Patents
Literature
31 results about "Soil fungi" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
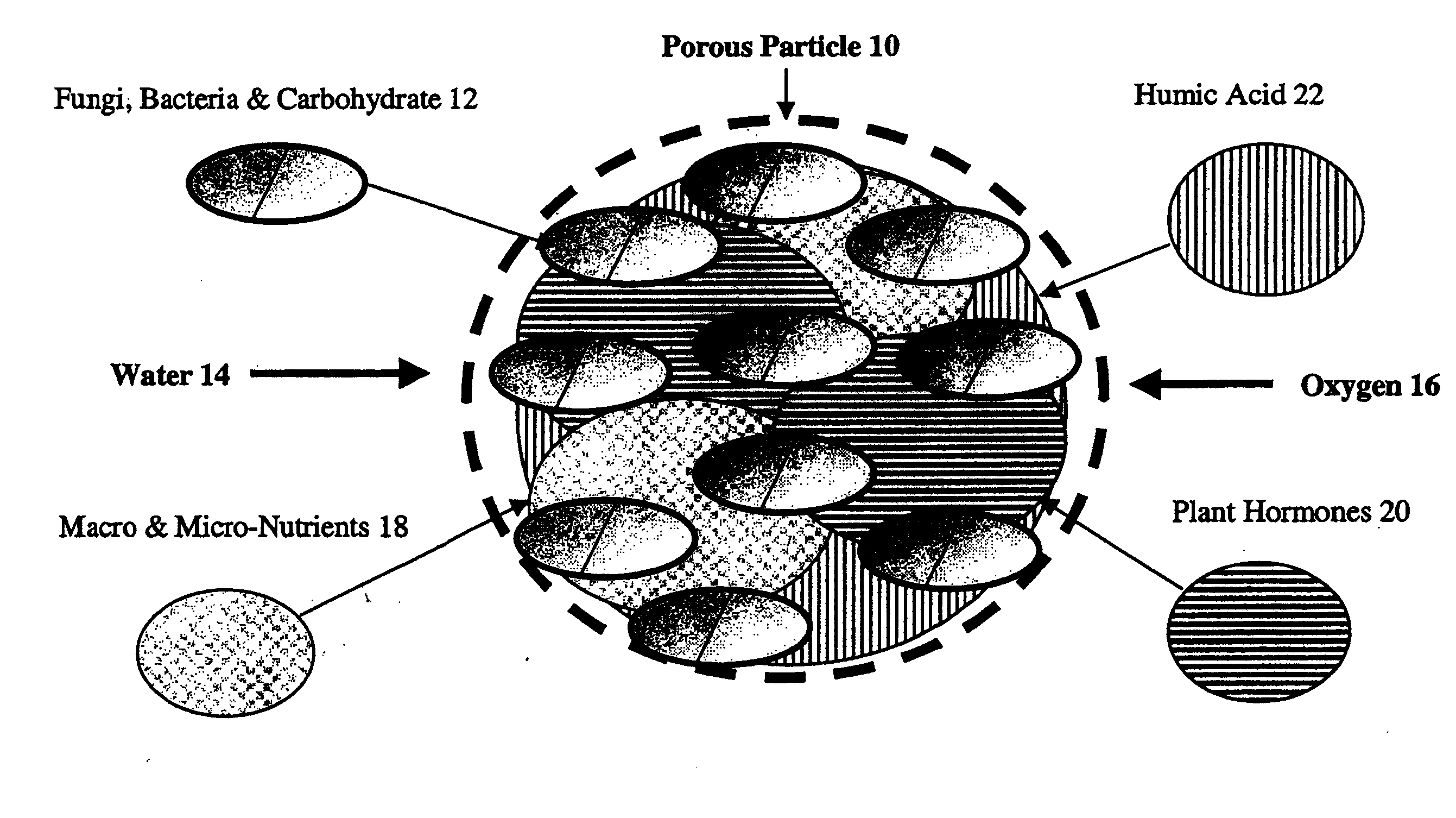
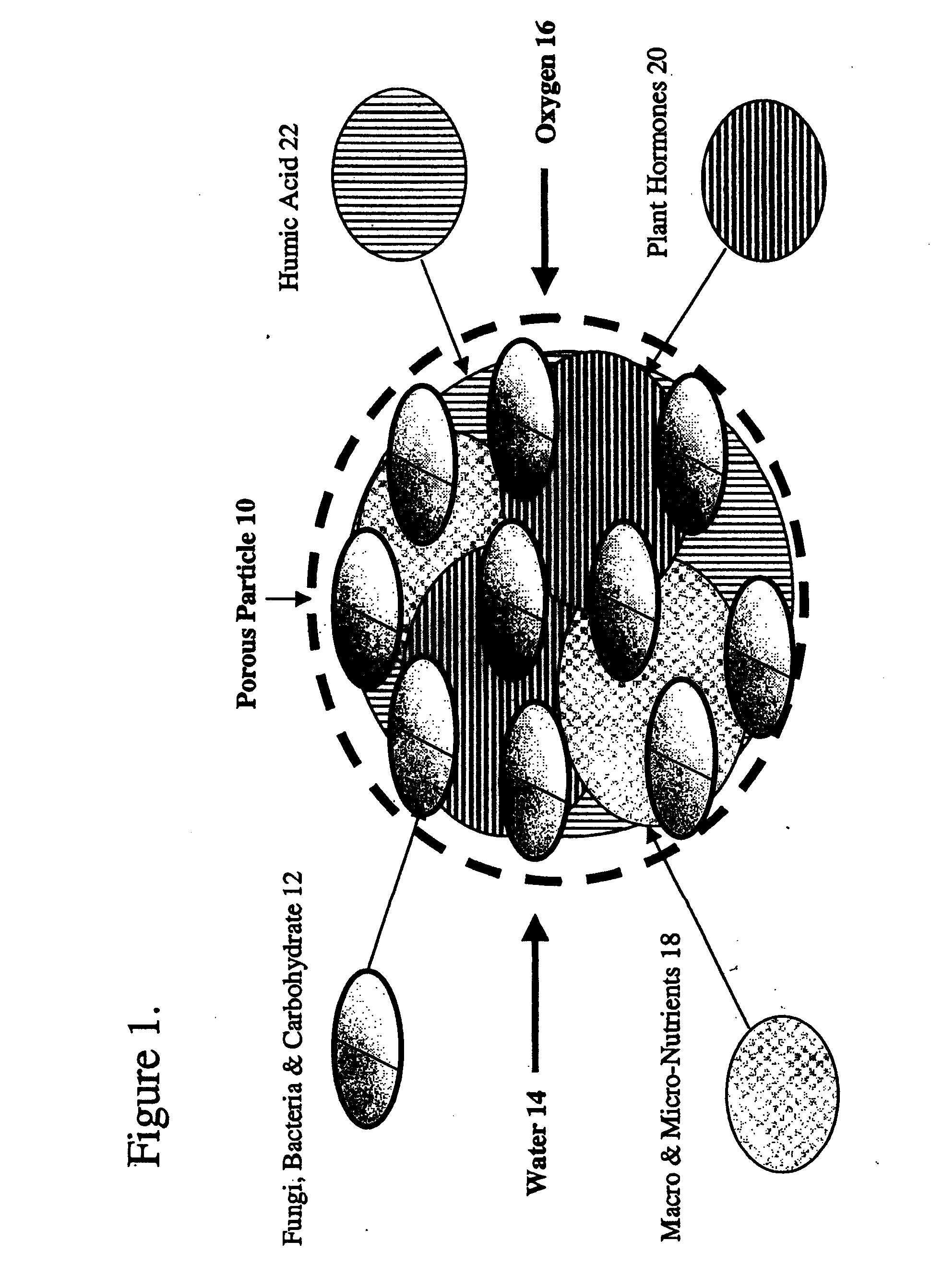
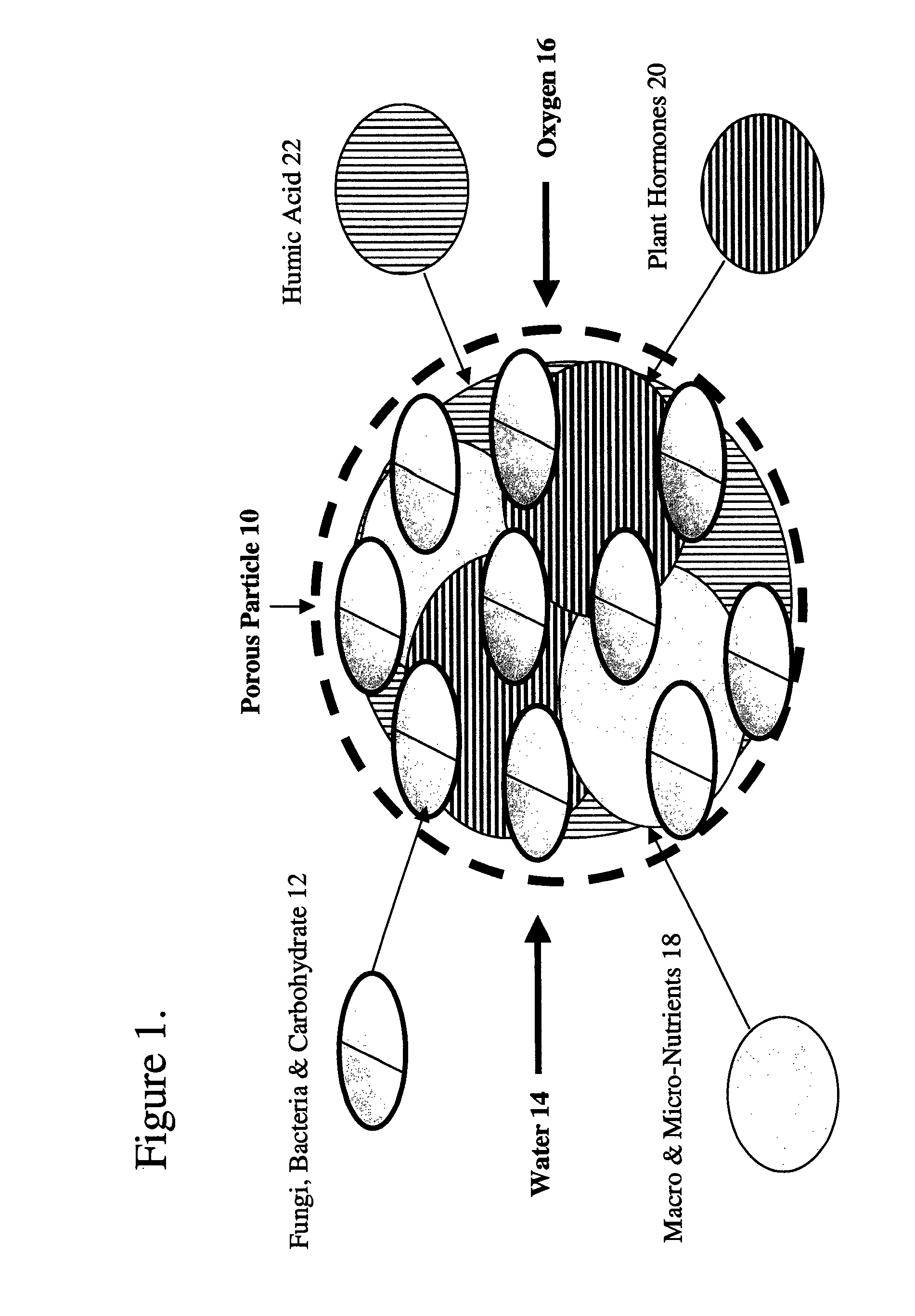
Biological soil nutrient system
ActiveUS20110003693A1Facilitate food and water usageSuccessful soil treatmentBiocideAnimal repellantsGrowth promotingBiology
A biological soil nutrient system that combines beneficial soil fungi and bacteria in a growth promoting nutrient medium, embedded in an inorganic porous ceramic particle for direct delivery during soil aerification to the rhizosphere of adventitious plants, including sports turf, landscape and agricultural applications.
Owner:PROFILE PRODS LLC
Biological soil nutrient system
ActiveUS7854926B2Facilitate food and water usageSuccessful soil treatmentBiocideDead plant preservationSoil fungiGrowth promoting
Owner:PROFILE PRODS LLC
Bacterial strain for preventing and treating soil-borne fungal diseases of peanuts in continuous cropping and applications of bacterial strain
The invention relates to a bacterial strain for preventing and treating soil-borne fungal diseases of peanuts in continuous cropping and a fungicide of the bacterial strain, wherein the bacterial strain is Pseudomonas protegens, and is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC No.11539. The 16s rRNA base sequence of the bacterial strain is shown as SEQ ID No:1. The bacterial strain has high activity in generating chitinase (degrading cell walls of pathogenic bacteria hyphae), and has the obvious degrading capacity for various soil-borne fungous pathogenic bacteria mycelia, such as fusarium, rhizoctonia and verticillium chlamydosporium. For the fungicide provided by the invention, the seed dressing use amount is only 20-30 kg / mu normally, the fungicide can be used for effectively preventing and treating the soil-borne fungous diseases, such as root rot, damping off and southern blight frequently occurring in peanuts continuously planted in dry fields, the control effect achieves 55% or above, in addition, the bacterial strain has the advantages of small use amount, wide antimicrobial spectrum, obvious yield-increasing effect and the like, so that the influence of the soil-borne diseases on the yield loss of the peanuts in continuous cropping is effectively alleviated.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Suspension seed coating agent containing tebuconazole and hymexazol
InactiveCN103719106APromote growth and developmentGood control effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseRoot growth
The invention relates to a suspension seed coating agent containing tebuconazole and hymexazol, and particularly relates to a suspension seed coating agent with an effective component of a binary compound of tebuconazole and hymexazol, and a preparation method thereof, wherein the mass ratio of tebuconazole and hymexazol in the effective component is 1-80:80-1. The suspension seed coating agent is mainly used for controlling various cereal crop diseases such as rust disease, powdery mildew, net blotch, root rot, gibberellic disease, smut, seed-infecting zonate spot disease, and the like, has significant control effect on pathogenic bacteria of soil fungi, fusaria, root rotting fungi, rhizoctonia, pythium, straw rotting fungi, corticiales and the like, and has the effects of promoting crop root growth, promoting rooting, strengthening seedlings, and improving survival rate.
Owner:HAILIR PESTICIDES & CHEM GRP
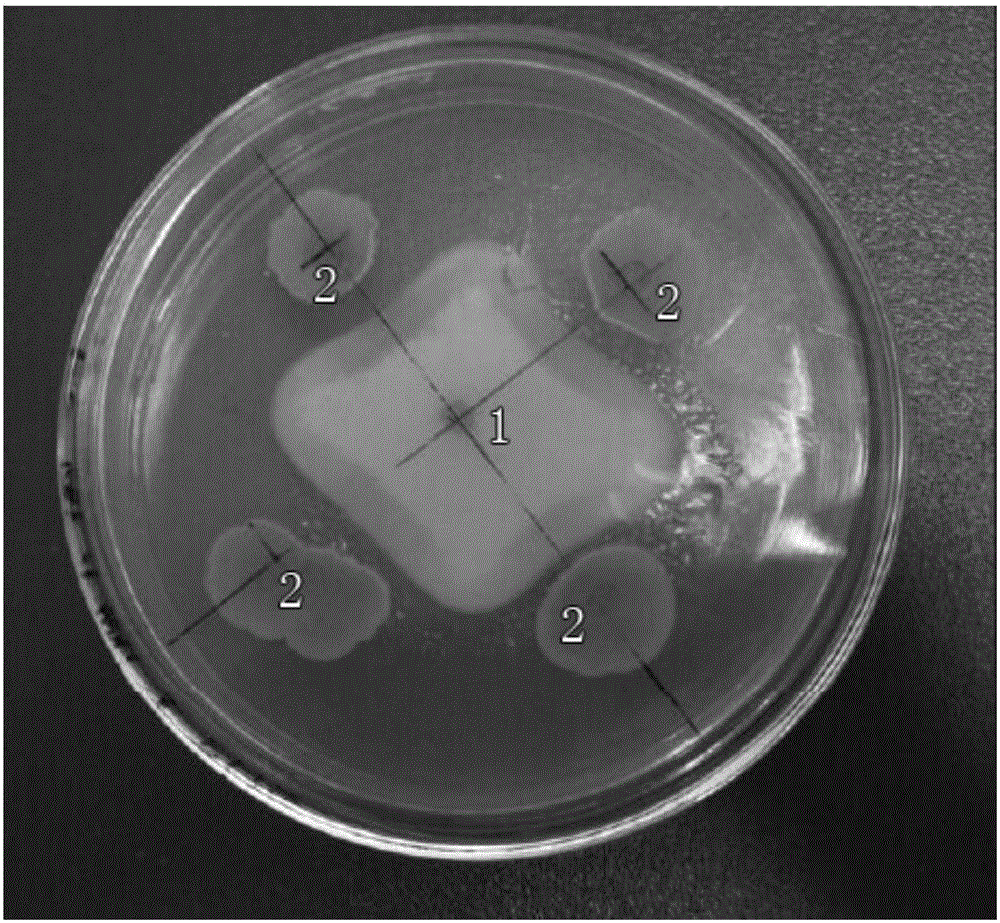
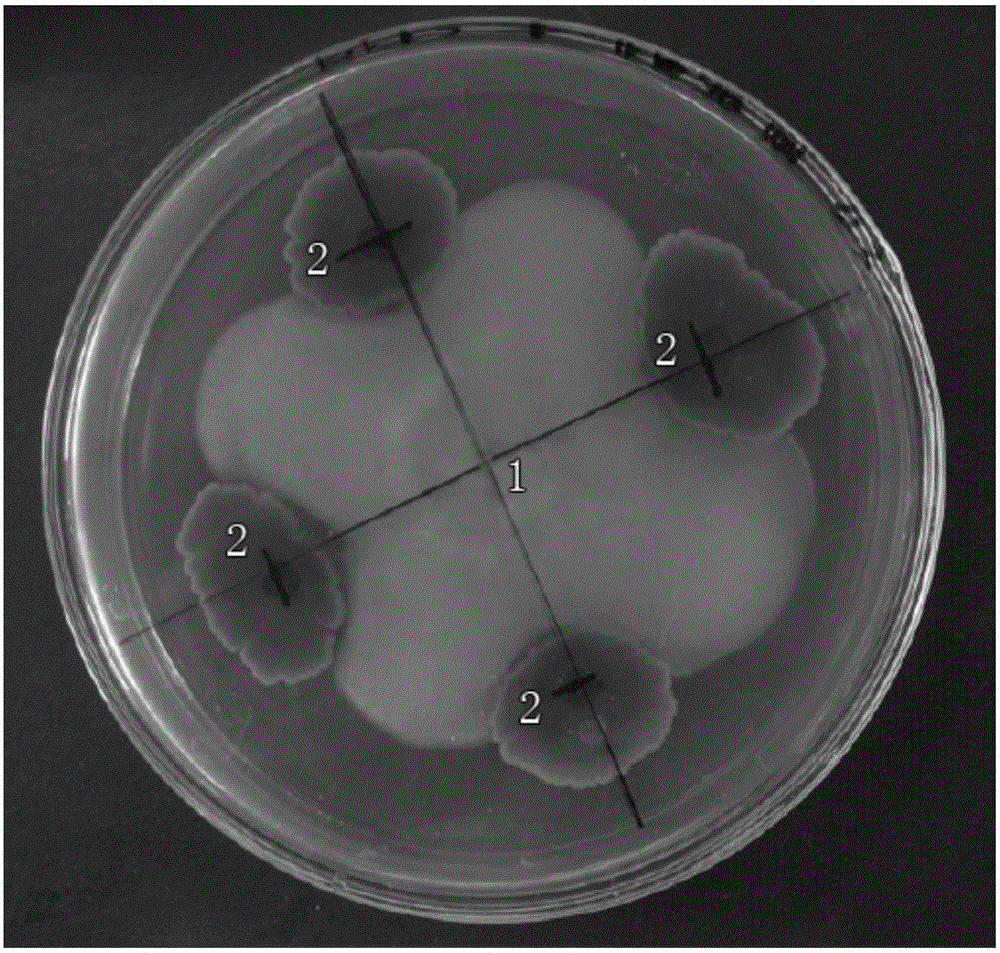
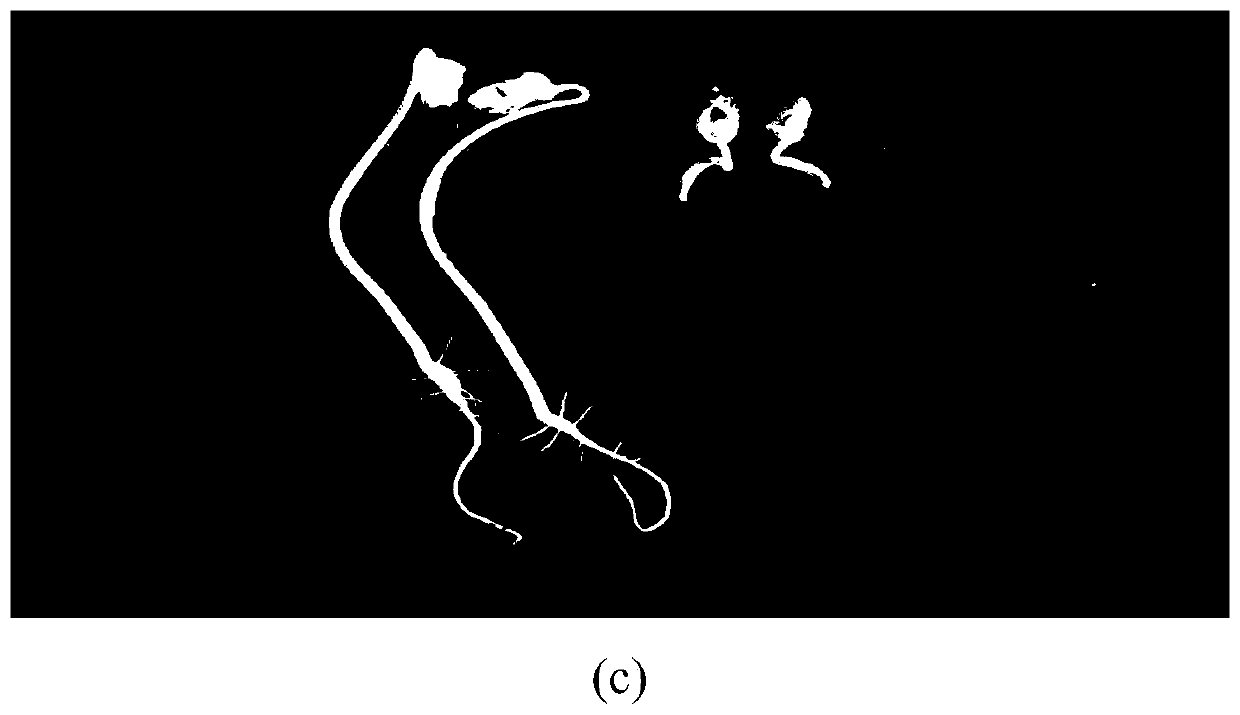
Aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain, fermentation broth, herbicide and active component enrichment method
The invention belongs to the technical field of herbicides, and discloses an aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain of which a fermentation broth has herbicidal activity, the fermentation broth and an herbicide which are prepared from the strain, and an enrichment method and an identification method of herbicidal active components in the aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain fermentation broth. By screening herbicidal activities of fermentation broths of 30 soil fungus strains, phenomena are found that inhibition rates of the aspergillus tubingensis L-27 strain fermentation broth on roots and stemsof amaranthus retroflexus, descurainia sophia and portulaca oleracea reach 100%; and regarding pharbitis purpurea, only stems grow weakly, and an inhibition rate still reaches 77.8%. A weak-base anion-exchange resin D301 is screened out to serve as an enrichment resin of the herbicidal active components, and after adsorption, growth inhibition rates of a residual liquid on roots and stems of wheat are only 1% and 7% respectively; and finally, a 100% ethanol solution of 0.1 mol / L HCL is determined to serve as a desorption agent of the active components enriched by the D301 resin. The herbicidal activity of the fermentation broth of the L-27 strain has potential development value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Special composite biological organic fertilizer for rice planting
InactiveCN108623406AMeet growth needsPromote growth and developmentExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a special composite biological organic fertilizer for rice planting. The special composite biological organic fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of pig manure, 4-7 parts of sugar dregs, 4-7 parts of sesame cakes, 20-30 parts of charcoal, 5-8 parts of rapeseed cakes, 3-7 parts of bamboo carbon powder, 4-9 parts of rice hull, 2-6parts of steamed bone meal, 3-5 parts of epsilon-polylysine, 1-4 parts of chitosan, 5-12 parts of potassium fulvic acid, 6-9 parts of coconut residues, 3-7 parts of nano kieselguhr, 3-12 parts of wheat shell carbon, 5-10 parts of humus, 12-18 pats of protein mud, 2-5 parts of microbial agents, 1-6 parts of a plant growth regulator and 1-3 parts of water-soluble trace elements. The organic fertilizer disclosed by the invention not only is rich in nutrition component such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and organic matters, but also meets rice growth requirements; by adopting the special composite biological organic fertilizer, growth and development of rice can be well improved, soil enzyme activity can be improved, and fungus community structures of soil are remarkably improved with the combination of the components.
Owner:桐城市天泰农业种植专业合作社
Oxygenating water-saving irrigation method for Lingwu long jujube
InactiveCN107493777APrecise control of dissolved oxygenOxygen utilizationClimate change adaptationWatering devicesSoil fungiSweetness
The invention provides an oxygenating water-saving irrigation method for jujube. By combining a physical method with a chemical method, the amount of dissolved oxygen in water can be accurately controlled; meanwhile, an underground irrigation water supply mode is adopted, so that oxygen is fully utilized, fungi, bacteria and actinomycetes in rhizosphere soil of jujube trees and related enzyme activities are improved, and further the yield and the sweetness of the jujube are effectively improved.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Method for degrading residual tylosin in medicine slag
The invention relates to a method for degrading residual tylosin in herb residues, in particular to a method for degrading residual tylosin in herb residues by utilizing microorganism, which mainly comprises the steps of preparation of soil fungi suspension, preparation of strain breeding cultural medium, preparation of strain domestication cultural medium, preparation of strain screening cultural medium, preparation of stain activation and rejuvenation cultural medium, preparation of drug residues fermentation cultural medium, screening of degrading strain and so on. The invention provides a compound bacterium that can be screened and cultured to degrade the residual tylosin in herb residues, while strains for degrading the residual tylosin in herb residues can be acquired by being separated and purified from the compound bacterium. Then the strains can be prepared to be corresponding herb residue cultural medium, which can degrade the residual tylosin in herb residues after being accessed the fermentation of the degrading bacteria.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
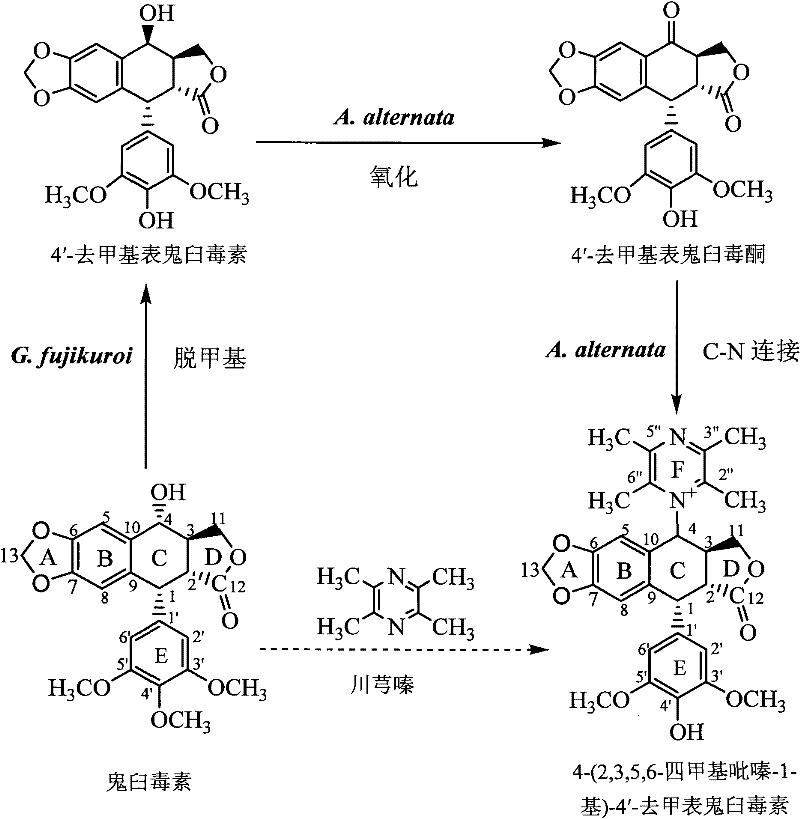
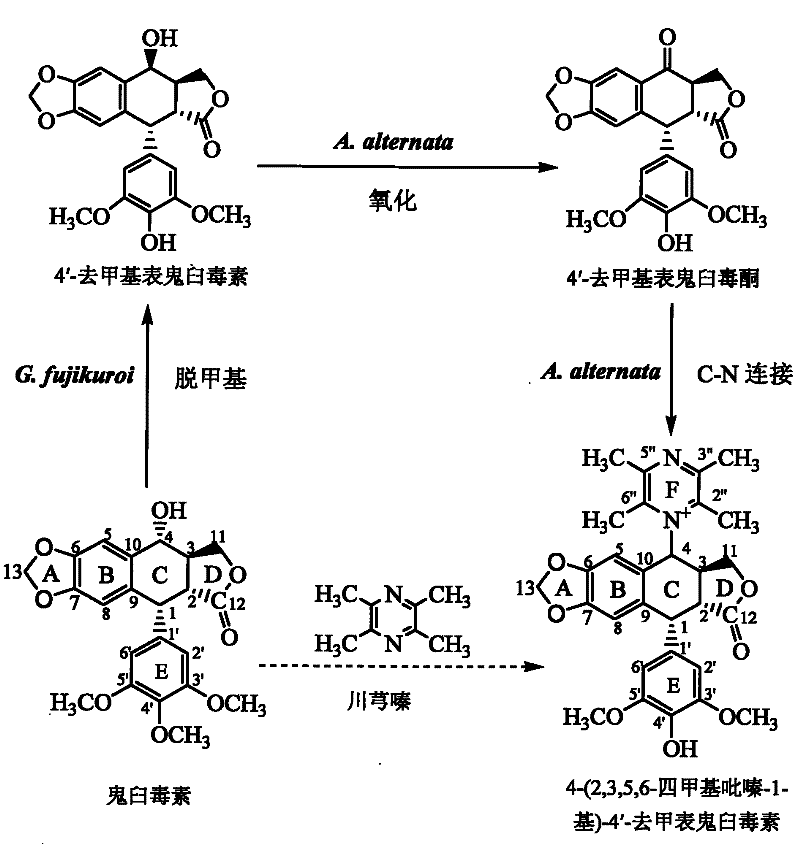
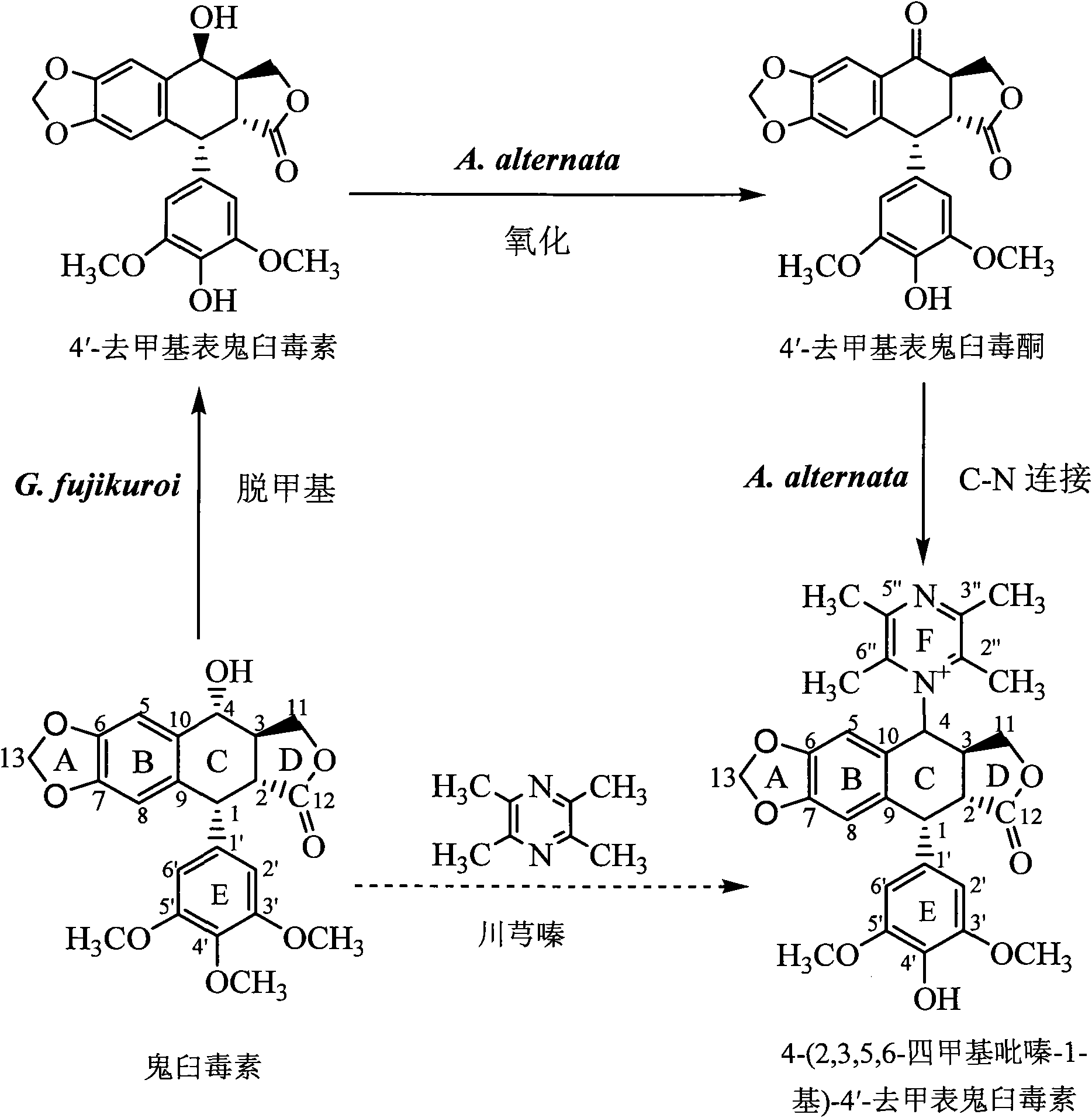
Biotransformation and purification method of 4-(2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine-1-group)-4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin
InactiveCN102234669ACultivableHas supplyOrganic chemistryComponent separationPurification methodsTetramethyl pyrazine
The invention discloses a method for transforming podophyllotoxin into 4-(2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine-1-group)-4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin, comprising the following steps of: (1) adding podophyllotoxin into a liquid fermentation medium, and carrying out biotransformation by inoculating second-class liquid seeds of humic soil fungi; (2) separating and purifying the product from the Step (1), followed by adding into the liquid fermentation medium, carrying out biotransformation by inoculating second-class liquid seeds of podophyllum taxa endophytes; then continuously carrying out biotransformation by adding ligustrazine, and collecting the transformation product. The invention also discloses a method for purifying 4-(2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine-1-group)-4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin from the above product and a method for detecting the content of 4-(2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine-1-group)-4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin. According to the invention, the molecular structure of podophyllotoxin is modified by the biotransformation method, which has advantages of mild reaction condition, low E-factor, quality controllability and simple separation process.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Special biochar composite organic fertilizer for planting wheat
InactiveCN108947688AMeet growth needsPromote growth and developmentExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersPenicillinMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a special biochar composite organic fertilizer for planting wheat. The special biochar composite organic fertilizer contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of human and livestock mature, 4-7 parts of cephalosporin residue, 4-7 parts of penicillin residue, 20-30 parts of biochar, 5-8 parts of corncobs, 3-7 parts of soybean curb residues, 4-9 parts of cotton seed hull, 2-6 parts of methylene succinic acid, 3-5 parts of epsilon-polylysine, 1-4 parts of chitosan oligosaccharide, 5-12 parts of ceramsite, 6-9 parts of coco coir, 3-7 parts of medical stone, 3-12 parts of wheat shell charcoal, 5-10 parts of bark powder, 12-18 parts of earthworm muck and 2-5 parts of a microbial agent. The organic fertilizer is rich in nutrients such as nitrogen,phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and organic matters and can meet the grow requirements of the wheat; and the biochar composite organic fertilizer is capable of well promoting the growth anddevelopment of the wheat and improving the activity of soil enzyme; and by virtue of the cooperation of the biochar composite organic fertilizer and the soil enzyme, the community structure of soil fungi is obviously optimized, and the gene copy number of fusarium oxysporum in the soil is decreased.
Owner:桐城市天泰农业种植专业合作社
Method for constructing chroogomphis rutillus fruiting body surrounding soil fungus community internet testing services (ITS) library
ActiveCN102559658ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionCommunity structure
The invention discloses a method for constructing a chroogomphis rutillus fruiting body surrounding soil fungus community internet testing services (ITS) library. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a metagenome of chroogomphis rutillus fruiting body surrounding soil; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using the metagenome as a template and using ITS1 and ITS4, and reclaiming DNA fragments of 700bp; connecting each DNA fragment and a pMD19-T vector, performing PCR amplification by using RV-M and M13-47, performing enzyme digestion on each PCR product by using HinfI, Hae III, Msp I, Taq I and Mbo I respectively, and performing electrophoresis to obtain a molecular map. By using the method, the chroogomphis rutillus fruiting body surrounding soil fungus community ITS library can be constructed; and the method has significance for determining the growth environment microbial fungus community structure, the heredity and the functional diversity of chroogomphis rutillus fruiting bodies, provides important information for deeply discussing artificial acclimation and culture of chroogomphis rutillus, and has important application value.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
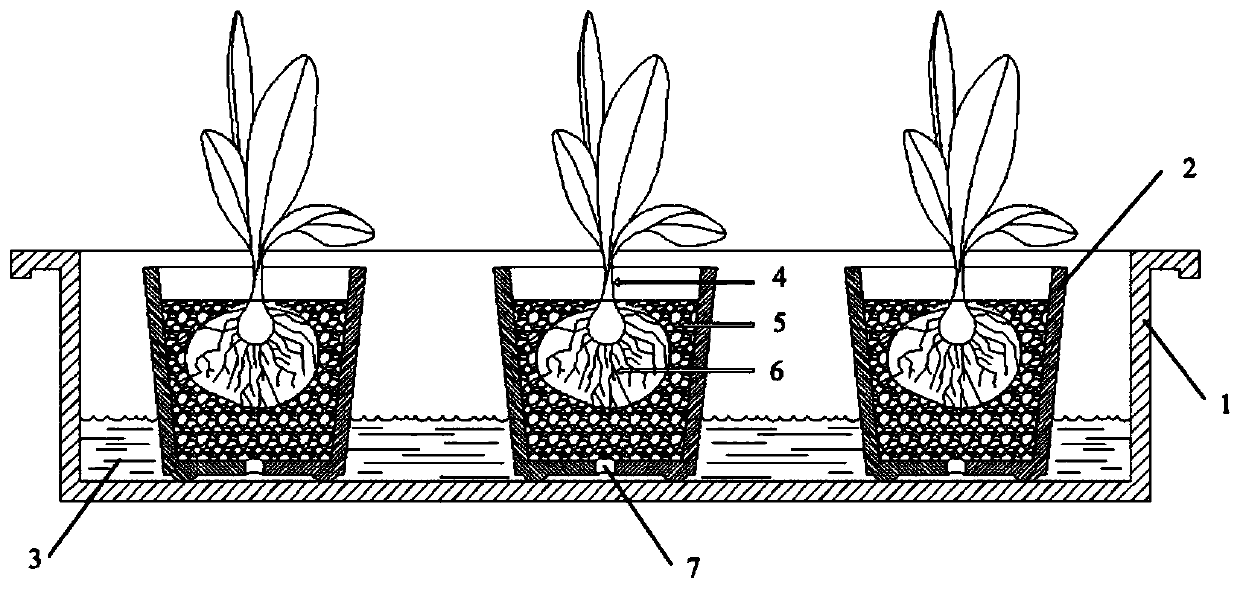
System and method for fast identifying disease resistance of banana fusarium wilt by soilless culture technology
InactiveCN110073957ASimple processImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologySoil fungi
The invention discloses a system and method for fast identifying disease resistance of banana fusarium wilt by a soilless culture technology. A culture pot is filled with a substrate; then, banana seedlings to be identified are planted in the substrate; next, a plurality of culture pots with banana seedlings are put into an outer pot; a solution is added into the outer pot; Fusariun oxysporun f.sp.cubense is added into the solution for culture; then, the banana seedlings are subjected to disease registration identification. Various culture pots with the banana seedlings can be put into the nutrition liquid of the outer pot for performing large-scale banana fusarium wilt resistance screening in one step; the single inoculation of each banana seedling with pathogenic bacteria is not needed;the flow process is greatly simplified; the efficiency is improved; the better standardization is realized; the influence of artificial random factors is avoided.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Medicine-fertilizer double-purpose plant nutrition conditioning product and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104557250AEfficient use ofLow costAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPlant nutritionSoil fungi
The invention discloses a medicine-fertilizer double-purpose plant nutrition conditioning product and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of novel fertilizers. The medicine-fertilizer double-purpose plant nutrition conditioning product comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 40%-70% of lime nitrogen, 20%-40% of a calcium-magnesium-phosphate fertilizer and 10%-30% of potassium humate. The preparation method of the medicine-fertilizer double-purpose plant nutrition conditioning product comprises the steps of firstly mixing the calcium-magnesium-phosphate fertilizer with the potassium humate, then adding lime nitrogen, and uniformly mixing. The medicine-fertilizer double-purpose plant nutrition conditioning product is low in cost and pollution-free, has efficacies of killing soil fungi, conditioning soil, improving soil acidification and nourishing soil; and meanwhile, the preparation method is easy and applicable to industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG
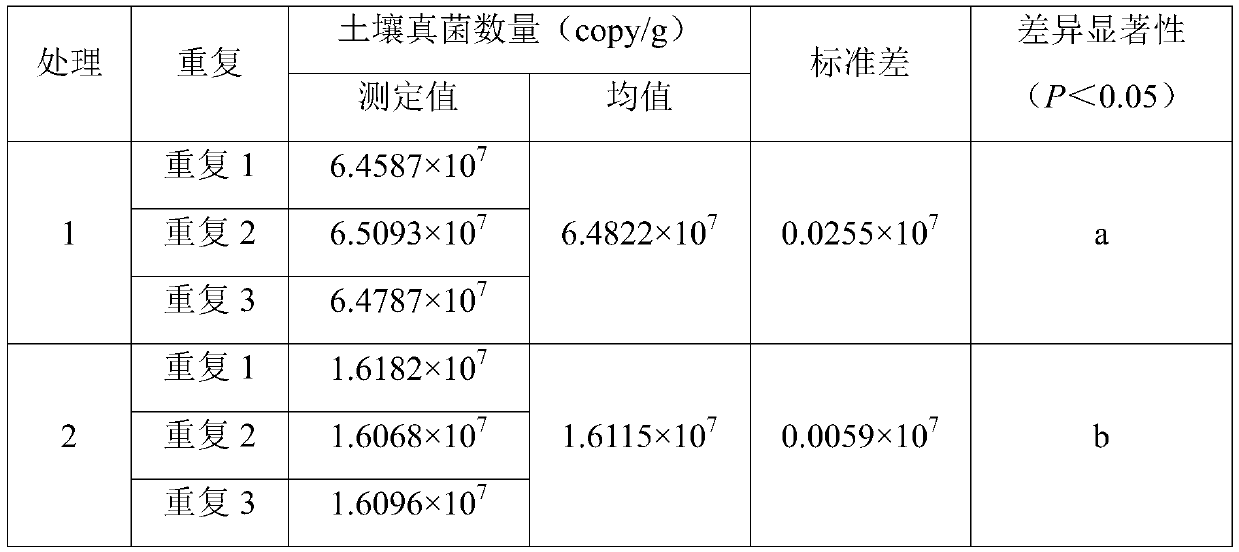
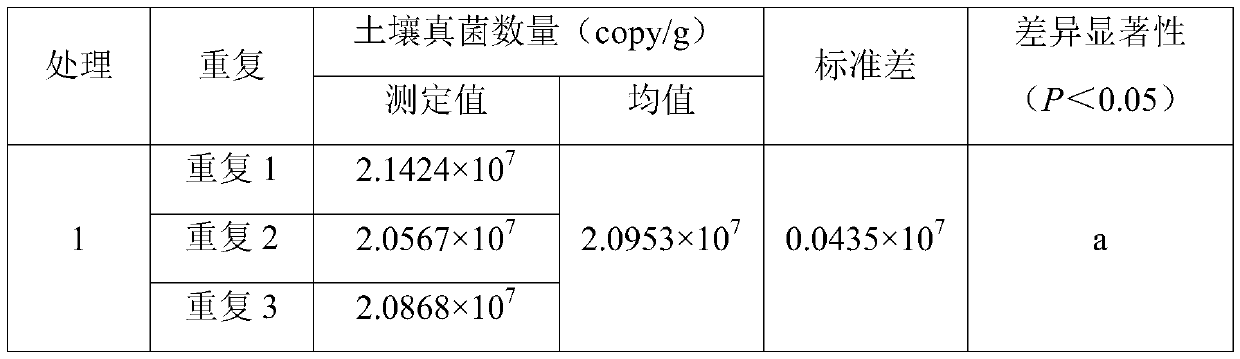
Method for detecting number of soil fungi based on real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR
PendingCN111057751ASimple and safe operationSave operating timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDNA Solutions
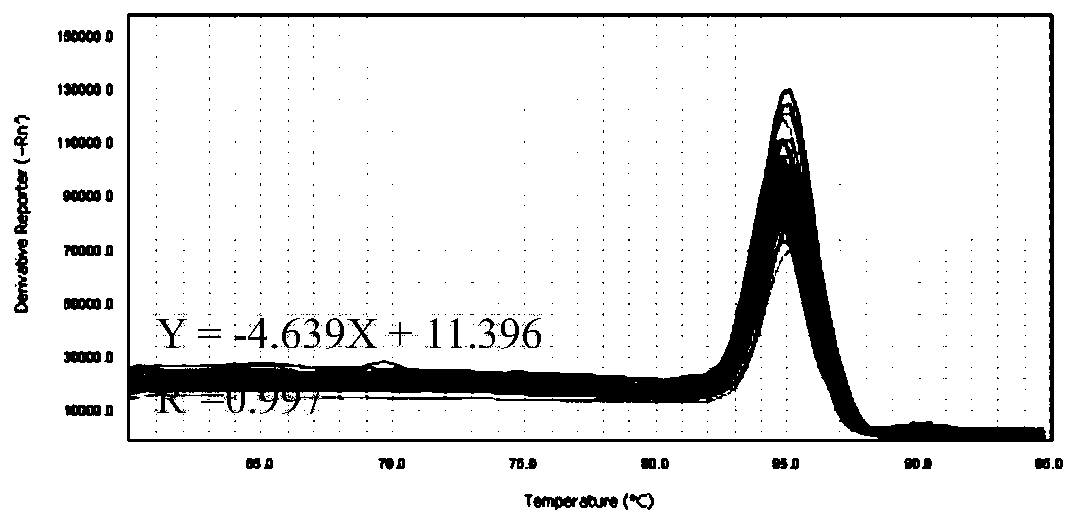
The invention discloses a method for detecting the number of soil fungi based on real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, and belongs to the field of detection of the number of soil fungi. The method disclosed by the invention mainly comprises the following steps: weighing sieved fresh soil, extracting total DNA of the soil by using A test kit, and uniformly diluting to a certain concentration; extracting total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from mycelia of moderately growing template Phlebia radiata by using a CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) method to prepare series template DNA solutionsof a standard curve; constructing a qPCR reaction system by using the standard curve or the to-be-detected soil template DNA solution, wherein the qPCR reaction system comprises a universal qPCR primer designed according to the conserved sequence of the rRNA of fungus 18S ribosome; carrying out qPCR reaction by using an ABI7500 real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument; drawing the standard curve; and calculating the number of fungi in each gram of dry soil. The method for detecting the number of soil fungi provided by the invention is safe and simple to operate, good in primer sequence specificity, high in sensitivity, accurate and reliable in result and good in reproducibility.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Multifunctional compound coated fertilizer with slow release and yield increase effects as well as preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107032865AMeet growth needsPromote absorptionCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingMicrobial agentNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses multifunctional compound coated fertilizer with slow release and yield increase effects. The fertilizer is characterized by being prepared from raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 60-65 parts of cottonseed hulls, 12-14 parts of calcium carbonate, 17-19 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 20-26 parts of urea, 15-18 parts of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 15-19 parts of potassium chloride, 1-2 parts of borax, 60-66 parts of tobacco powder, 45-48 parts of mushroom bran, 36-39 parts of starch residues, 2-3 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1-2 parts of ammonium molybdate, 16-19 parts of polyethylene, 6-8 parts of an EM microbial agent, 7-9 parts of a soil conditioner and a proper amount of water. Organic matter components such as the calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer and the tobacco powder or inorganic element fertilizer is added and the plant growth requirement is met; the soil conditioner is added, and the synergistic effect and the effect of promoting plants to absorb nutrients are realized; a coating process is adopted, the slow release effect is good, the fertilizer is applied to farmland once, the activity of soil nitrifying bacteria is inhibited, soil fungi are killed, soil acidification can be avoided, and the crop yield can be increased.
Owner:凤台县余跃蔬菜专业合作社
Method for preparing biocontrol bacterial fertilizer and eliminating continuous cropping obstacle of muskmelon by using biocontrol bacteria
InactiveCN109836190AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthBio-organic fraction processingFertilising methodsBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
A method for preparing a biocontrol bacterial fertilizer by using biocontrol bacteria comprises the following steps: using bacillus subtilis obtained by separation in a kiwi fruit garden as a strain,and separating and identifying the strain; adding sterilized soybean meal, ammonium nitrate, cane sugar, magnesium sulfate and manganese sulfate into a sterilized carrier matrix, adding sterile waterand a seed liquid of the biocontrol bacteria, fully and uniformly stirring to obtain a fermentation raw material; fermenting the fermentation raw material to guarantee that the biocontrol bacteria count of the matrix carrier reaches 1010 CFU / g DW carrier matrix, and uniformly spraying the prepared biocontrol bacterial fertilizer into a muskmelon field according to 135 kg / mu one month before transplantation of muskmelon seedlings. Thereby, soil fungi growth can be inhibited, soil microflora is balanced, and the content of the main ingredient cumaric acid of muskmelon root exudates in soil is reduced. And then, continuous cropping obstacle in muskmelon production is eliminated, agricultural sustainable development is realized, and the ecological environment is maintained.
Owner:曹翠玲
Method for determining content of Thelephora ganbajun mycelia in soil
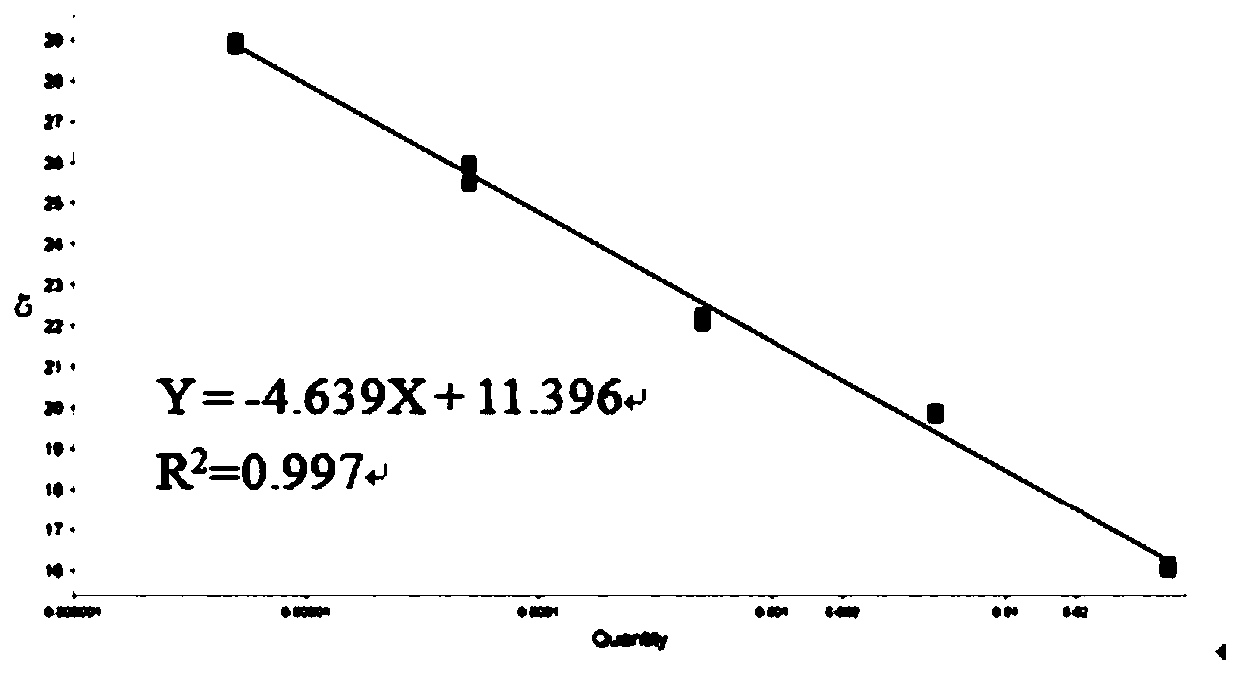
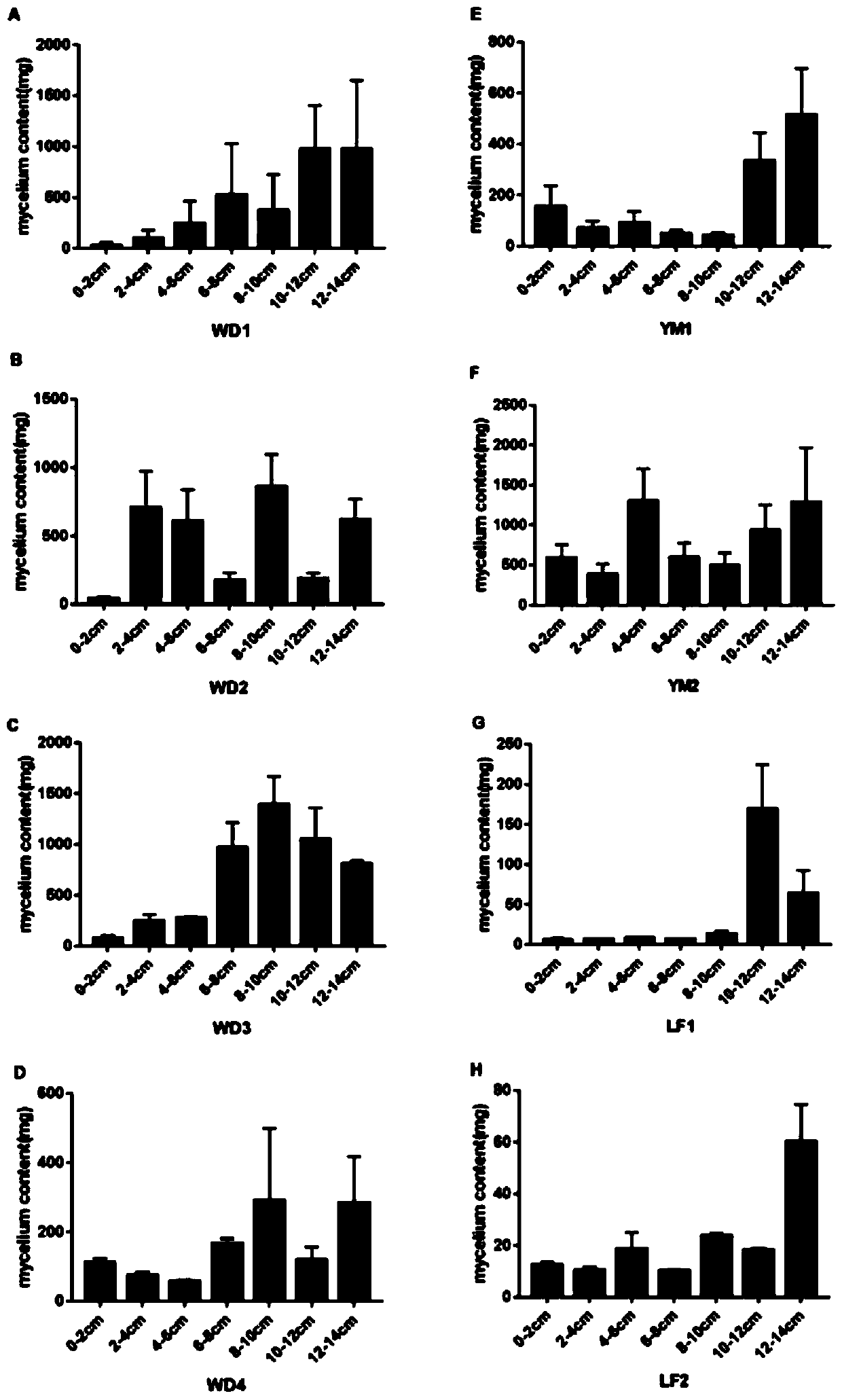
InactiveCN111020051AQuick checkSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSoil scienceSoil depth
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of Thelephora ganbajun mycelia in soil. The method comprises the following steps: in a Thelephora ganbajun growing field, taking seven soilsamples at different depths from soil in a circular area where sporocarp is taken as a center, a radius is 5 cm and a depth is 14 cm through a five-point method, wherein a depth of 2 cm is taken as one soil depth, putting the seven soil samples into prepared sterile sampling bags, numbering the sterile sampling bags, and storing the soil samples at a temperature of -80 DEG C; carrying out DNA extraction on the soil sample to obtain a liquid which is a mixed liquid of DNAs of soil fungi, and naturally cooling the mixed liquid of the DNAs of the soil fungi at -20 DEG C for later use; and carrying out a qPCR test by adopting a primer Tg, and substituting a detected Ct value into a standard curve equation to calculate the mycelium content of the soil. The method can achieve the purpose of rapidly detecting the content of Thelephora ganbajun mycelia in soil, and is simple and efficient.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for preparing biocontrol bacterial fertilizer from bacteria and method for eliminating continuous cropping obstacles of muskmelons
InactiveCN113336601AGrowth inhibitionImprove physical and chemical propertiesCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
The invention discloses a method for preparing a biocontrol bacterial fertilizer from bacteria and a method for eliminating continuous cropping obstacles of muskmelons, and the method comprises the following steps: by taking bacillus subtilis separated in a vineyard as a strain, separating and identifying the strain; sterilizing the carrier substrate; and adding sterilized soybean meal, ammonium nitrate, cane sugar, magnesium sulfate, calcium sulfate and manganese sulfate. The biocontrol bacteria can effectively inhibit the growth of soil fungi and promote the growth of soil bacteria through biocontrol bacteria, the biocontrol bacteria fertilizer produced from rice bran, wheat bran or crushed corn particles is applied to melon continuous cropping soil, the biocontrol bacteria can be brought in, a large amount of organic matter can be brought into the soil, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the price is low, and the operation is easy; lime nitrogen and quicklime are applied to soil, most pathogenic bacteria in the soil can be killed, soil-borne diseases are effectively reduced, the amino acid foliar fertilizer is sprayed, crop growth is promoted, crop quality is improved, and the quality and yield of muskmelons can be improved by spraying the amino acid foliar fertilizer in the growth period of the muskmelons.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Oxygen aeration coated fertilizer capable of overcoming production successive cropping obstacles
InactiveCN106146174AEnsure aerobic respirationEnsure normal aerobic respirationAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSoil fungiOxygen
The invention discloses an oxygen aeration coated fertilizer capable of overcoming production successive cropping obstacles. The oxygen aeration coated fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.4-0.5 part of calcium cyanamide, 34-36 parts of cottonseed meal, 23-25 parts of poultry feather, 0.3-0.5 part of propylene glycol alginate, 1-2 parts of nickel sulfate, 6-7 parts of potassium carbonate, 8-10 parts of clay powder, 14-16 parts of urea, 20-22 parts of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution, 2-3 parts of laxogenin powder, 0.8-1.0 part of butyl acrylate, 2-3 parts of sodium dihydrogen phosphate dry powder, 1.5-1.8 parts of nano-zinc oxide and a proper quantity of water. The fertilizer adopts various low-salt raw materials, the raw materials are cooperated with compost organic materials to effectively prevent soil fungi from breeding, overcome soil acidification, lower the vitality of nitrobacteria, improve the nutrition releasing capability of the fertilizer in the soil, quickly supplement soil nutrition imbalance caused by successive cropping, effectively solve the production successive cropping obstacles of crops and improve the yield.
Owner:ANHUI LUHU BIOTECH
A kind of bacterial strain and application for preventing and treating soil-borne fungal diseases of continuous cropping peanut
The invention relates to a bacterial strain and a bacterial agent thereof for preventing and treating fungal diseases of peanut soil in continuous cropping. The bacterial strain is a kind of Pseudomonas protegens, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11539. The 16s rRNA base sequence of the strain is shown in SEQ ID No:1. The strain of the present invention produces chitinase (degrades mycelium cell wall of pathogenic fungus) with high activity, and has remarkable degrading ability to mycelium of various soil-borne fungal pathogens such as Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Verticillium and the like. The seed dressing dosage of the bacterial agent of the present invention is generally only 20-30 kg / mu, which can effectively prevent and control frequent soil-borne fungal diseases such as peanut root rot, blight, and silkworm in dry land, with a control effect of more than 55%. It has the advantages of small dosage, wide antibacterial spectrum, and significant yield-increasing effect, and can effectively reduce the impact of soil-borne diseases on the yield loss of continuous cropping ground peanuts.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
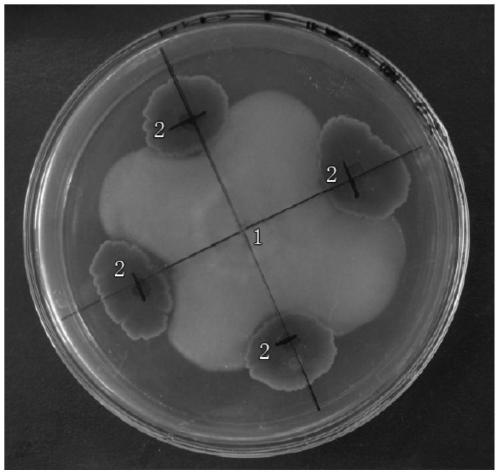
Method for constructing soil fungal antagonism model
InactiveCN101413934AThe construction method is simple and feasibleShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to biological technology, in particular to a method used for establishing a soil fungi antagonistic model. The method comprises the concrete steps as follows: the collected soil sample is disposed under high temperature and high pressure so as to establish the soil fungi antagonistic model with the soil fungi-inhibiting capability being gradually reduced. The soil fungi antagonistic model is established by the following steps: 1) sampling soil samples; 2) disposing the soil samples by high pressure and high temperature; 3) detecting the fungi antagonistic model. The method used for establishing model is simple, convenient and feasible, can be operated in common laboratories, and has short time consumption; furthermore, the model can be applied to different soil samples, can be used for researching the fungi antagonistic function of different soils and discovering specific fungi-inhibiting microorganism of the soil, can research the bacterial community structure of the soil and can research the relationship between the community structure composition of other microorganisms such as fungi, actinomycete and the like and the fungi antagonistic function.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for degrading residual tylosin in medicine slag
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Soil remediation composition and application thereof
InactiveCN110041148AEfficient decompositionAvoid churnAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPotassium nitrateCalcium biphosphate
The invention discloses soil remediation composition and an application thereof. The soil remediation composition is prepared from, in parts by weight, 15-22 parts of fermentation microorganism colonies, 5-13 parts of an ammonium sulfate solution with the concentration of 19-22 mol / L, 3-8 parts of a calcium phosphate solution with the concentration of 15-19 mol / L, 3-6 parts of potassium permanganate and 11-15 parts of a potassium nitrate solution with the concentration of 5-12 mol / L. According to the soil remediation composition and the application thereof, harmful substances in soil can be effectively decomposed through combined bacteria of soil bacteria, soil actinomycete and soil fungi, and the soil remediation effect is realized.
Owner:广东筑奥生态环境股份有限公司
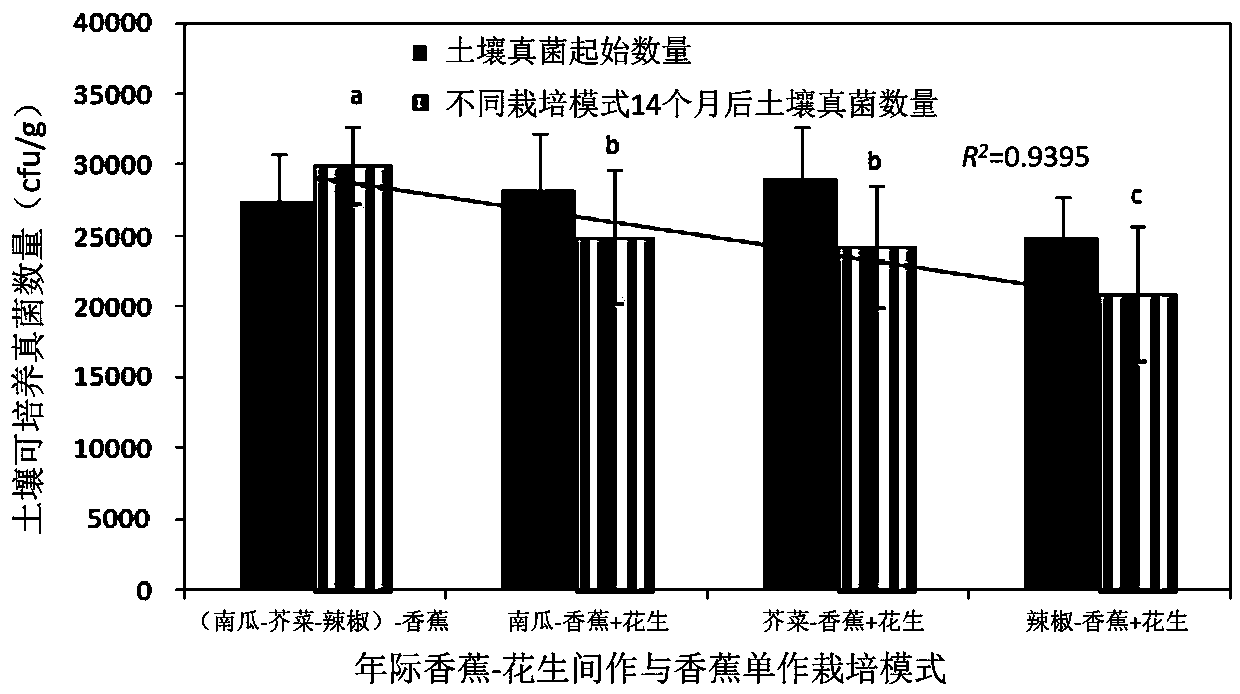
High-efficiency cultivation method of improving soil acidity-precision fertilization-matching intercropping to comprehensively prevent and control banana wilt
ActiveCN106852250BReduction of fungal (phytopathogenic) populationsReduce the incidence of Fusarium wiltFabaceae cultivationCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses an efficient cultivation method for improving soil acidity, precise fertilization and matched intercropping to comprehensively prevent and control banana wilt. Soil pH is regulated through a soil testing formula, precise fertilization is performed according to soil fertility, main banana nutrition NPK absorption amount, the rate of absorption and utilization and target yield, meanwhile peanut intercropping is performed to conserve water and soil, nodule nitrogen fixation is beneficial to banana growth, the soil microbial diversity is improved, and the occurrence rate of the banana wilt is remarkably reduced. The cultivation method is simple and clear to operate, the soil pH and the diversity of organic matter, bacteria and actinomycetes are remarkably improved, the amount of soil fungi (phytopathogens) is decreased, and the banana wilt is decreased. In addition, the fertilizer usage amount is effectively decreased, the high peanut and banana yield is obtained. The efficient cultivation method has the positive significance on prevention and control of the banana wilt and chemical fertilizer decrease and replacement through land applying and maintaining biological measures and efficient cultivation mode and has the application values on remarkable improvement of banana productivity, economic benefits, environment protection of producing areas and sustainable development of banana production.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
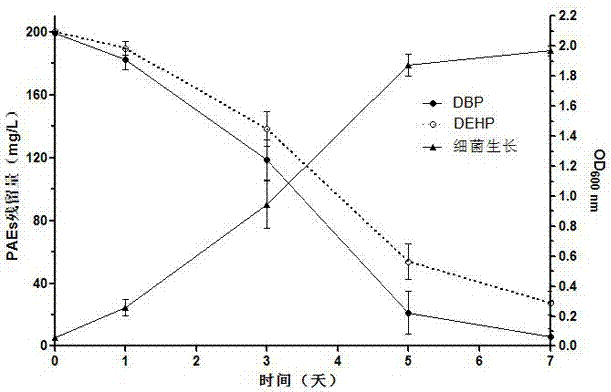
Application of Agromyces sp. MT‑E in Degradation of Various Phthalates
ActiveCN104845890BWidely distributedEasy to trainFungiWater contaminantsInorganic saltsAgromyces sp.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Biotransformation and purification method of 4-(2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine-1-group)-4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin
InactiveCN102234669BSolve industrialization problemsAvoid organic residuesOrganic chemistryComponent separationBiotechnologyPodophyllum
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
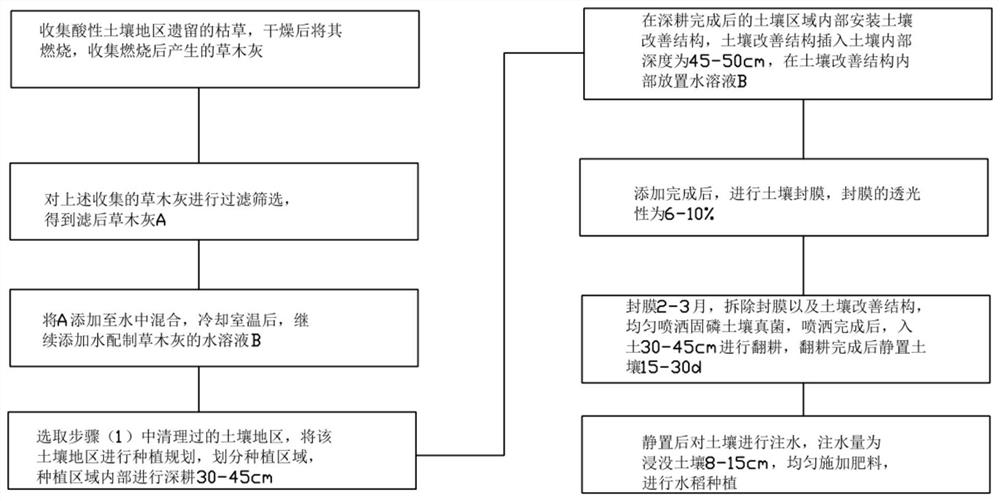
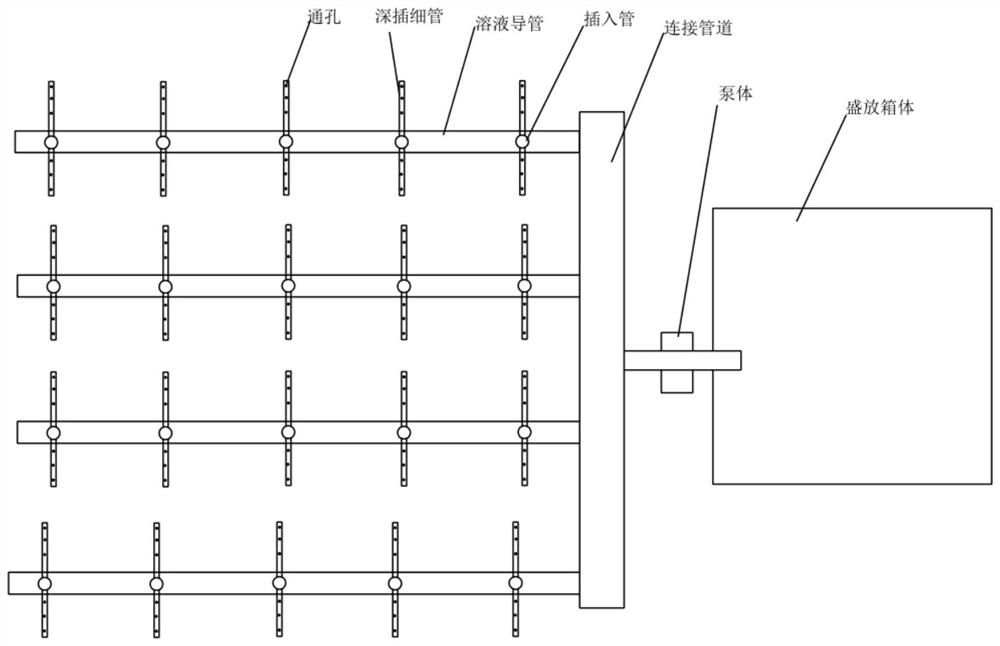
Rice fertilizing method and fertilizer in acid soil area
InactiveCN113545212AIncrease alkalinityReasonable useExcrement fertilisersFertilising methodsSoil scienceSoil fungi
The invention discloses a rice fertilizing method and fertilizer in an acid soil area, and belongs to the technical field of rice fertilizing planting. The rice fertilizing method in the acid soil area comprises the following steps: collecting withered grass left in the acid soil area, drying and burning the withered grass, and collecting plant ash generated after burning; performing filtering and screening to obtain filtered plant ash A; preparing an aqueous solution B of the plant ash; conducting deep ploughing in the planting area by 30-45 cm; installing a soil improvement structure in the soil area after deep ploughing is completed, and placing the aqueous solution B in the soil improvement structure; after adding is completed, carrying out film sealing on soil; after 2-3 months of film sealing, evenly spraying phosphorus-fixing soil fungi , ploughing the soil by 30-45 cm, and after ploughing is completed, leaving the soil to stand for 15-30 d; and after standing, injecting water into the soil, evenly applying fertilizer and planting rice. The fertilizer absorption capacity of rice is improved while the acid soil is improved , various microelements needed by rice growth are fully provided, and the rice yield can be greatly increased.
Owner:胡铁军
A method for predicting the growth of spoilage fungi based on hyperspectral images
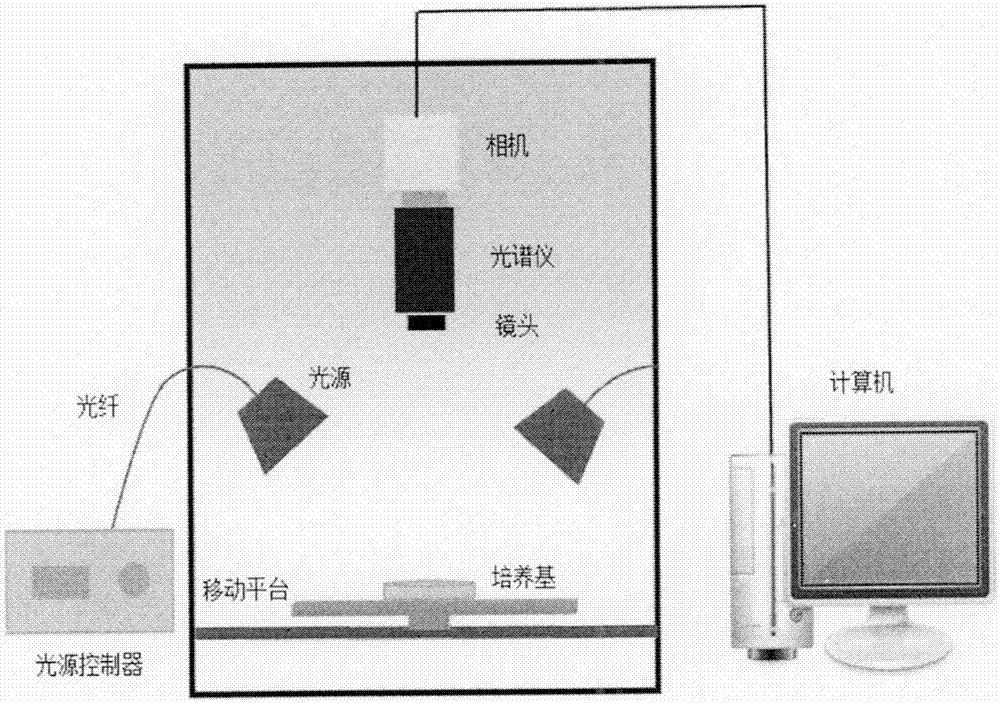
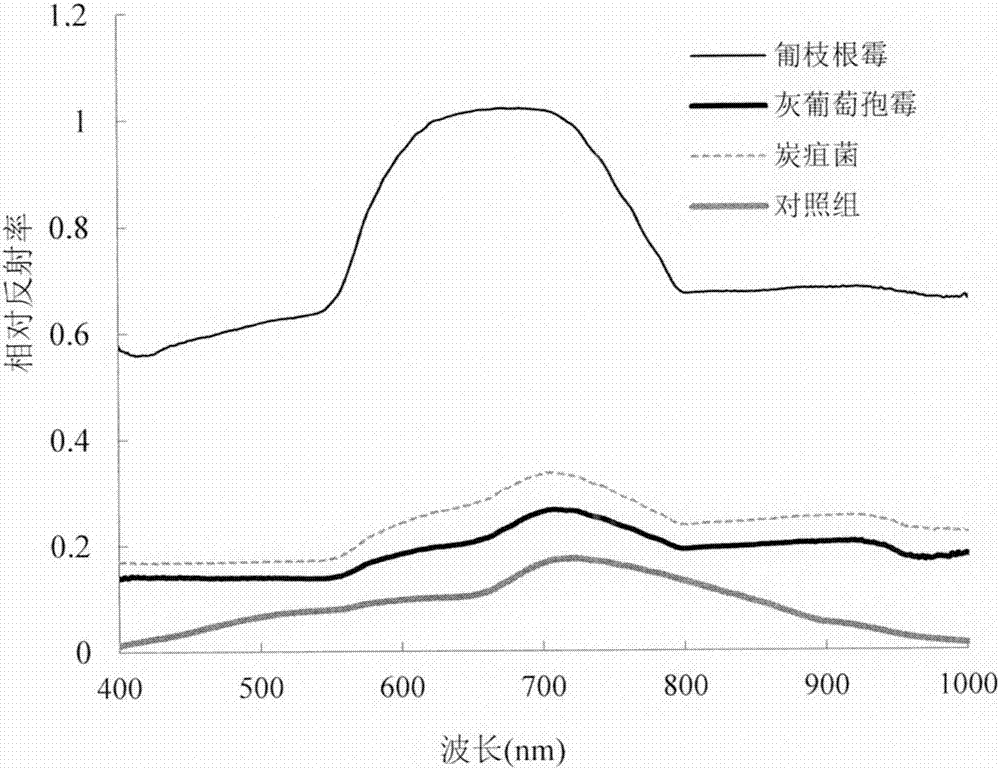
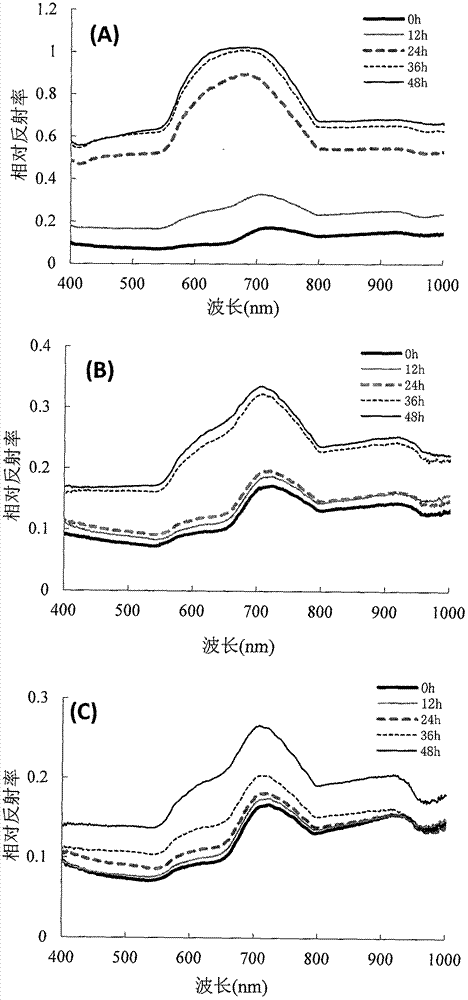
InactiveCN104297165BReduce usageShorten the timeColor/spectral properties measurementsSoil fungiPlant disease
The invention provides a hyperspectrum-based method for creating a growth curve of rot funguses in a fruit, and belongs to nondestructive technology of food quality safety quick detection and monitoring. Hyperspectral images of the funguses at different growth stages can be acquired respectively through a hyperspectral imager, so as to analyze difference between images of different types of funguses at different stages and a spectrum, extracting corresponding images and corresponding spectrum characteristic parameters, and respectively creating the growth models of three types of funguses. Compared with the fungus growth conditions obtained through the conventional microbe growth detection manner, the related coefficient ranges from 0.88 to 0.96. The method provides a new concept and a new technology for growth detection of microbes in the foods, can be used for creating a fungus growth curve more conveniently and faster, and can be used for detecting, monitoring and controlling fruit rot fungus diseases.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Granular edible fungus seasoner
The invention relates to a granular edible fungus seasoner which is prepared by the following steps: mixing single edible fungi powder and Chinese yam powder; and preparing into granules. The seasoner comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 88-92% of the single edible fungi powder and 8-12% of the Chinese yam powder. The seasoner provided by the invention is easy to dissolve, is not clotted, and can be quickly dissolved in soups or a small amount of liquid in cold dish with dressing. A small amount of Chinese yams are used as auxiliary material and a solidifying material, so that the single fungi powder can be better prepared into granules. When the granular edible fungus seasoner is put in a small amount of liquid or directly mixed in the soups, instant Chinese yams are quickly liquefied, so that the fungi powder is further quickly liquefied. The Chinese yams are free from other peculiar smells and cannot cover the main flavor but make the taste of the single fungi more outstanding without affecting the taste of the fungi. In addition, the seasoner provided by the invention breaks through a conventional manner of adding food additives into a conventional seasoner. The seasoner provided by the invention has the remarkable advantages of being natural, healthy and pollution-free.
Owner:NANHUA HONGYI MUSHROOM DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com