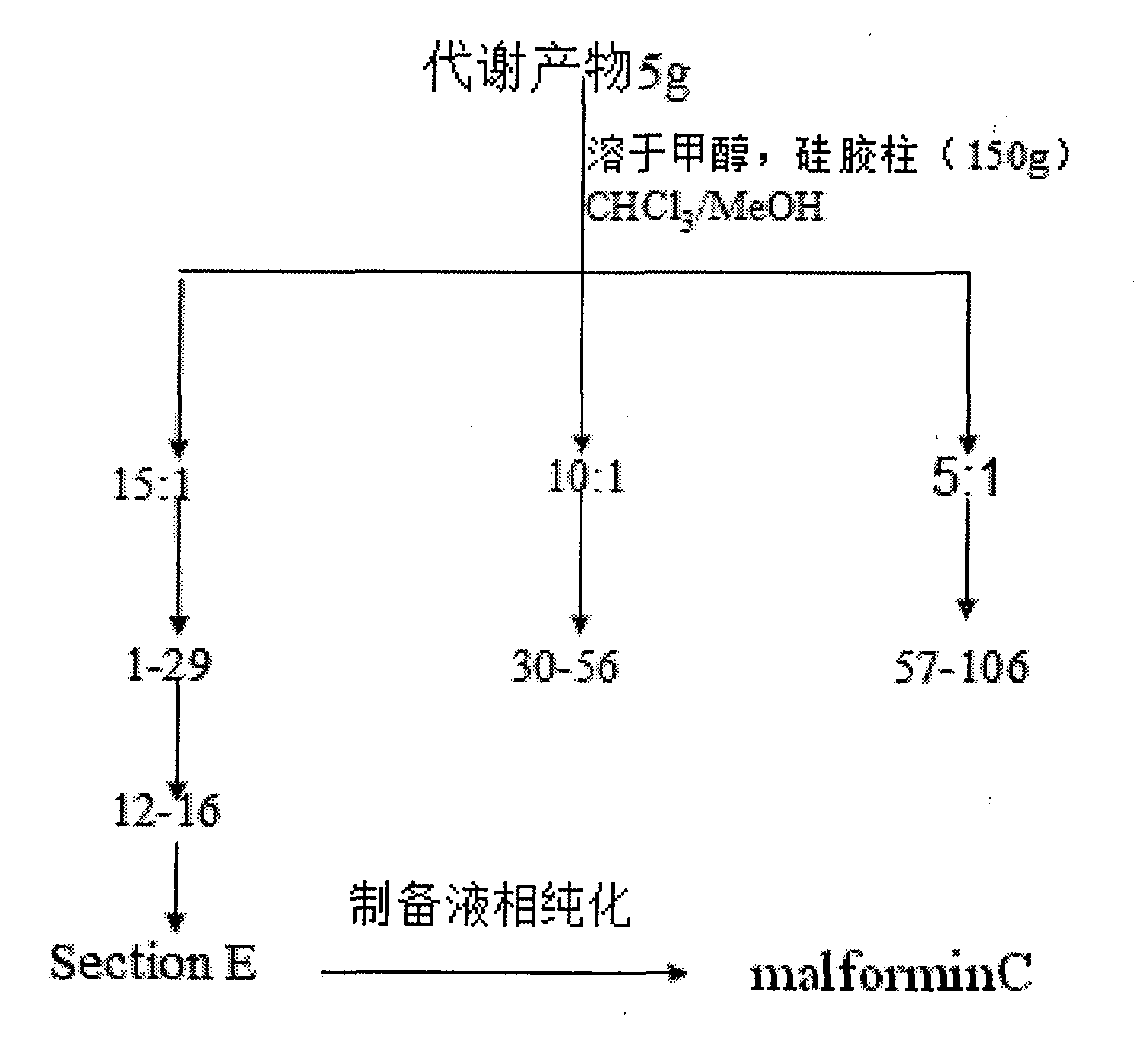
Preparation method for malformin C
The invention discloses a biological fermentation method for preparing a strain of malformin C and a method for separating and purifying malformin C from metabolite of the strain. The strain is separated from soil acquired in Phuket Island of Thailand on June, 2007; the bacterial colony of the strain is black on a PDA medium; and the stain is identified as Aspergillus tubingensis with a laboratory accession number of SYP2612 and a CGMCC accession number of XXX. The methods provided by the invention are advanced, employ low-cost raw materials, are suitable for large-scale industrial production, do not discharge harmful substances during production, have no pollution and no public hazard to a surrounding environment and accord with environmental protection requirements.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
Dicumarol derivative as well as extraction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108503616AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial goodAntibacterial agentsFungiSolventSilica gel
The invention discloses a dicumarol derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out strain culture on decaisnea insignis endophytic fungus aspergillus tubingensis DS37 in a strain culture medium; (2) carrying out fermentation culture on a strain obtained by step (1) in a fermentation culture medium; then extracting for a plurality of times by utilizing petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and methanol; combining extracting solutions and filtering; recycling a mixed solvent and decompressing and concentrating filtrate to obtain crude extract; finally, carrying out silica-gel column chromatography to obtain the dicumarol derivative. The dicumarol derivative prepared by the invention has good effects of inhibiting pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus lactis and alternaria alternata and can be used for agricultural prevention and control and pesticide prevention and control technologies; the dicumarol derivative has relatively strong activity of resisting A549, MCF-7 and HepG2 cell lines and provides possibility for developing anti-tumor medicines.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
'Tabin' aspergillus capable of producing pectase in high yield, and application in production of solid-state fermentation
A novel strain of Aspergillus tubingensis able to prepare the pectase with high output and its application in the solid-state fermentation of pectase are disclosed. The resultant pectase has high enzyme activity (more than 250 u / g at pH=2.5-4.2, or more than 120 u / g at pH=5.5).
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
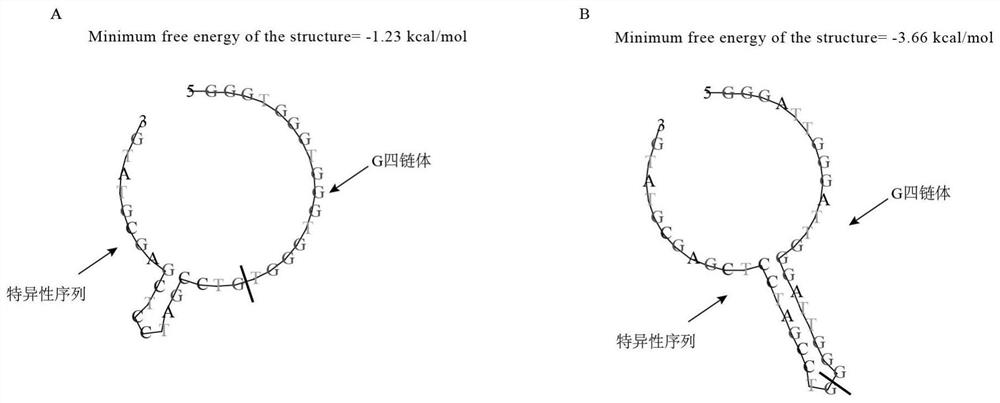
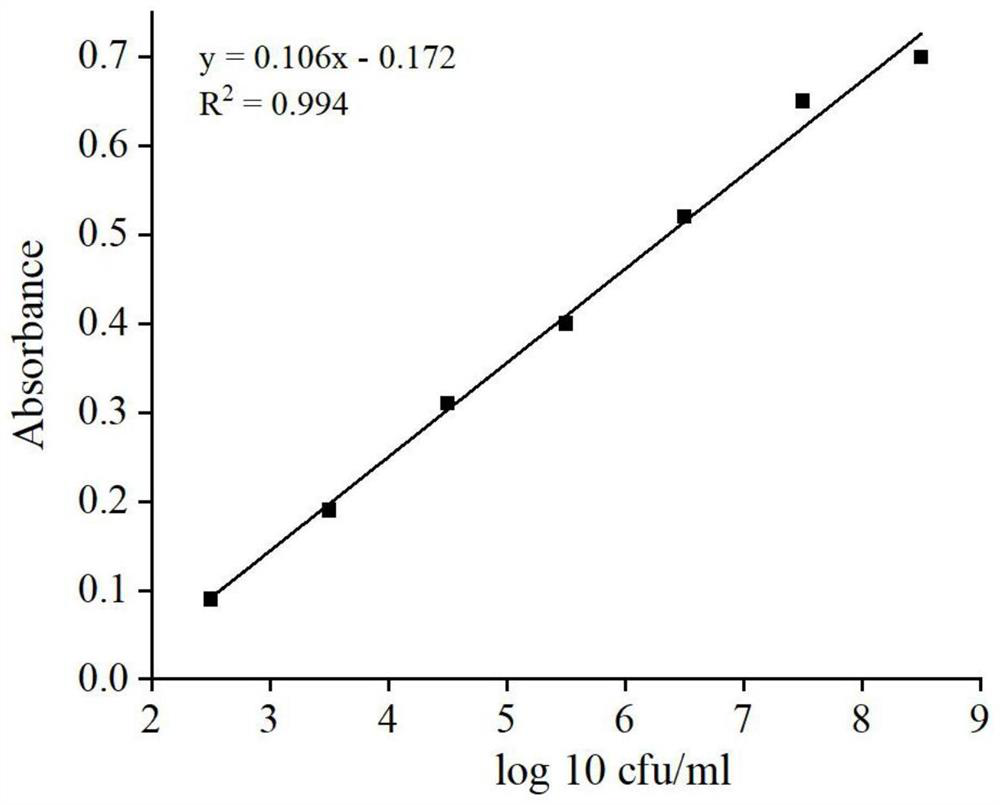
Probe for absolute quantification of Aspergillus tubingensis and application thereof
ActiveCN112782145ARealize the total detectionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a probe for absolute quantification of Aspergillus tubingensis and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biology, the field of fermentation and the field of detection. According to the Aspergillus tubingensis quantitative probe and the kit disclosed by the invention, the total amount detection of the Aspergillus tubingensis can be realized, expensive instruments are not required to be used when the Aspergillus tubingensis quantitative probe and the kit are used for detecting and quantifying the Aspergillus tubingensis, and the quantitative work can be quickly completed within 2.5 hours. Meanwhile, nucleic acid extraction does not need to be carried out on a sample used in the method. Based on the probe and the detection kit provided by the invention, the detection kit is used for Aspergillus tubingensis quantification, and has the characteristics of rapidness, convenience, cheapness and accuracy.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
In-situ remediation method of surface water polluted by hexavalent uranium using aspergillus tubingensis and phytate
InactiveCN109626598AWide variety of sourcesReduce repair costsFungiMicroorganism based processesSurface waterHydrolysis
The invention provides an in-situ remediation method of surface water polluted by hexavalent uranium using aspergillus tubingensis and phytate. The method comprises the steps that a modified Martin culture medium taking the phytate as the sole phosphorous source is added to the water body polluted by the hexavalent uranium, and aspergillus tubingensis spore suspension which is obtained by screening and separating from uranium mill tailing water reservoir sediments is inoculated. Under the threatening of uranium, and phosphatase is generated by the aspergillus tubingensis to promote the releasing of orthophosphate by the hydrolysis of the phytate. The orthophosphate and uranium in the water body are mineralized to generate a stable U-PO43 mineral, and therefore the remediation of the surface water polluted by the hexavalent uranium is achieved. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the remediation cost is low, the remediation effect is good and the interference onthe environment is low.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Aspergillus tubingensis and method for producing fructooligosaccharides through whole-cell catalysis of aspergillus tubingensis
InactiveCN105483027ANo purification involvedSimple methodFungiMicroorganism based processesLaboratory cultureAspergillus tubingensis
Owner:山东星光生物科技有限公司
High-yield pectinase strain and application thereof
InactiveCN107151631ALow source costSimple operation processFungiMicroorganism based processesPectinaseMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high-yield pectinase strain and application thereof. The high-yield pectinase strain is named aspergillus tubingensis Rn14-88A and is already preserved in the Common Microorganism Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on November 18th, 2016, and a preservation number of the high-yield pectinase strain is CGMCC No. 13184. The high-yield pectinase strain and the application have the advantage that the high-yield pectinase strain is screened from soil from vineyards.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
A probe for absolute quantification of aspergillus tubingensis and its application
ActiveCN112782145BRealize the total detectionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a probe for absolute quantification of Aspergillus tubingensis and an application thereof, belonging to the fields of biology, fermentation and detection. The Aspergillus tubingensis quantitative probe and kit of the present invention can realize the detection of the total amount of Aspergillus tubingensis, do not need to use expensive instruments for the detection and quantification of Aspergillus tubingensis, and can quickly complete the quantitative work within 2.5 hours. At the same time, the samples used in the present invention do not necessarily have to undergo nucleic acid extraction. The probe and detection kit based on the present invention are used for Aspergillus tubingensis quantification, and have the characteristics of fast, convenient, cheap and accurate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbial sludge dehydrating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN114409225AEasy to dehydrateTo achieve the purpose of deep dehydrationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBiological sludge treatmentBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a microbial sludge dehydrating agent and a preparation method thereof. The sludge dehydrating agent comprises an acidophilic bacteria solution, an aspergillus tubingensis solution, a bacteria secreted extracellular enzyme solution, a lysozyme solution, polyacrylate, wood cellulose, tourmaline powder, a polyacrylamide solution, a sludge stripping agent solution, a sludge wall breaking agent solution and a sludge surface structure modifier solution. By adding the acidophilic bacteria solution, the aspergillus tubingensis solution, the bacterial secreted extracellular enzyme solution and the lysozyme solution, under the combined action of acidophilic bacteria, aspergillus tubingensis, bacterial secreted extracellular enzyme and lysozyme, the adsorption and wrapping effects of sludge extracellular polymeric substances on water can be thoroughly destroyed, so that the sludge is easier to dehydrate, and the water content is reduced. And the biological cell wall structure in the sludge can be destroyed, so that the sludge floc structure is thoroughly disintegrated, water in the sludge can be fully released, and the purpose of deep dehydration of the sludge is achieved.
Owner:南京瑞特莱生态环境有限公司
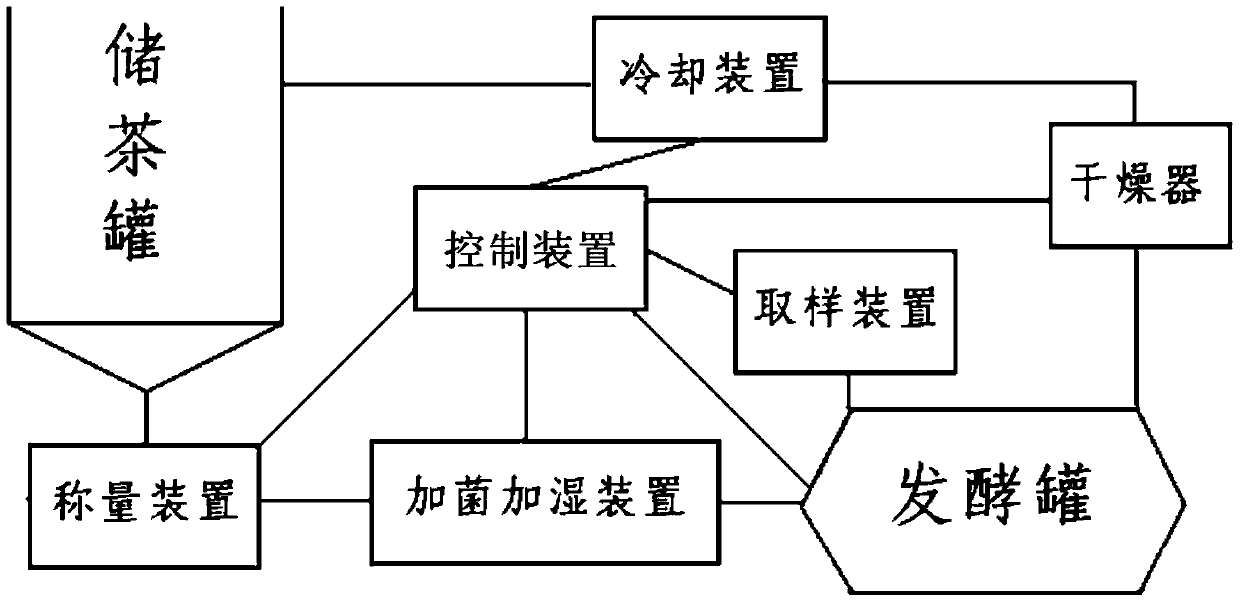
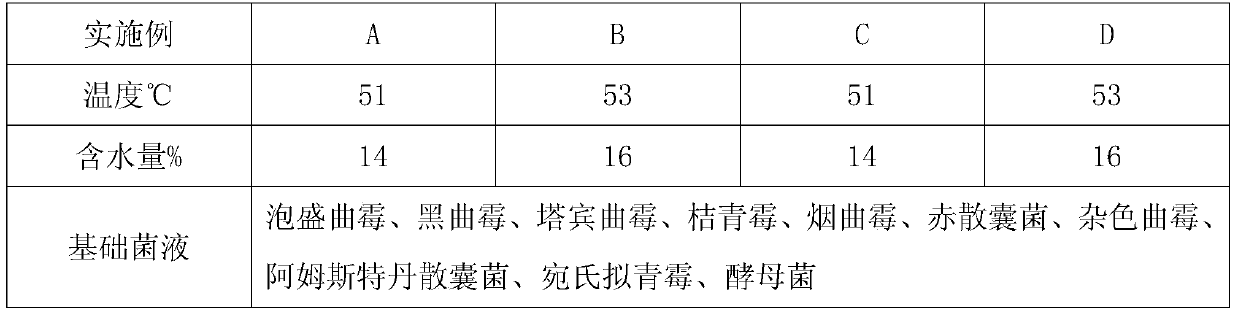
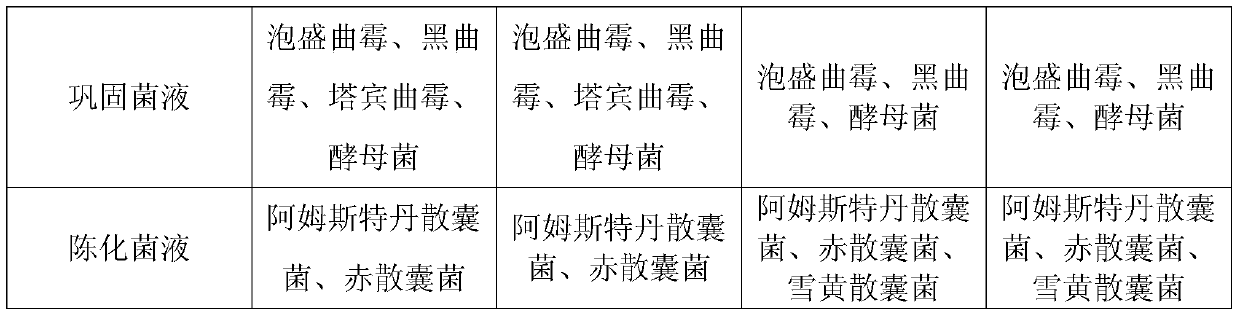
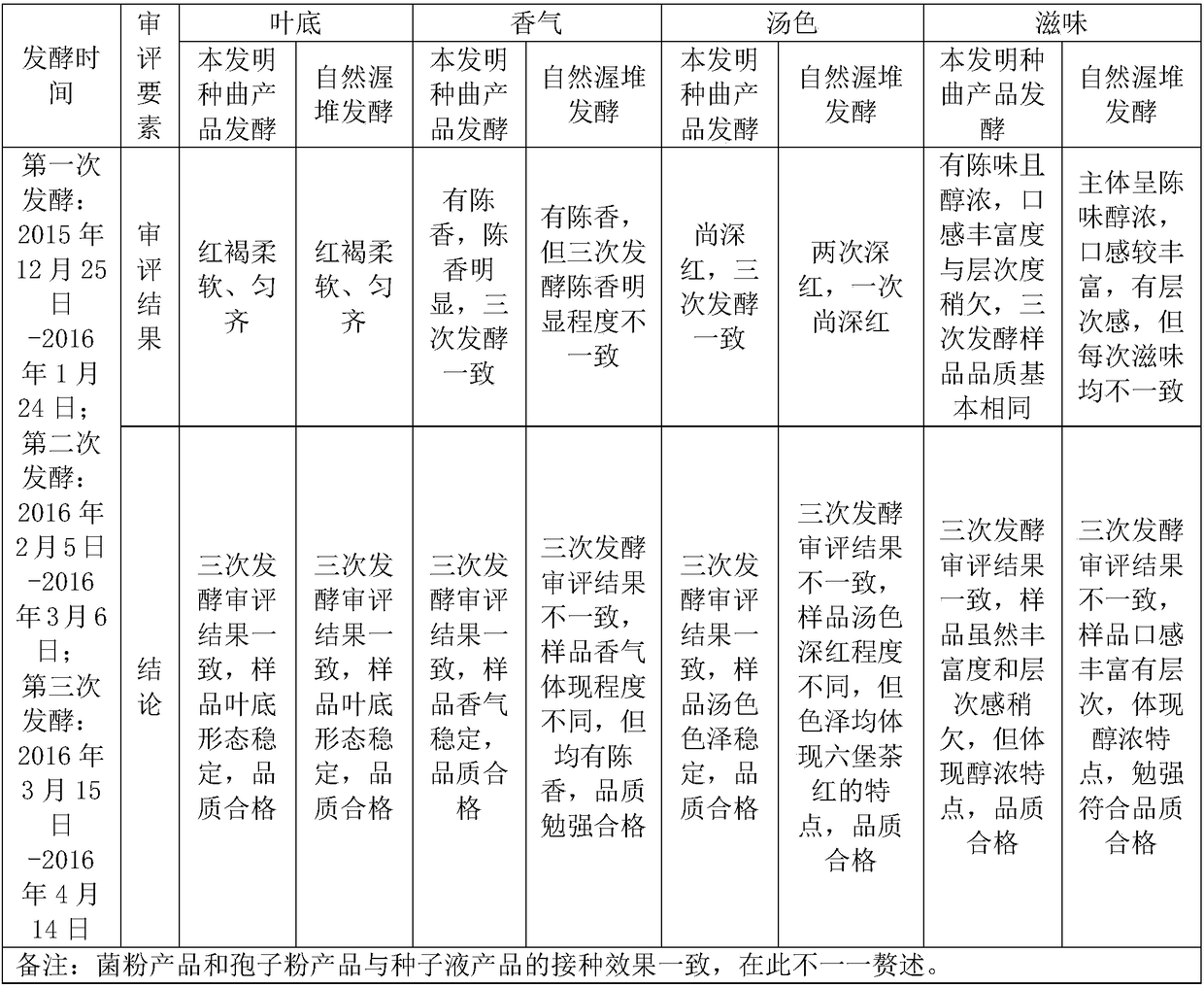
Liubao tea automatic stacking fermentation process and fermentation strain composition
ActiveCN105695339BImprove filtration efficiencyProduct quality and safetyFungiPre-extraction tea treatmentPaecilomyces variotiiAutomatic control
The invention discloses a Liupao tea automatic pile fermentation strain composition which comprises a base bacterium solution, a consolidation bacterium solution and an aging bacterium solution. The bacterium solutions contain Aspergillus awamori, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus tubingensis, penicillium citrinum, Aspergillus fumigatus, Eurotium rubrum, Aspergillus versicolor, Eurotium amstelodami, Paecilomyces variotii, Eurotium niveoglaucum, saccharomycetes and other beneficial microorganisms. On such basis, the inventor establishes the corresponding fermentation technique and equipment; and on the premise of not changing the upstream and downstream main production techniques of the original pile fermentation, the beneficial microorganism florae are added to control the growth of harmful infectious microbes, thereby enhancing the fermentation efficiency, shortening the pile fermentation period, and keeping the special thick flavor of the traditional Liupao tea. The pile fermentation automatic control system is utilized to dynamically monitor and control the changes on temperature, humidity and florae in the whole fermentation process, thereby implementing automation, continuity and high efficiency of the production technique, and ensuring the Liupao tea product to have safe and reliable quality and high and stable quality.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Desertorin B, and extraction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108640896AHigh antibacterial activityGood antitumor activityBiocideOrganic chemistrySolventEthyl acetate
The invention discloses Desertorin B, and an extraction method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the Desertorin B is C25H20O8. The extraction method is as the follows: (1) carrying outstrain cultivation on decaisnea insignis endophytic fungi aspergillus tubingensis DS37, (2) carrying out fermentation cultivation on the strain obtained in the step (1) in a fermentation culture medium, then carrying out extraction with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and methanol for a plurality of times, mixing the extracting solutions, carrying out filtering, recovering the mixed solvent, carrying out reduced pressure concentration on the filtrate to obtain a crude extract, and finally carrying out silica gel column chromatography to obtain the Desertorin B. The Desertorin B prepared by themethod has a good effect of inhibiting setosphaeria turcica, and can be used for the technologies of agricultural prevention and control and chemical prevention and control. In addition, the Desertorin B has strong activity for resisting MCF-7 and HepG2 cell lines, and can provide a possibility for the development of anti-tumor medicines. At the same time, the Desertorin B has certain antioxidantactivity.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
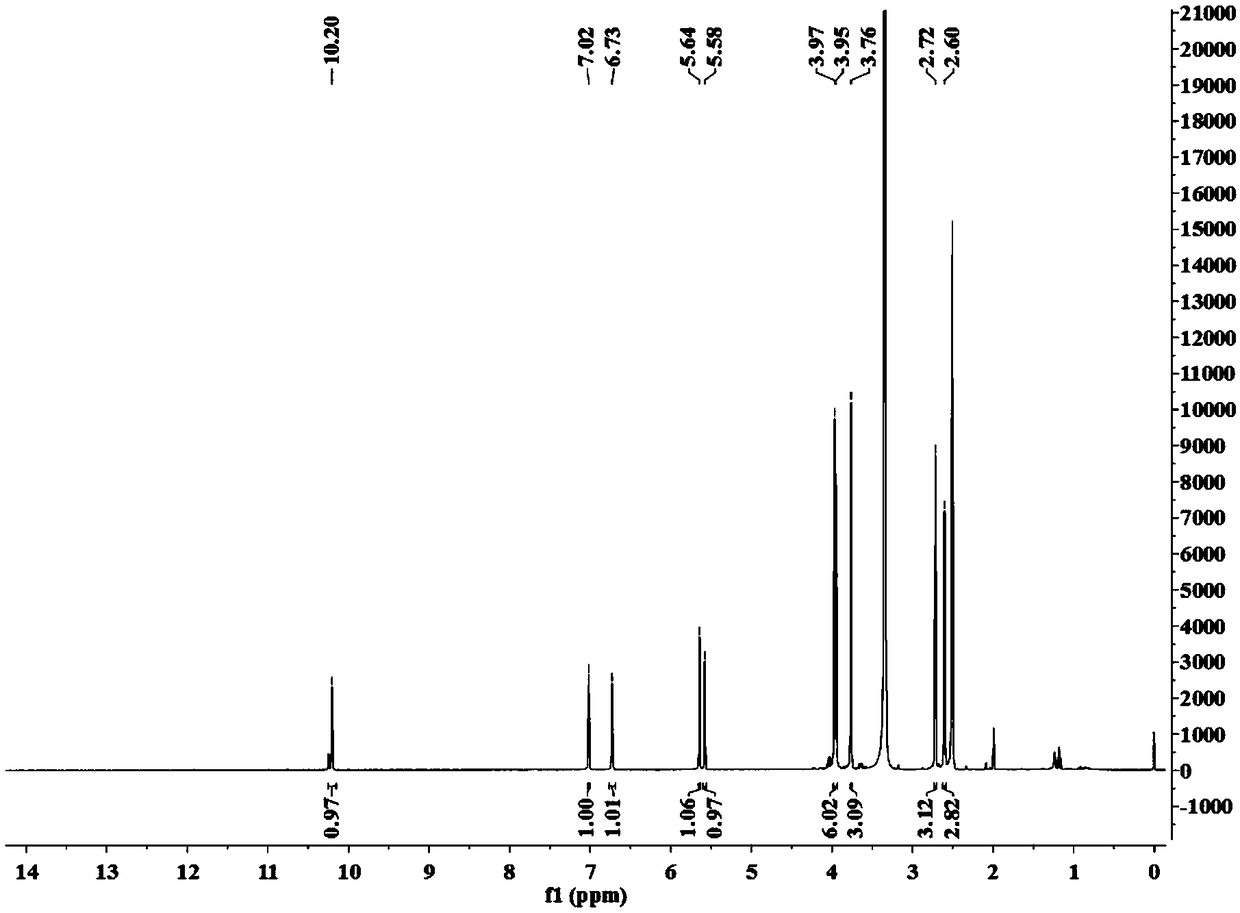
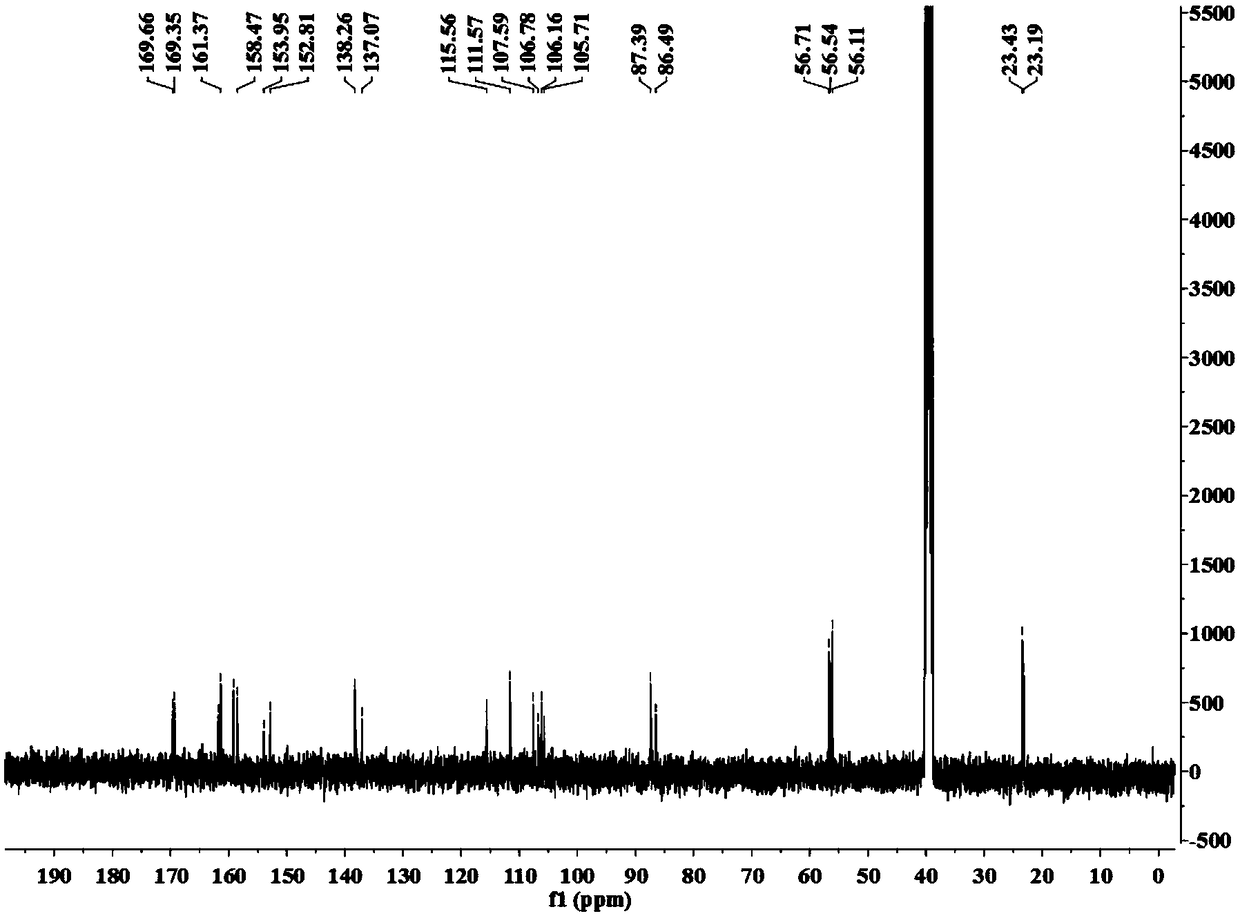
Liupao tea fermentation seed koji and Liupao tea fermentation seed koji product preparation method
The invention discloses a Liupao tea fermentation seed koji product preparation method, which comprises: separating Aspergillus tubingensis as Liupao tea fermentation seed koji from Liupao tea, and preparing the Liupao tea fermentation seed koji product from the Aspergillus tubingensis. According to the present invention, with the application of the Aspergillus tubingensis as the Liupao tea fermentation seed koji in the fermenting, the only one main strain Aspergillus tubingensis and the one determined inoculation time are used, such that the final product has characteristics of red tea soup,infusion resistance, old fragrance and mellow taste of the Liupao tea, and the stability of the product quality after each fermentation can be ensured.
Owner:云南大益微生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com