Separation method of aspergillus tubingensis and application of aspergillus tubingensis
A technology of Aspergillus tabin and separation method, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, separation microorganisms, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of limited degradation efficiency and limited types of microorganisms, and achieves efficient and simple separation methods and promotes efficient utilization. , the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
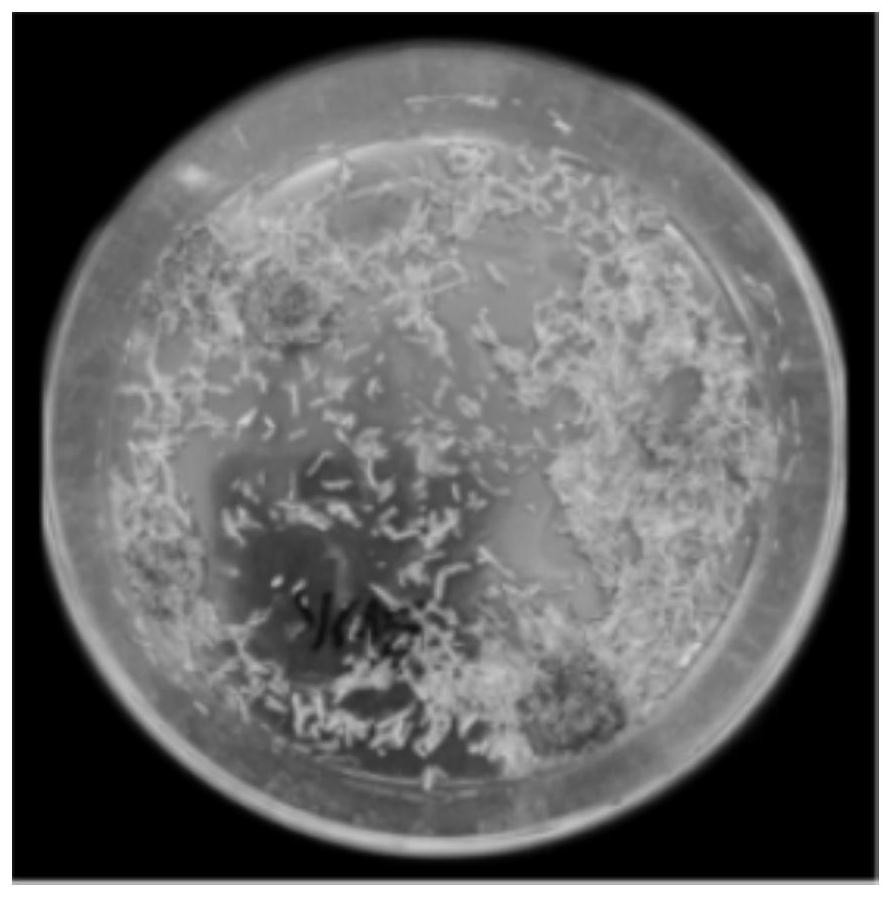
[0054] according to Figure 1-Figure 4 As shown, the present embodiment proposes that the process of isolating bacterial strains from stalks is specifically:
[0055] A method for isolating Aspergillus tubingensis, comprising the following steps:
[0056] Step S1: material preparation, clean the straw and dry it at room temperature to a water content of 6.5% to 7.3%, then cut it into straw grains with a length of 0.3 to 1.5 cm; the straw is rice straw, and the initial water content of the straw is 8.1 ~9.2%;
[0057] Step S2: Cultivate, weigh the straw grains and place them in a clean and sterilized glass petri dish, add a 1% sterilized sucrose solution, the ratio of the straw grains to the sterilized sucrose solution is 0.3g / mL, and place in the incubator Incubate in the dark at a constant temperature of 28°C for 10 days, then transfer to a Erlenmeyer flask, then place in a constant temperature incubator at 40°C, and shake at 220rpm for 1 hour to obtain a suspension;
[00...
Embodiment 2
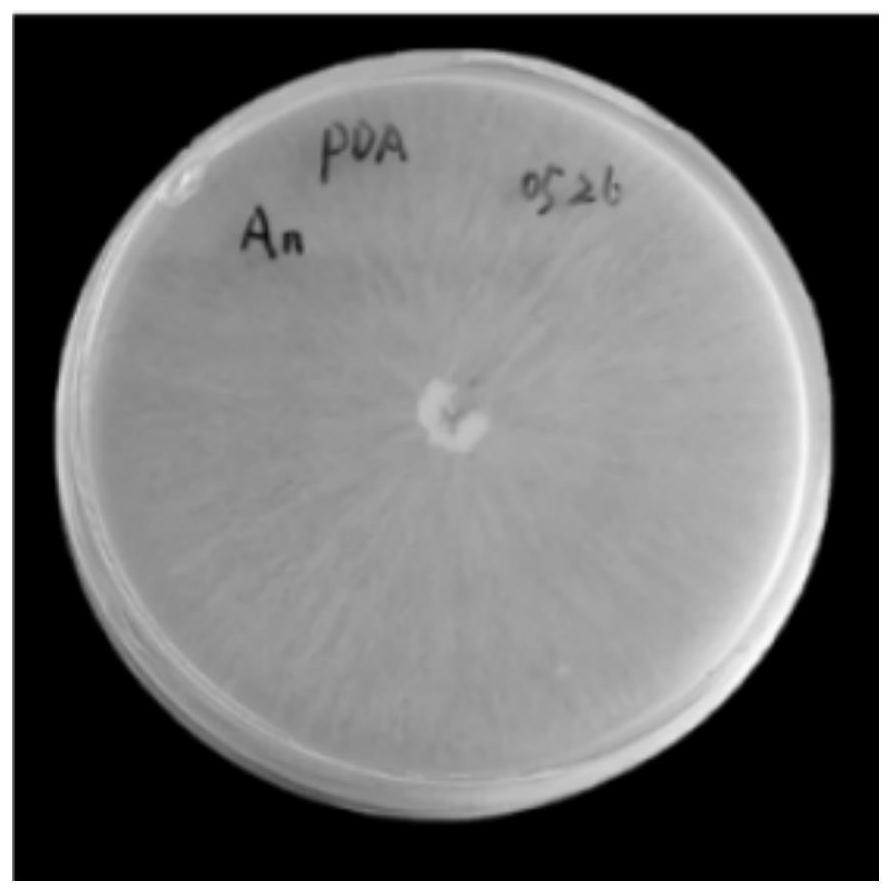
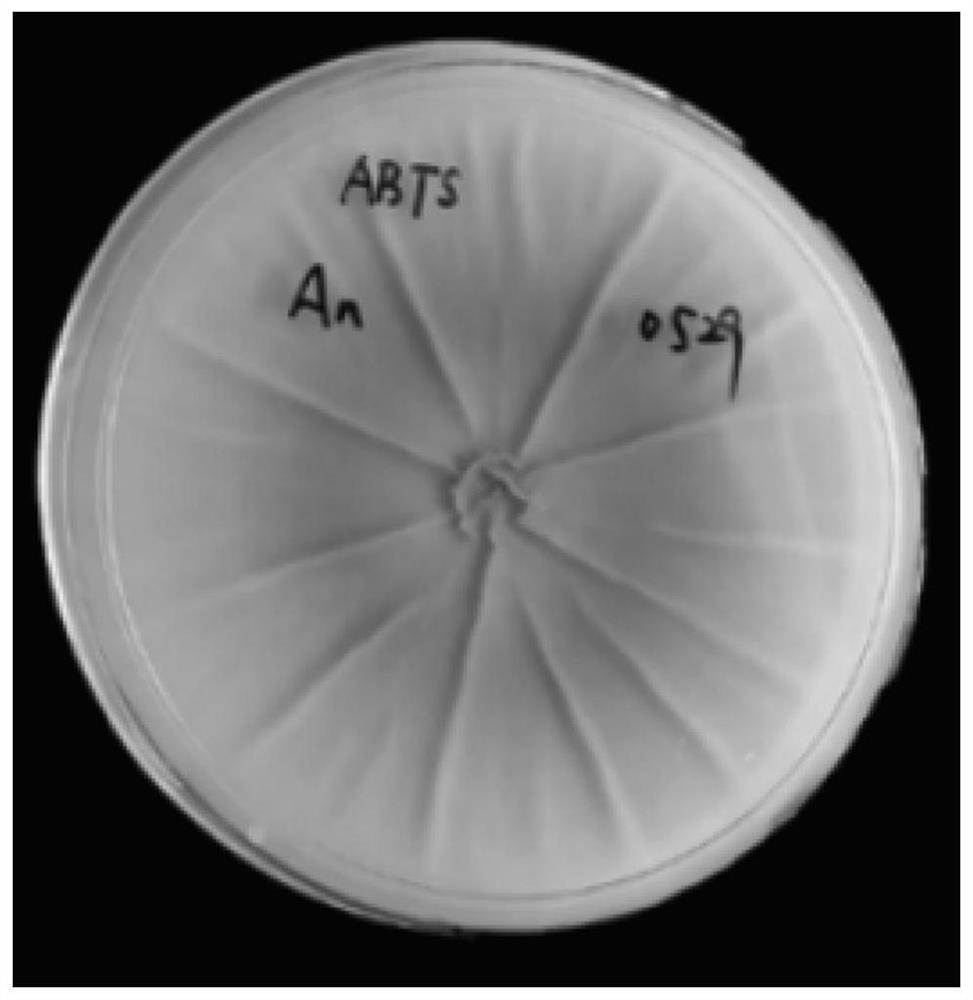
[0069] The bacterial strain ST-3 that obtains according to the isolation method of above-mentioned Aspergillus tubingensis, reference Figure 5-Figure 6 , observe the strain morphology, hyphae and spore morphology of the strain in the aniline blue color-developing solid medium under a microscope, Bar=200 μm, and its morphological identification: cultured on the aniline blue color-developing solid medium for 5 days at 30°C, the colony diameter Reaching 68-73mm, the conidia heads are spherical or radial, and gradually spread outward from the center of the fungus, with a diameter of 155-420μm. Most of the molecular spore peduncles are born from the matrix, with smooth walls and dense apical vesicles, which are spherical or nearly spherical. The diameter is 25-62 μm, and the sporulation structure is mostly double-layered. The spores are mostly spherical or nearly spherical, and the wall is rough. From the morphological point of view, the fungus belongs to the genus Aspergillus.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com